Impreza 2.5 RS Sedan AWD F4-2.5L SOHC (2002)
Oxygen Sensor: Description and Operation
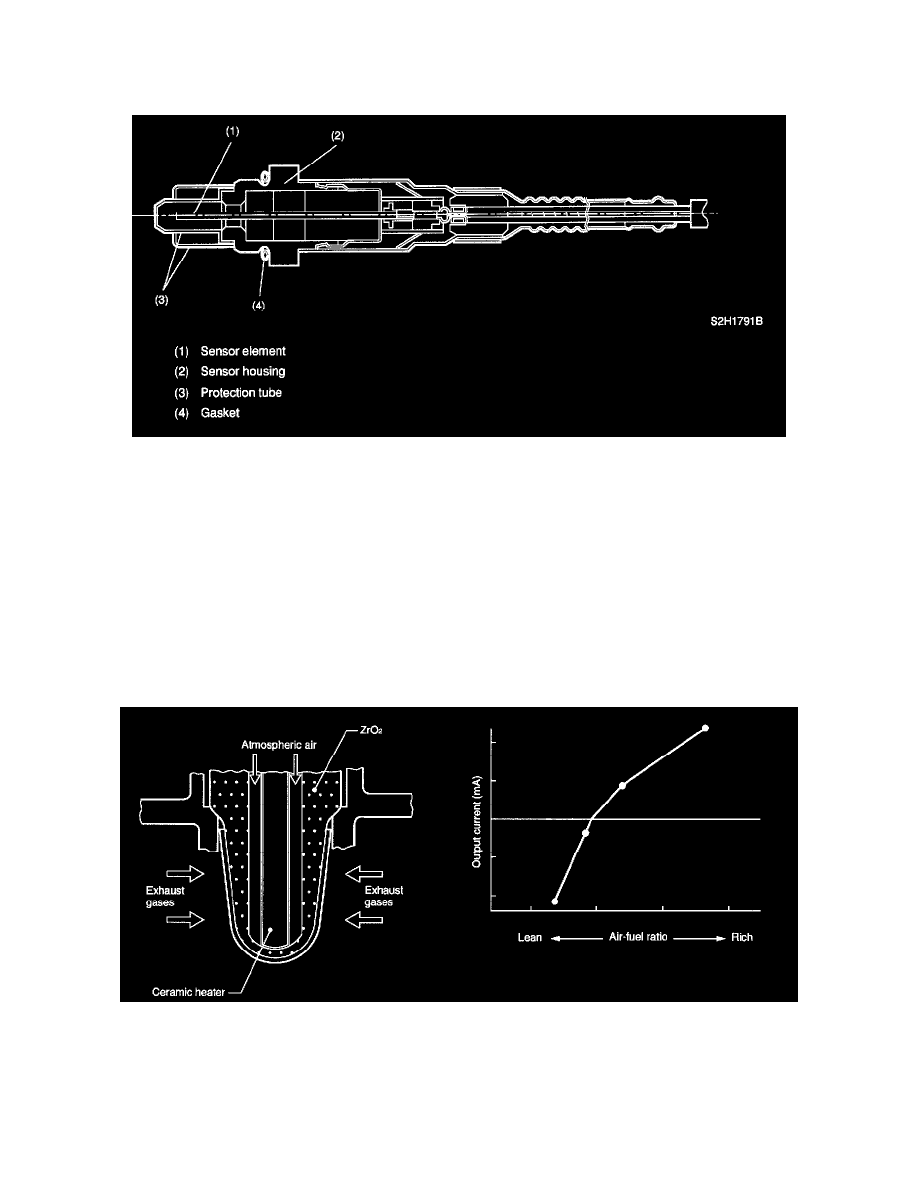
Front Oxygen (A/F) Sensor
FRONT OXYGEN (A/F) SENSOR
-
The front oxygen sensor uses zirconium oxide (ZrO2) which is a solid electrolyte, at portions exposed to exhaust gas.
-
The zirconium oxide has the property of generating electromotive force when its both sides are exposed to oxygen ions of different concentration
and the magnitude of this electromotive force depends on how much the difference is.
-
The front oxygen sensor detects the amount of oxygen in exhaust gases by making use of this property of the zirconium oxide material.
-
The zirconium oxide material is formed into a closed end tube and its external surface is exposed to exhaust gases with smaller oxygen ion
concentration, whereas its internal surface is exposed to atmospheric air. The external surface has a porous platinum coating. The sensor housing is
grounded to the exhaust pipe and the inside is connected to the ECM through the harness to be able to use the current output from the sensor.
-
The sensor incorporates a ceramic heater to improve its performance at low temperatures.
-
When rich air-fuel mixture is burnt in the cylinder, the oxygen in the exhaust gases is almost completely used in the catalytic reaction by the
platinum coating on the external surface of the zirconia tube. This results in a very large difference in the oxygen ion concentration between the
inside and outside of the tube, and the electromotive force generated is large.
-
When a lean air-fuel mixture is burnt in the cylinder, relatively large amount of oxygen remains in the exhaust gases even after the catalytic action,
and this results in a small difference in the oxygen ion concentration between the tube's internal and external surfaces. The electromotive force in
this case is very small.
-
The difference in oxygen concentration changes drastically in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio, and hence the change in the
electromotive force is also large. By using this information, the ECM can determine the air-fuel ratio of the supplied mixture easily. The front
oxygen sensor does not generate much electromotive force when the temperature is low. The output characteristics of the sensor stabilize at a
temperature of approximately 700 °C (1,292 °F).
