Impreza Coupe FWD F4-1820cc 1.8L SOHC (1995)
Brake Proportioning/Combination Valve: Description and Operation
With ABS
Operation During Normal Conditions
OPERATION DURING NORMAL CONDITIONS
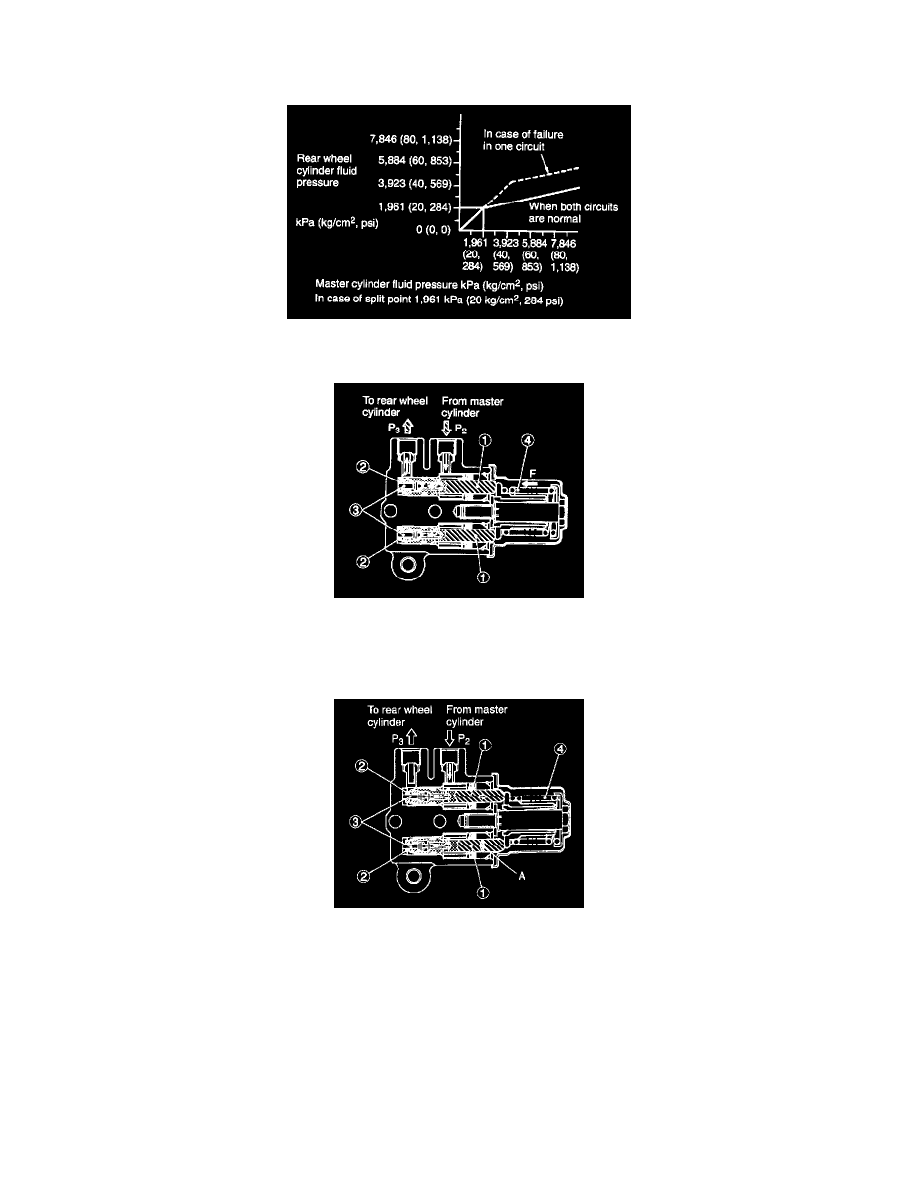
1) Operation before the split point
Piston (1) is held by spring (4) so that valve (3) is kept away from valve seat (2).
Under this condition, fluid pressure "P3" to rear wheel cylinders equals fluid pressure "P2" from master cylinder.
2) Operation near the split point
Force "f1", applied to piston (1) by spring (4), is one-half of spring force "F". In other words, "f1" = 1/2 "F".
Force "f2" is also applied to piston (1) in the direction opposite to spring force "F" due to fluid pressure "P2" generated by master cylinder
according to cross sectional area "A".
Spring force "f2" increases respondingly with fluid pressure "P2" When "f2" is greater than "f1", piston (1) moves in direction opposite to spring
force "F". This causes valve (2) to come in contact with valve seat (3), blocking fluid passage.
3) Immediately before fluid passage is closed, fluid pressure "P2" is held equal to pressure "P3". When brake pedal is depressed to increase fluid
pressure "P2" piston (1) moves in the same direction as spring force "F", opening fluid passage.
However, since fluid passage is closed again immediately after pressure "P2" equals "P3", pressure "P3" is held at a value of less than pressure
"P2"
Operation In Case of Circuit Failure
