V70 2.4 L5-2.4L VIN 61 B5244S (2001)
Variable Valve Timing Actuator: Description and Operation
Camshaft Control (CVVT)
Camshaft Control (CVVT)
The engine control module (ECM) controls the camshaft reset valve (CVVT) steplessly. The pressure of the engine oil is used to regulate the CVVT
unit.
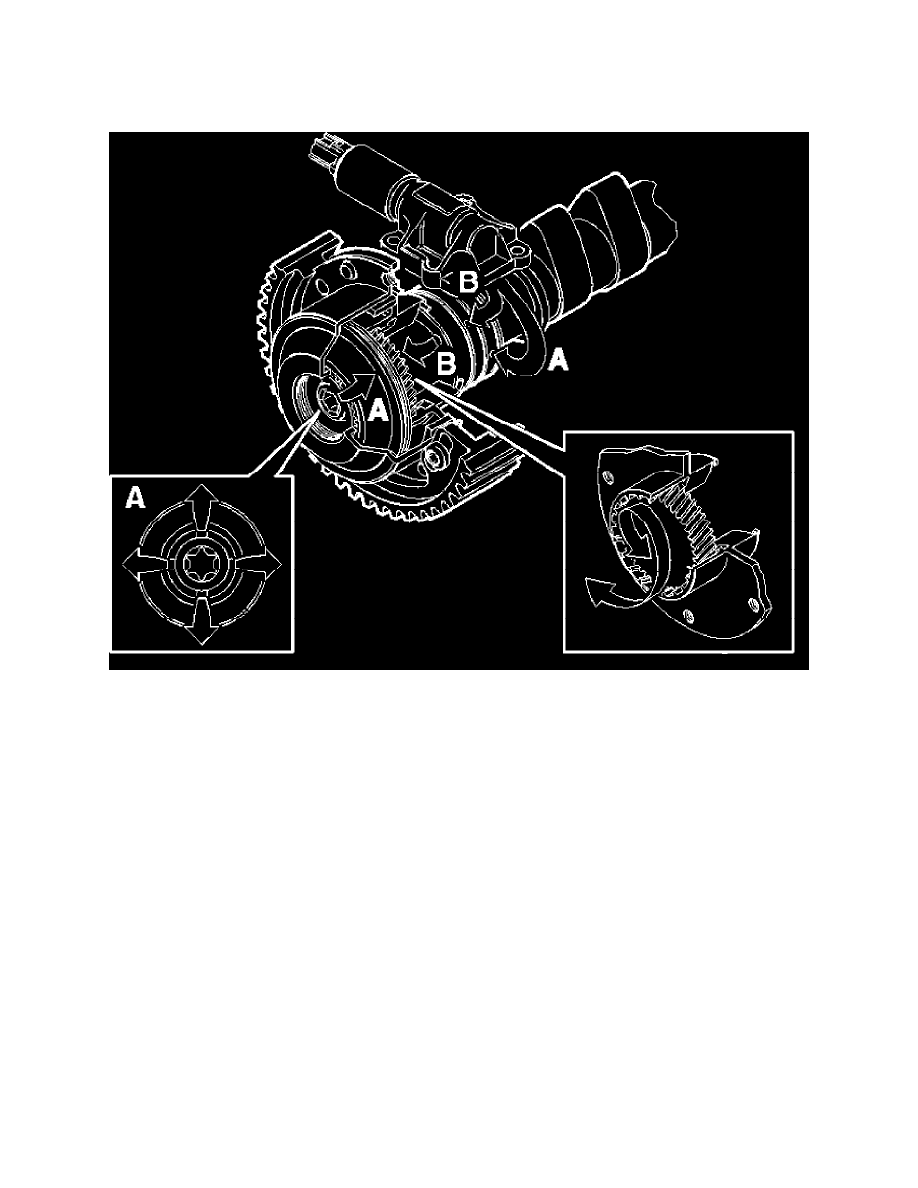
The CVVT is installed on the intake camshaft on all B5244 engines.
There are 30 camshaft degree (60 crankshaft degree) between the limit positions.
The variable camshaft is hydraulically controlled by the engine oil. The camshaft turns when the camshaft reset valve (CVVT) releases lubricating oil
into the front (A) or rear chamber (B) of the CVVT unit. The chambers are separated by a piston which is secured in the camshaft. The piston is secured
in the cover of the CVVT unit by splines so that it moves easily. When the oil acts on the piston, the piston twists. The pulse wheel for the timing belt is
on the outer cover of the CVVT unit.
Regulation is precise and rapid.
The camshaft reset valve (CVVT) has extremely fine ducts. This allows for precise regulation. However as a result the reset valve is sensitive to
contaminants.
The main role of the variable camshaft is to reduce exhaust emissions, especially during cold starting. Idle quality is also improved.
Before the engine starts, there is an internal check consisting of the following stages:
1. When the ignition is switched on, there is an electrical check of the signal cable, the power supply cable and the solenoid. This check checks for a
short-circuit to supply voltage or ground and open-circuits
2. The camshaft is checked to ensure that it is in the correct position in relation to the flywheel, with the camshaft in its 0 position (mechanical resting
position). This can be done by comparing the signals from the camshaft position (CMP) sensor and the engine speed (RPM) sensor. If there is too
much deviation between these, the camshaft reset valve (CVVT) is not activated and a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored
3. During greater control of the variable camshaft, the amount of time taken to deploy the camshaft to the desired value is measured. This time is
