Sidekick JS 2D Soft Top 2WD L4-1.6L (1997)
^
Remove all carbon from valves.
^
Inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its face and stem and, as necessary, replace it.
^
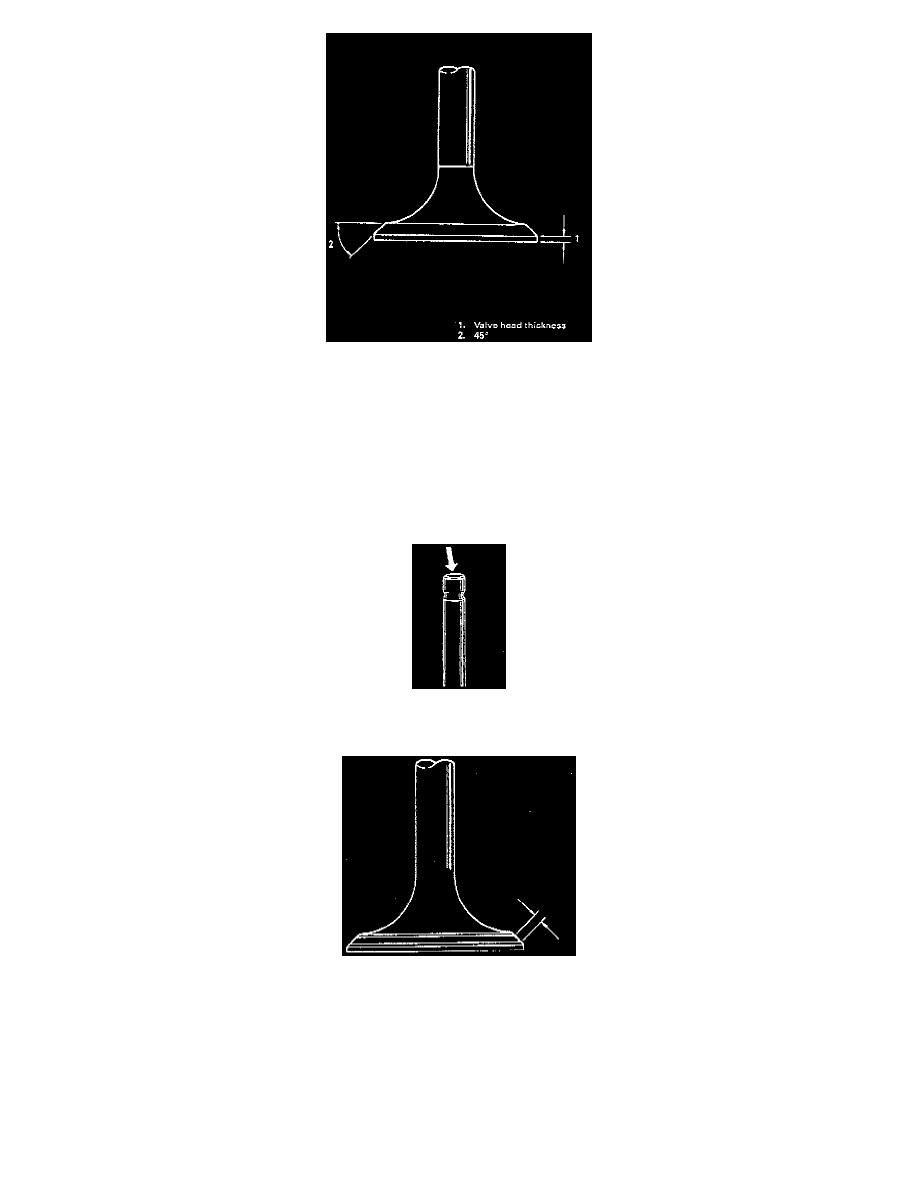
Measure thickness of valve head. If measured thickness exceeds limit, replace valve.
Valve Head Thickness:
Intake:
Standard: 0.8- 1.2 mm (0.03 - 0.047 inch).
Limit: 0.6 mm (0.024 inch).
Exhaust:
Standard: 0.8- 1.2 mm (0.03 - 0.047 inch).
Limit: 0.7 mm (0.027 inch).
^
Inspect valve stem end face for pitting and wear. If pitting or wear is found there, valve stem end may be resurfaced, but not so much as to grind
off its chamfer. When it is worn so much that its chamfer is gone, replace valve.
^
Seating contact width: Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking compound to valve seat
and by rotatingly tapping seat with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping) must be used. Pattern produced on seating face of valve
must be a continuous ring without any break, and the width of pattern must be within specified range.
Standard Seating Width Revealed By Contact Pattern On Valve Face:
Intake And Exhaust: 1.1- 13 mm (0.0433 - 0.0512 inch).
Valve Seat Repair
A valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of specified range must be repaired by
regrinding or by cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
