V50 AWD L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 68 B5254T3 (2005)
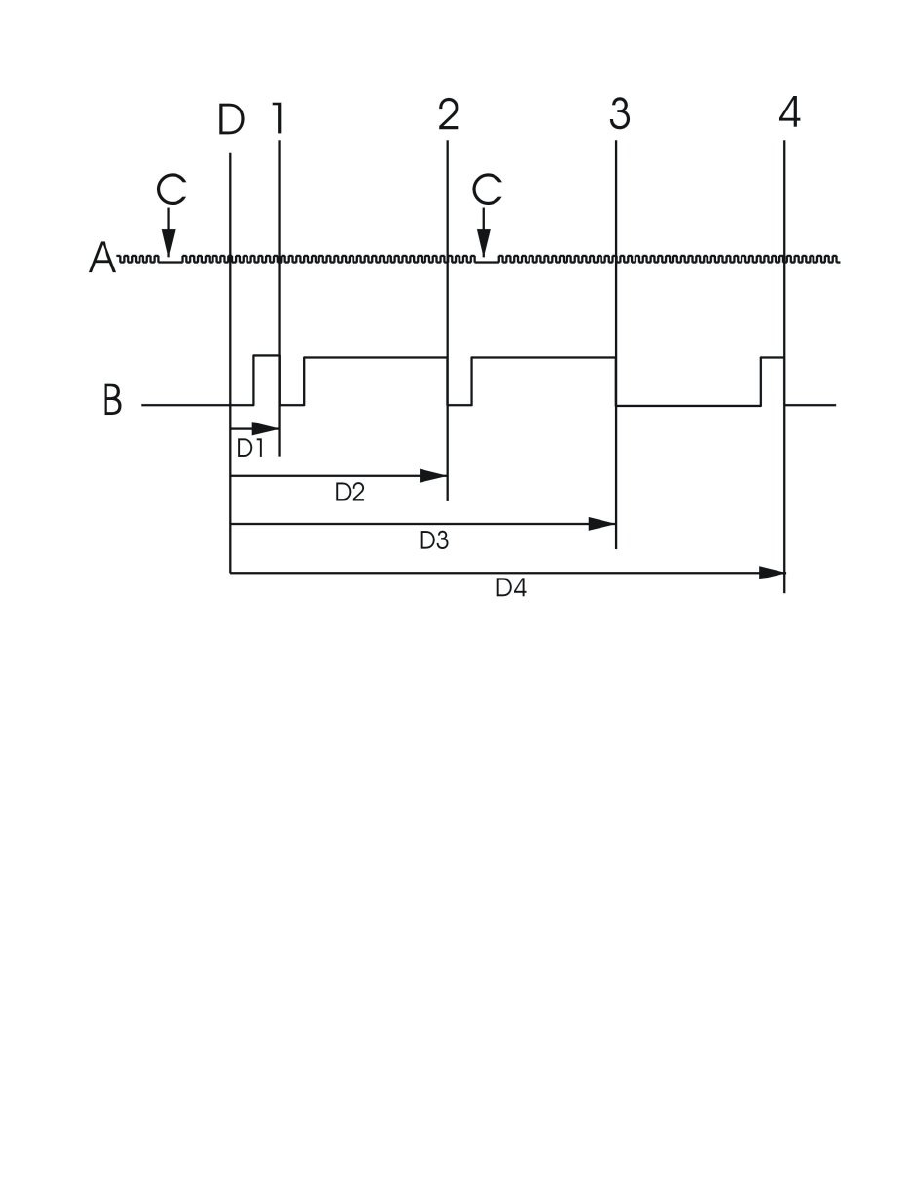
Detecting the position of the camshaft in relation to the position of the crankshaft
Each camshaft flank aligns with pre-defined positions on the crankshaft when the camshaft is in its 0 position. These positions on the crankshaft are
called reference positions for the flanks.
The illustration shows how the signals relate to each other when the camshaft is in its 0 position (the camshaft is not deployed).
A: Engine speed (RPM) sensor signal.
B: Camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal. From high to low signal when the teeth on the camshaft pulley leave the camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
C: Low engine speed (RPM) sensor signal because of the holes in the flywheel/carrier plate.
D: Top dead center (TDC) cylinder 1, 0°CA (84°CA after hole "C" in the flywheel/carrier plate).
1: Detection of flank 1, reference position 47°CA "D1".
2: Detection of flank 2, reference position 227°CA "D2".
3: Detection of flank 3, reference position 407°CA "D3".
4: Detection of flank 4, reference position 587°CA "D4".
If the flanks do not correspond to the reference positions on the crankshaft when the camshaft is in the 0 position (not deployed), the engine control
module (ECM) will store the difference. There may be a difference from the camshaft 0 position if the timing belt is incorrectly seated or the camshaft
are not correctly set for example. A mechanically damaged camshaft reset valve may prevent the camshaft moving to the 0 position when the engine
control module (ECM) stores the adaptation value for the deviation of the camshaft. This may result in high deviation and a diagnostic trouble code
(DTC) being stored.
The difference can be read out in VIDA.
Regulating the camshaft position
The engine control module (ECM) controls the camshaft reset valve steplessly. The valve controls the flow of engine oil to the continuous variable valve
timing (CVVT) unit which is affected by the oil pressure that builds up. This allows the CVVT unit to change the position of the camshaft. Also see
Control (below) and Design See: Computers and Control Systems/Description and Operation/Engine Control Module (ECM)/Design
