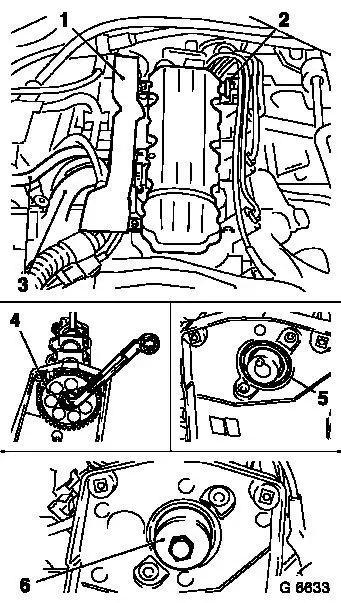
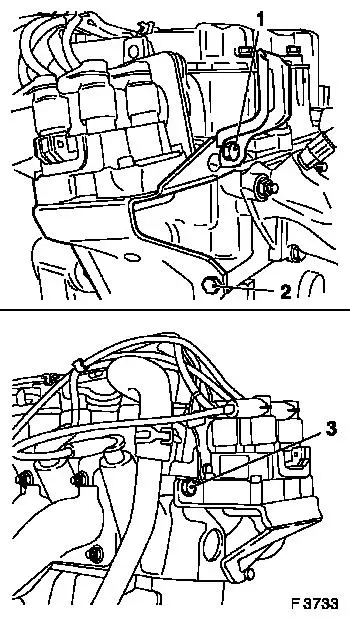
Omega B
|
Ignition, Secondary (STD Single)
Preparation
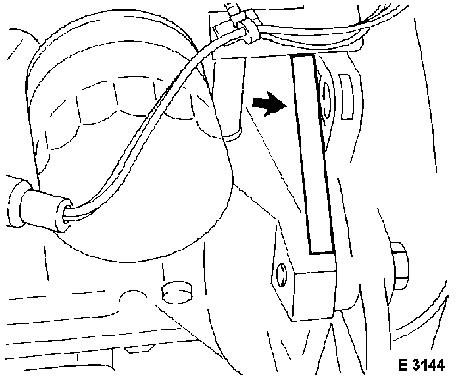
Connections
Procedure Start the engine and allow it to idle.
Notice: On 4-valve engines the mixture swirl within the combustion chamber is so intense that the combustion voltage plot behaves very erratically and as a result this does not necessarily indicate soiling of the spark plugs on these engines.
Notice: On 4-valve engines the mixture swirl within the combustion chamber is so intense that the combustion voltage plot behaves very erratically and as a result this does not necessarily indicate soiling of the spark plugs on these engines.
Notice: If the fault occurs on all of the cylinders, check the intake side for unmetered air. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||