Polo Mk3
|
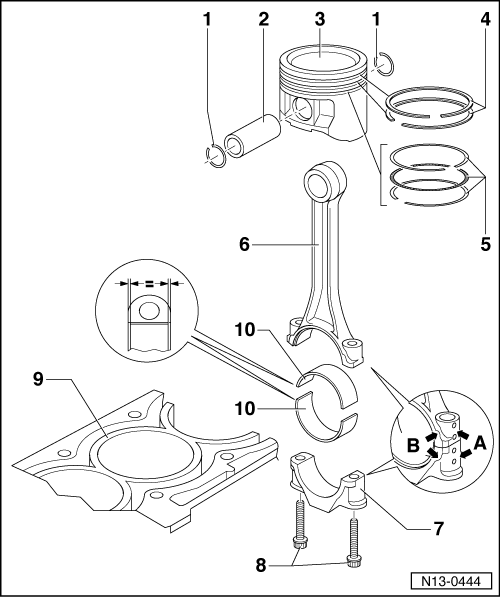
Dismantling and assembling pistons and conrods
Dismantling and assembling pistons and conrods
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|||||||||||||
|
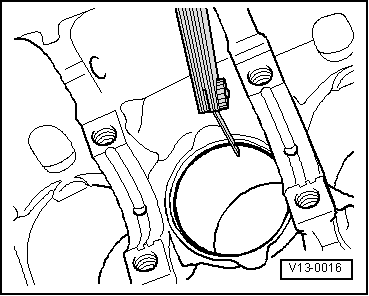
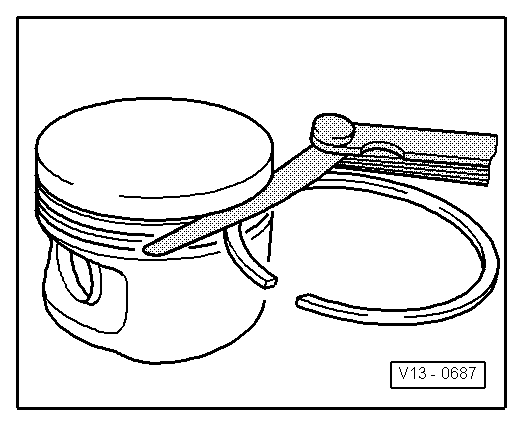
→ Fig. 2 Checking ring to groove clearance Clean groove before check.
| |||||||||||||
 |
|
|
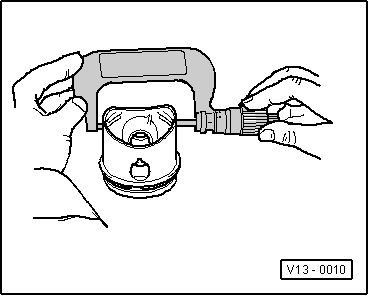
→ Fig. 3 Checking piston Special tools, workshop equipment, testers, measuring instruments and auxiliary items required
|
 |
|
|
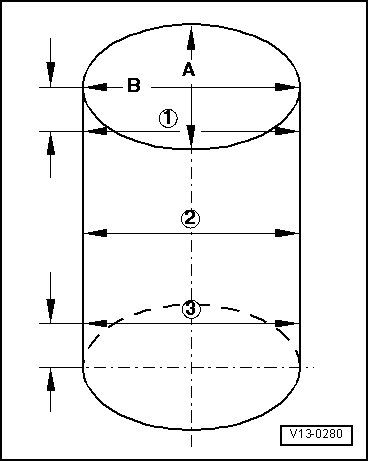
→ Fig. 4 Checking cylinder bores Special tools, workshop equipment, testers, measuring instruments and auxiliary items required
Note: Measuring the cylinder bores must not be done when the cylinder block is mounted on a repair stand with adapter bracket VW 540, as incorrect measurements would then be possible. |
 |
|
|
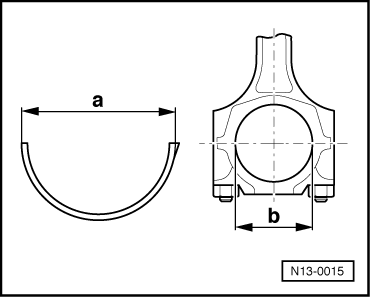
→ Fig. 5 Measuring bearing shell pretension Special tools, workshop equipment, testers, measuring instruments and auxiliary items required
The bearing shell pretension is calculated as follows:
Bearing shell dimension -a- Minimum dimension: 1.5 mm If the pretension is not achieved:
|