940 L4-2320cc 2.3L DOHC VIN 89 B234F FI (1991)
of the cover.
-
Inspect the tensioner/idler/water-pump pulleys for wobble or looseness. The pulleys should spin freely with no rough spots or lateral (side-to-side)
movement.
-
Inspect the tensioner/idler/water pump pulley surfaces. They should be clean and free of nicks and burrs. If any damage is noted the pulleys should
be replaced.
-
Inspect the water pump for signs of leakage, replace if necessary.
-
Inspect the camshaft and crankshaft oil seals for leakage. Any seal which shows signs of leakage should be replaced.
CAUTION: Oil leakage will damage the new timing belt.
TIMING BELT INSTALLATION
-
When positioning or moving the camshaft and crankshaft pulleys, do not grasp the teeth of the pulleys with pliers or any other metal object.
CAUTION: Any nick or burr left on the pulleys may result in premature belt failure.
-
When installing the timing belt:
-
Do not use any device to pry the belt over a pulley
-
Do not lubricate the pulleys with any type of fluid or penetrating oil to ease in slipping the belt on.
-
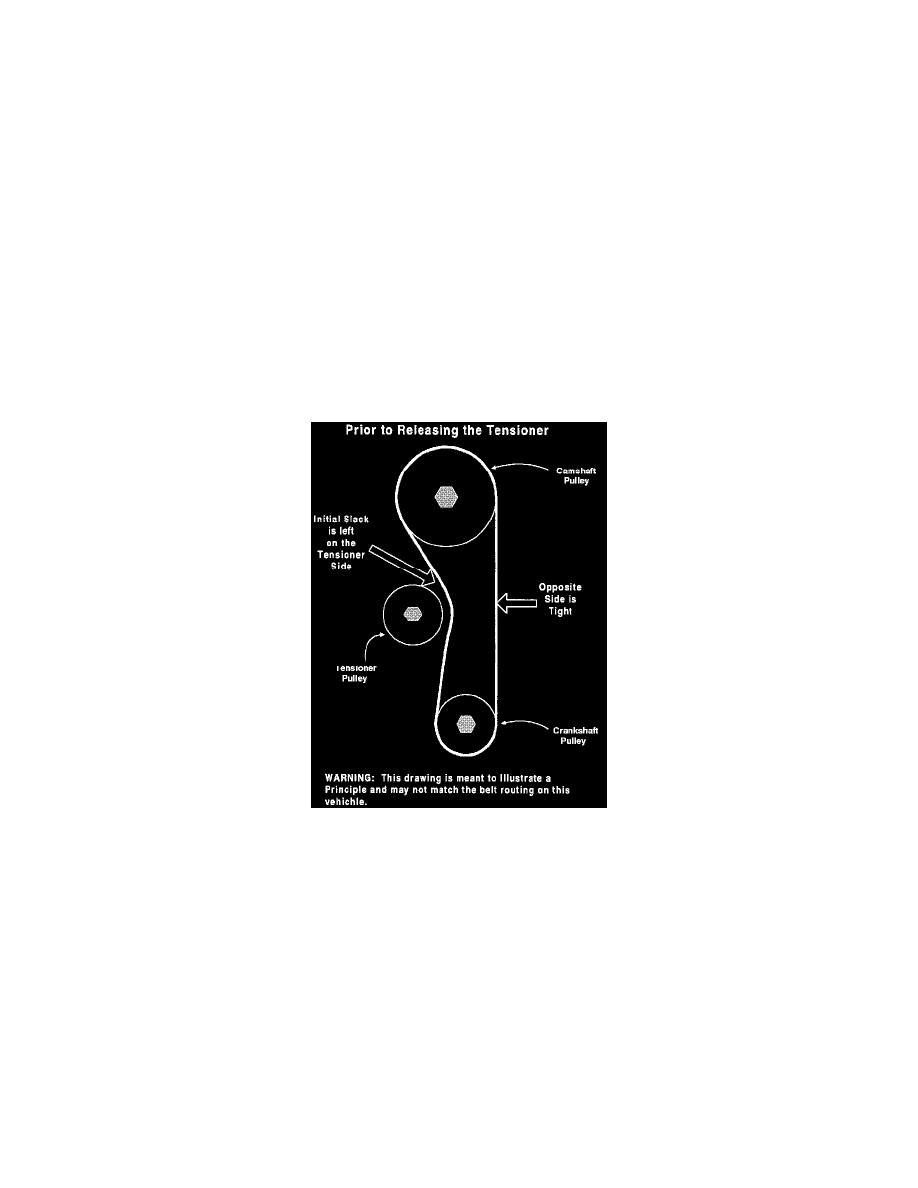
Always install the belt such that the initial slack is on the tensioner side of the pulleys. If any slack is left on the opposite side, when the tensioner
is released the pulleys will turn and the belt alignment will be incorrect.
-
After installing and tensioning the belt, recheck the alignment of the camshafts and crankshafts.
Positioning Crankshaft to Number 1 TDC
POSITIONING CRANKSHAFT TO #1 TDC, Compression
NOTE: If the timing belt is broken, pre-position only the crankshaft and ignore references in this article to compression stroke, camshaft, and
distributor position. Rotating the camshaft with a broken timing belt may damage the valves.
WHY
Timing belt installation alignment marks correspond to the crankshaft positioned at #1 Top Dead Center (TDC), during the compression stroke.
Moving the crankshaft to this point prior to removing the belt allows you to verify the original alignment of the crankshaft and camshaft. This also
reduces crank/cam pulley movement once the belt is removed which helps to minimize any possible confusion.
The alignment marks may be dirty and difficult to locate. Pre-positioning the crankshaft will make it easier to locate the marks.
