S80 AWD V8-4.4L VIN 85 B8444S (2008)
Certain factors, for example, tolerance deviations on certain components such as mass air flow (MAF) sensor and injectors, air leakage on the intake
side, fuel pressure etc. affect the fuel / air mix. In order to compensate for this, the engine control module (ECM) has adaptive (self learning) functions.
When the engine is new the short term fuel trim varies cyclically around a nominal central line (A) 1.00, with, for example, a ±5% change of injection
time when fuel trim is in operation.
If there is air leakage for example, the short-term fuel trim will quickly be offset to a new position (B) and will then work for example between 1.10
(+10%) and 1.20 (+20%), although still at an amplitude of 5%, but with an offset in relation to the original center line (A). The injection period has then
been increased to compensate the increase in the amount of air.
The adaptive functions will correct the change, so that the short-term fuel trim will work around the new center line (B) where it will again have its full
range of control available.
Put simply, fuel trim is a measurement of the difference (C) between the original short-term fuel trim center line (A) and the new center line (B).
The adaptive functions are split into various operational ranges based on the load and speed of the engine.
The different adaption ranges can be read off.
The adaptive adjustments of injection time are continuously stored in the engine control module (ECM). This means that, at different operating ratios,
the correct mixture ratio is achieved before the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) reaches operating temperature.
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored in the engine control module (ECM) if any adaption value is too high or too low.
Fuel pressure regulation
General
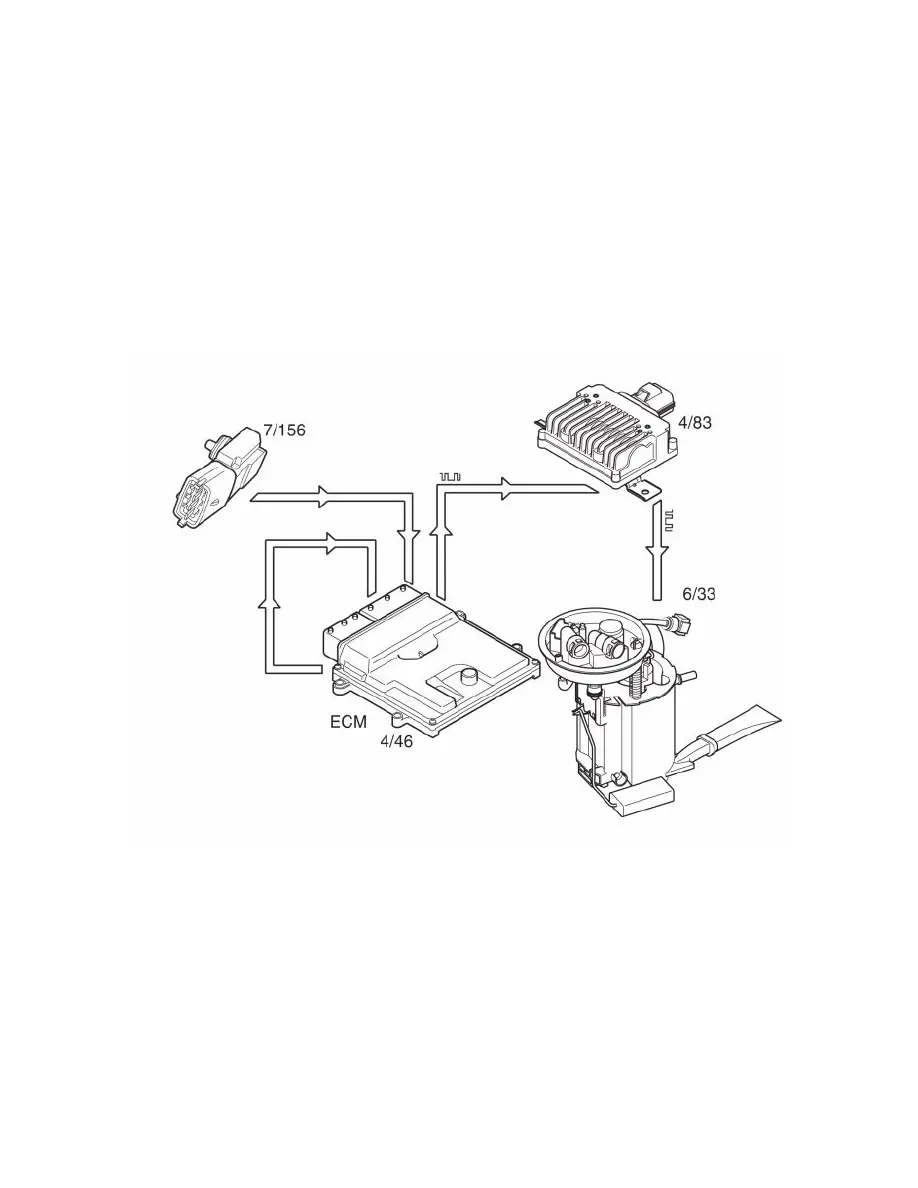
Fuel pressure regulation for demand controlled fuel pumps means that the fuel pressure/flow is controlled steplessly by varying the output of the fuel
pump. The design of the system means that the fuel pressure can be regulated between 300 and 500 kPa. The high pressure is used in extreme situations,
such as heavy engine load for example and hot starts.
The following components are used for fuel pressure regulation:
-
engine control module (ECM) (4/46)
-
fuel pump control module (4/83)
-
fuel pressure sensor with fuel temperature sensor (7/156)
-
fuel pump (FP) (6/33).
The time taken for the engine start procedure can be reduced by rapidly increasing the pressure in the fuel rail when the engine control module (ECM)
receives a signal about the position of the start control module (SCU) from the central electronic module (CEM).
The injection period for the injectors can be better calculated by the engine control module (ECM) since the signal from the fuel pressure sensor
provides information regarding actual fuel pressure and temperature. Special cold starting properties for the engine are improved.
