XC70 L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 59 B5254T2 (2003)
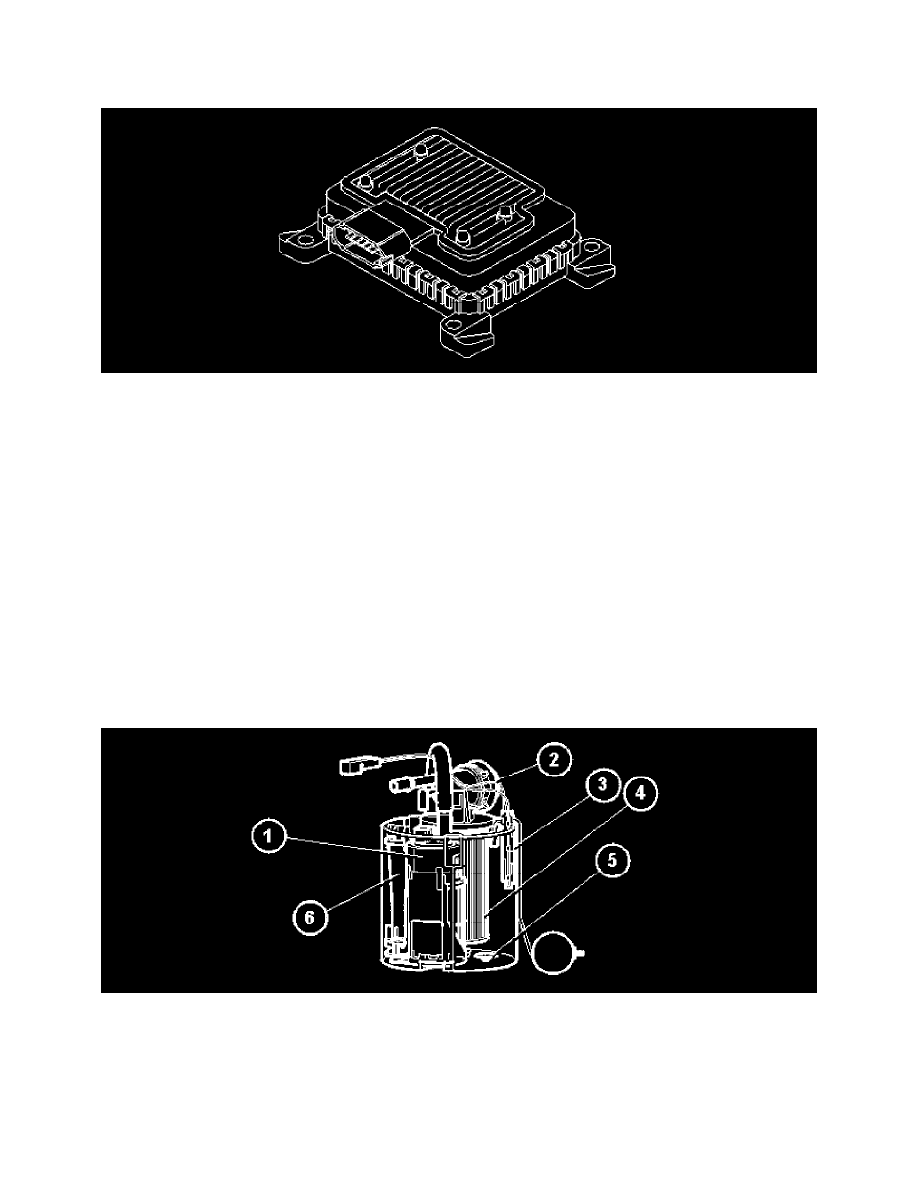
Fuel Pump Control Unit: Description and Operation
Fuel Pump Control Module (only Vehicles With Demand Controlled Fuel Pumps)
The fuel pump control module powers the fuel pump and regulates the output of the pump. The fuel pressure changes with the output of the pump.
The fuel pump control module is supplied with battery voltage by the fuel pump (FP) relay and is grounded in the car body. The fuel pump (FP) relay is
controlled by the central electronic module (CEM) when requested by the engine control module (ECM).
The engine cannot be started if the power supply to the fuel pump control module is faulty because the fuel pump will not then be powered.
The fuel pump control module is controlled by the engine control module (ECM) via serial communication. The fuel pump control module then controls
the fuel pump by transmitting a PWM voltage on the ground lead for the fuel pump. This means that the voltage drop across the pump changes, and with
it the output of the fuel pump. Also see Function.
There are no diagnostics for the fuel pump control module. The engine control module (ECM) has diagnostics for fuel pressure regulation and the
associated components. Also see Fuel pressure regulation, diagnostics.
The pulse width modulated (PWM) signal from the engine control module (ECM) to the fuel pump control module can be read off using VADIS/VIDA.
The fuel pump control module is on the outside on the right-hand side of the fuel tank.
Fuel pump (only vehicles with demand controlled fuel pumps)
The function of the fuel pump is to ensure that the pressure is correct at the delivery lines for the injectors when requested by the fuel pump control
module.
The fuel pump consists of:
1. An electrical pump with an integrated safety valve
2. A pressure equalization valve. This valve equalizes rapid pressure peaks which occur, for example, when the injectors close during engine braking.
It also contains a non-return valve which ensures that the pressure in the system does not drop when the engine is switched off
3. Fuel level sensor
