780 V6-2849cc 2.8L SOHC B280F (1987)
Oxygen Sensor (Lambda Sond): Description and Operation
Oxygen Sensor (Lambda Sond)
Used by the fuel injection ECU:
PURPOSE AND LOCATION
Under normal conditions, the optimum air/fuel mixture ratio is 14.7kg air to 1kg fuel. The ratio is monitored by measuring the exhaust gas oxygen
content. The oxygen sensor (lambda sond) senses the oxygen content in the exhaust and sends a voltage signal to the fuel injection ECU.
The oxygen sensor is mounted in the exhaust system ahead of the catalytic converter.
CONSTRUCTION
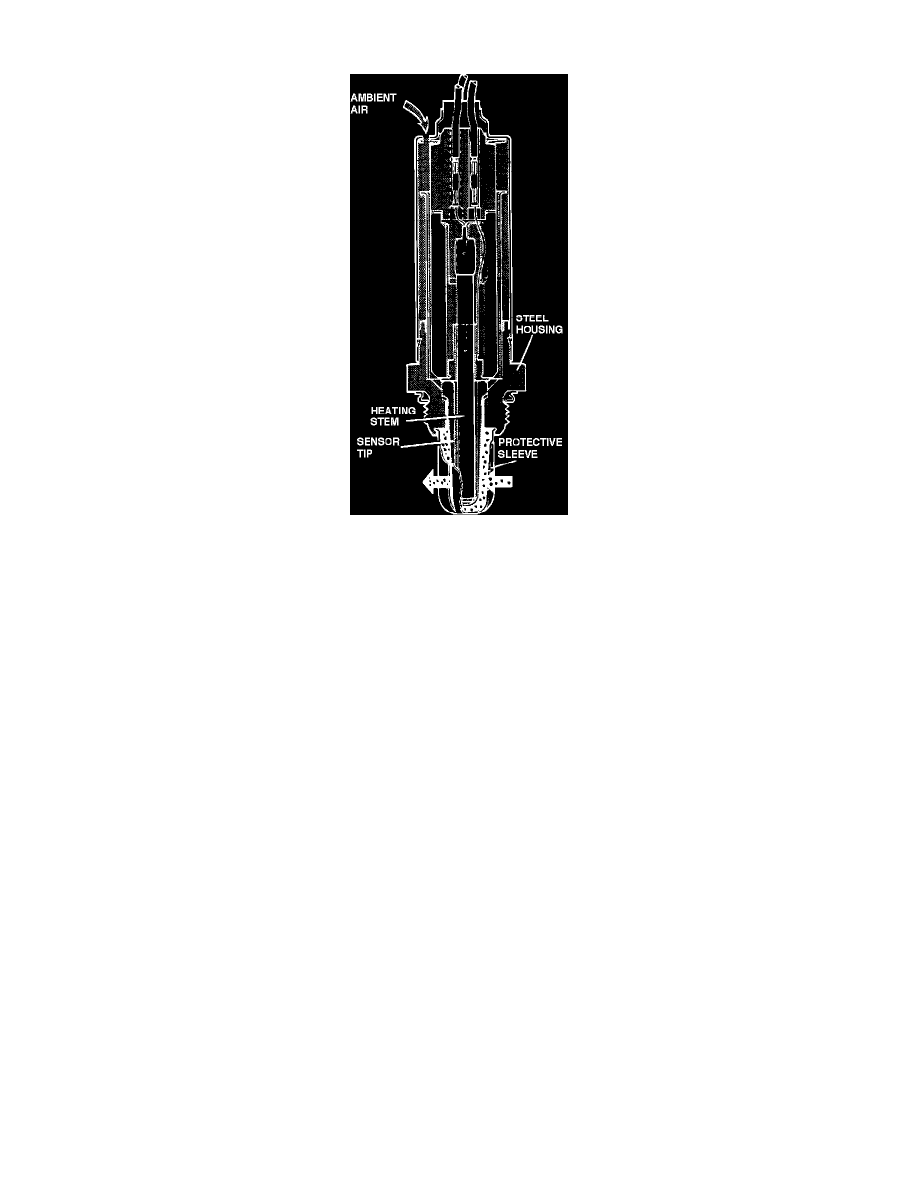
The sensor consists of a steel housing, heating stem (element), sensor tip and its protective sleeve. The sensor tip itself is made from a platinum covered
zirconium-oxide pipe.
OPERATION
This particular model of oxygen sensor is known as a "comparing oxygen sensor". It produces a measureable voltage by comparing the amount of
oxygen in the exhaust gas with the amount in the ambient air.
The sensor operates only within a certain temperature range of approx. 545 - 1530°F (285 - 850°C). It is electrically heated to reach its operating
temperature as fast as possible. When the ignition is turned ON, current is sent to the PTC (positive temperature coefficient) resistor (heating stem)
whose resistance increases as temperature increases.
The exhaust gases reach the outer surface of the oxygen sensor tip via the openings in the protective sleeve. Ambient air reaches the sensor's inner
surface via channels. The differance in oxygen content produces a voltage read by the ECU.
