Swift L4-1298cc 1.3L SOHC MFI (1997)
OPERATION
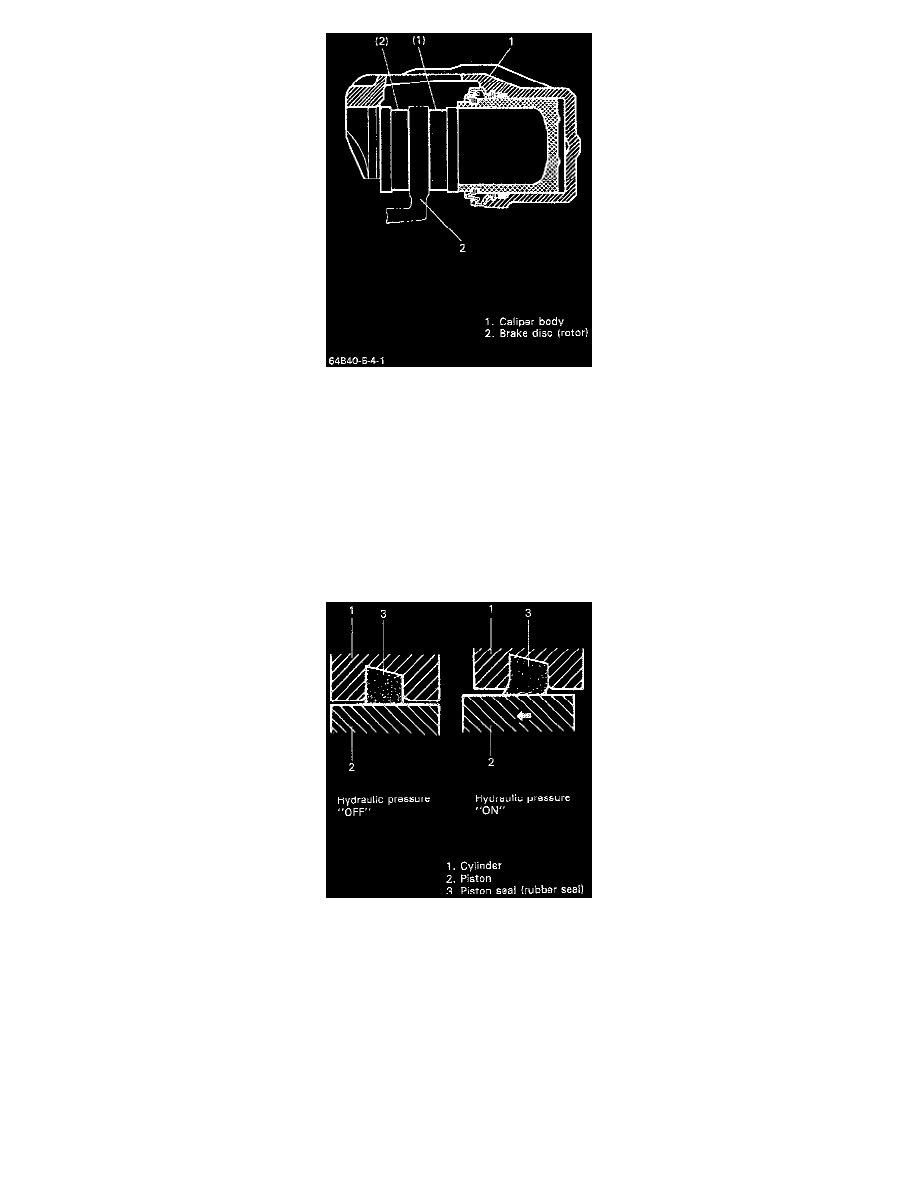
Floating Type Caliper
The single piston floating caliper type brake is employed in this model. One cylinder and one piston are used for this type. (The cylinder is
constructed as a monoblock with the caliper.) Fluid pressure generated in the cylinder causes the pad on the piston side to press against the disc. At
the same time, the floating type caliper body is moved to the right by the cylinder pressure, as shown in above image, which pulls pad against the
disc causing the braking action at the wheel.
No Servo Assist
The disc brake has no servo assistant as in drum braking, and it is necessary to increase the working pressure of the piston and pad. For this
purpose, the wheel cylinder has a large bore. Even only a little change in clearance between the disc and pad has therefore a large influence on the
brake pedal stroke. It is necessary to keep the clearance adjusted to the minimum at all times, by means of the piston (rubber) seal.
PISTON SEAL
Pressure Is Applied - to the piston, the piston moves forward. The rubber seal, which exerts considerable pressure against the piston, moves with
the cylinder. However, as a part of the rubber seal has been fixed into a groove in the cylinder, the shape of the rubber seal is distorted toward
internal end of the cylinder, as shown in above image.
When Pressure Is Taken Off - from the foot brake pedal and fluid pressure is released from the piston, a restoring force is generated at the seal
and pushes the piston back.
As The Pads Wear Away - and the clearance between the disc and pads becomes larger, the piston moves a larger distance. The seal then could
change in shape further but, since the end of the seal is fixed into the groove in the cylinder, the distortion is limited to the same amount as
previously described.
