Outback L.L.Bean Edition AWD F6-3.0L (2002)
For this reason, gear shift shock may become larger after the power supply is interrupted (disconnection of battery, flat battery, etc.) or immediately
after the ATF is replaced.
Larger gear shift shock after power supply interruption occurs because the correction data is reset to those for the new vehicle condition.
The TCM starts learning function again as soon as the power supply is restored. After driving for a while, therefore, the transmission will become able
to make gear shifts at the optimum timing.
Larger shift shock immediately after ATF change is caused by change in friction characteristics of the transmission internal parts. Also in this case, the
transmission recovers shockless gear shifting after driving for a while.
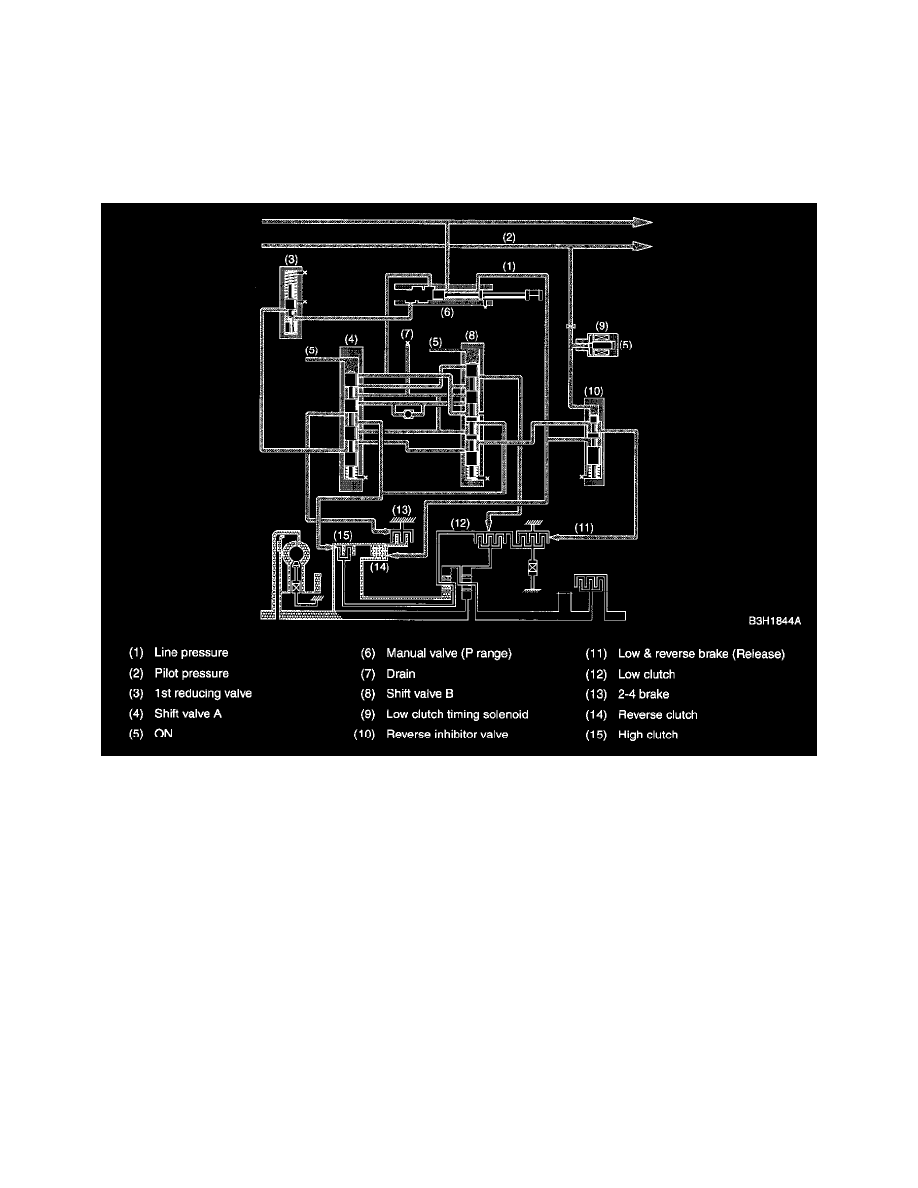
REVERSE INHIBITION CONTROL
This control prevents the transmission from shifting into the reverse gear when the select lever is accidentally placed in the R position, thus protecting
the components such as reverse clutch from being damaged.
If the selector lever is moved to the R position during driving at a speed faster than the predetermined speed, the low clutch timing solenoid is
energized. Then, the pilot pressure is supplied to the reverse inhibitor valve. This causes the reverse inhibitor valve to move downward, closing the
low & reverse brake port.
In this condition, the low & reverse brake does not engage since the ATF flowing from the manual valve is blocked by the reverse inhibitor valve.
As a result, the transmission is put into the neutral state, and the shifting into the reverse gear is inhibited.
