Impreza 2.5 RS Sedan AWD F4-2.5L SOHC (2002)
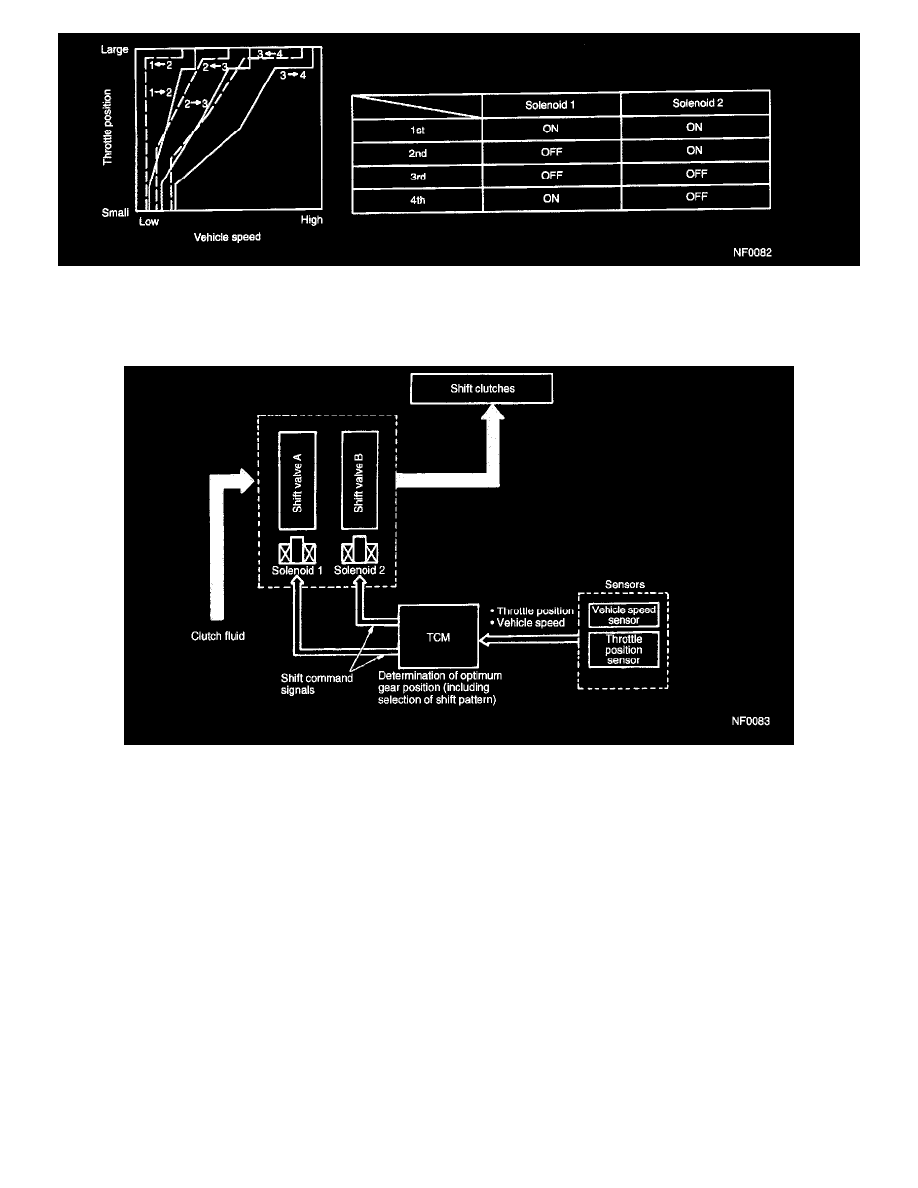
The TCM performs gear shifting control according to driving conditions by using the shift point characteristic data stored in its memory. Appropriate
solenoids are operated at the proper timing corresponding to the shift pattern, throttle position, and vehicle speed for smooth shifting.
NOTE: When the ATF temperature is below approximately 10°C (50°F), the gear cannot be shifted to the 4th speed.
^
The TCM activates both solenoids 1 and 2 in response to throttle and vehicle speed signals.
^
Shift valves move in response to operation of the solenoids, supplying or interrupting the line pressure to each clutch.
^
A shift to each gear takes place according to ON-OFF operation of both the solenoids as indicated in the table above.
D: LOCK-UP CONTROL
^
The TCM has pre-programmed lock-up clutch engagement and disengagement conditions for each gear and shift pattern. In addition, it specifies
engagement of the clutch whenever the 4th gear is selected in the D range. The engagement and disengagement conditions are defined in terms of
the throttle valve position and vehicle speed.
^
The TCM controls the operation of the lock-up clutch by means of the duty solenoid which in turn controls the lock-up control valve as described
below:
1. NON-LOCK-UP OPERATION
The duty solenoid allows the pilot pressure (supplied from the pilot valve) to be applied to the "disengaging" end of the lock-up control valve
spool. The lock-up control valve then opens the clutch disengaging circuit port to allow the lock-up operating pressure (torque converter clutch
regular pressure) to build up in the circuit. On the other hand, the valve opens the clutch engaging circuit's port and allows the fluid in the circuit to
flow to the ATF cooler, thus lowering the pressure in the circuit. As a result, the lock-up clutch is disengaged due to difference in pressure between
both circuits.
This operation is performed for all the speed gears except the 4th gear of the D range.
2. LOCK-UP OPERATION
The duty solenoid allows the pilot pressure to be applied to the "engaging" end of the lock-up control valve spool. The lock-up control valve then
opens the clutch engaging circuit's port that communicates to the torque converter's impeller chamber, allowing high pressure fluid to flow to the
lock-up clutch. The clutch then engages.
