900 SE Convertible V6-2498cc 2.5L DOHC (1995)
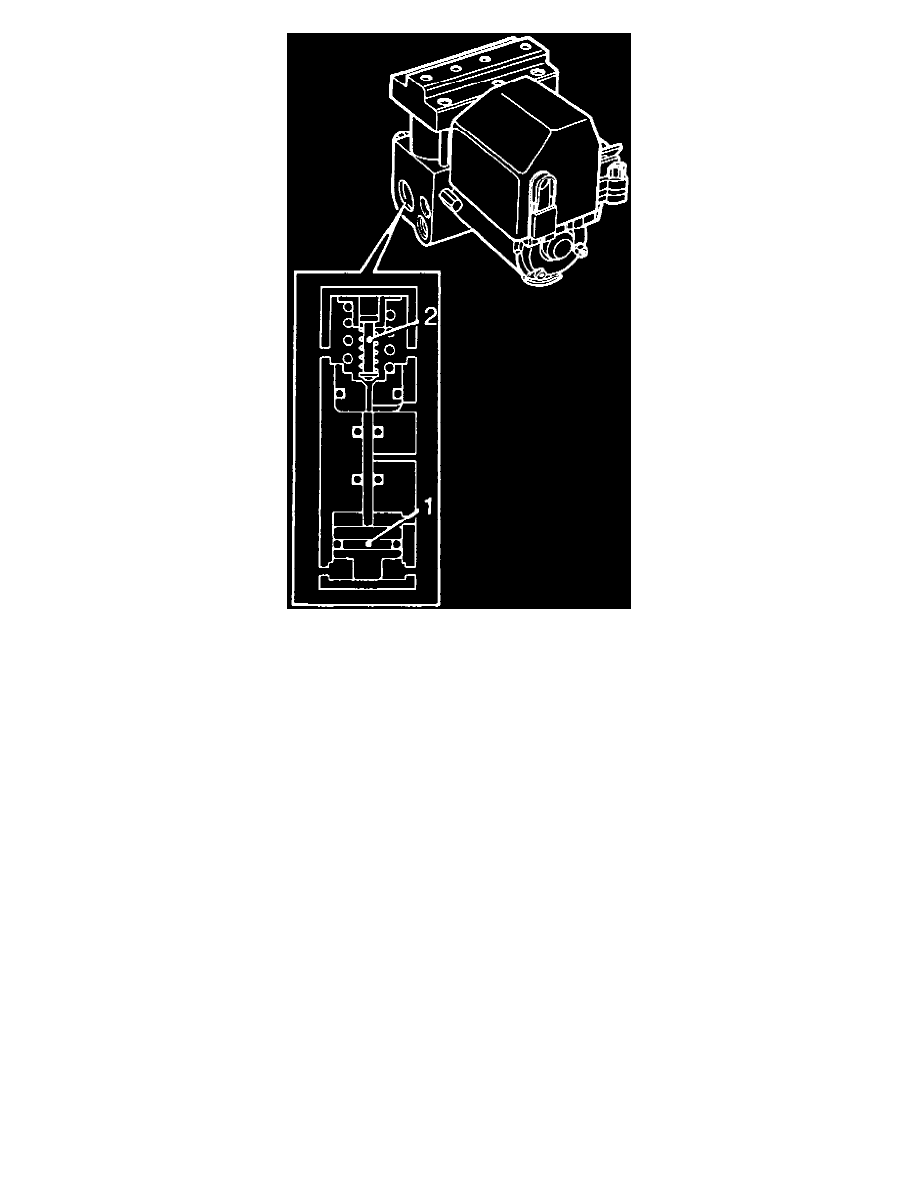
Fig. 5 Rear Wheel Equalization Valve
In addition to the solenoid valve, there is an equalization valve, Fig. 5, for the rear wheel circuit so both rear wheels can be operated with only one
solenoid valve.
The equalization valve ensures both rear wheels receive the same brake pressure in ABS control. This means the vehicle has good directional
stability.
In the case of ABS control of the rear wheels, the solenoid valve moves to the pressure holding position. The channel to the rear right wheel is now
blocked. If the pressure from the master cylinder rises, a pressure difference develops below and above the piston (1). The piston is raised and the
valve (2) closes the pressure to the rear left wheel. If the pressure to the rear right wheel drops (pressure relief), a greater pressure difference
develops above and below the piston (1), and the piston is lifted further upward until the pressure for the right and left rear wheels has balanced
out.
The hydraulic unit consists of the valve block with three 3/3 solenoid valves (1 valve for front right wheel, 1 for front left wheel and 1 for both rear
wheels), equalization valve and control module with main and pump relays and return pump.
When the ignition key is turned to drive position and the wheels start to rotate, the return pump is always tested by the control module starting the
pump for approximately .5 seconds.
The master cylinder is separated from the hydraulic unit and is connected via two pipes from the primary and secondary circuits.
