L300 V6-3.0L VIN R (2001)
Fuel: Testing and Inspection
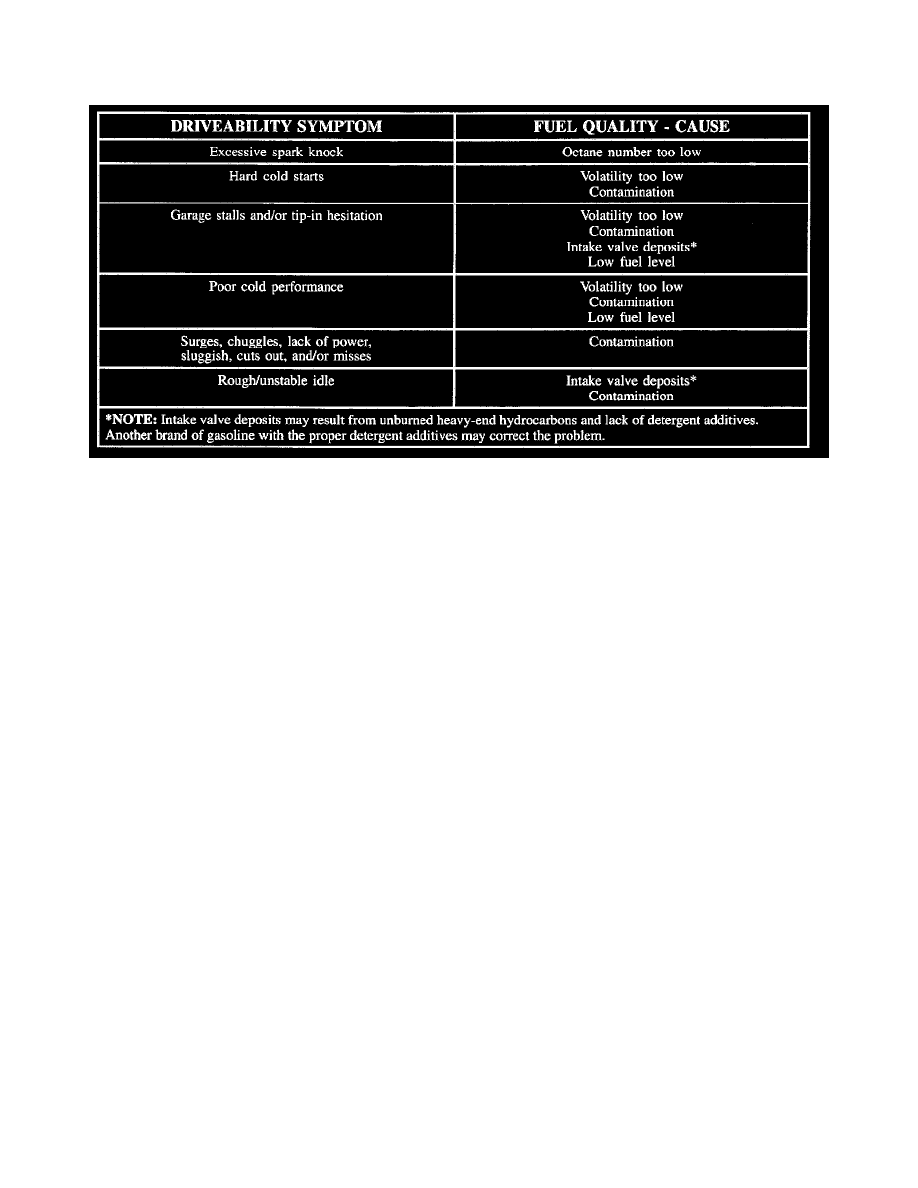
Driveability Symptoms Vs Fuel Quality (Engine SYS Functioning Properly)
Symptom Table
Diagnostic Hints
^
Start diagnosis by verifying complaint. Keep vehicle overnight before verifying a cold driveability problem.
^
Remember that the symptom(s) may indicate a fuel delivery/pressure or fuel control problem. Use DTC codes and fuel system diagnostic
procedures for diagnosis.
^
If engine is functioning properly, suspect fuel volatility/fuel quality.
-
Determine if customer is using premium grade fuel. If so, suggest trying a different brand of fuel or regular unleaded fuel except when a
premium-grade is recommended because of operating conditions. Some premium grade gasolines may actually cause cold engine driveability
problems because of their lower volatility in the warm-up range. Inform customers that it may require more than one tankful of a different
brand of fuel to correct a fuel quality problem.
-
Determine if customer has old fuel in tank. If so, the volatility may be too low because the "light-ends" have evaporated.
-
Consider the possibility that an unseasonable cold snap has made fuel volatility wrong for the weather.
Diagnosing Fuel Quality Problems
SYMPTOMS
A fuel-quality problem may be indicated by the following driveability symptoms:
^
Spark knock/detonation
^
Hard cold start and garage stalls
^
Poor cold performance
^
Tip-in hesitation, sag, or stumble (momentary lack of response during initial acceleration)
^
Surges and/or chuggles
^
Lack of power, sluggish, or spongy
^
Cut out or misses
^
Rough/unstable idle (intake or exhaust valve deposits)
Reformulated Gasoline
Reformulated gasolines (1995-1996) are gasolines with a revised formula that:
^
lowers Reid Vapor Pressure
^
lowers benzene content
^
contains a minimum 2% oxygen content
Oxygenated Fuels
Beginning Nov. 1, 1992, oxygenated fuels are required in 39 carbon monoxide non-attainment areas of the U.s. during the winter months. By slightly
increasing the oxygen in the air/fuel mix, combustion can be improved and carbon monoxide emissions reduced.
Oxygenated fuels contain oxygen in their chemical makeup. Common oxygenated fuels are methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethanol. When
blended with gasoline, oxygenated fuels increase the octane rating and lower carbon monoxide emissions.
Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether (MTBE) - MTBE is an ether manufactured by reacting methanol and isobutylene. Present laws permit fuel to contain a
