XC70 AWD L6-3.2L VIN 98 B6324S (2009)
The function of the knock sensor (KS) is to monitor combustion knocking from the engine. Knocking may damage the engine and reduces the efficiency
of engine combustion.
If the engine control module (ECM) registers knocking from any of the cylinders, the ignition will be retarded for that cylinder at the next combustion
stage. If repeated ignition retardation does not prevent knocking, the injection period will be increased. This has a cooling effect.
The sensor is made up of a piezo electrical crystal. If there is engine knock, vibrations (sound waves) spread through the cylinder block to the knock
sensor (KS). The resultant mechanical stress in the piezo electrical material in the knock sensors generates a voltage. This signal is transmitted to the
Engine Control Module (ECM). The signal corresponds to the frequency and amplitude of the sound waves. This allows the Engine Control Module
(ECM) to determine if the engine is knocking. The camshaft position (CMP) sensor and engine speed (rpm) sensor are used to determine the operating
cycle of the engine (which cylinder is igniting) and thereby which cylinder is knocking.
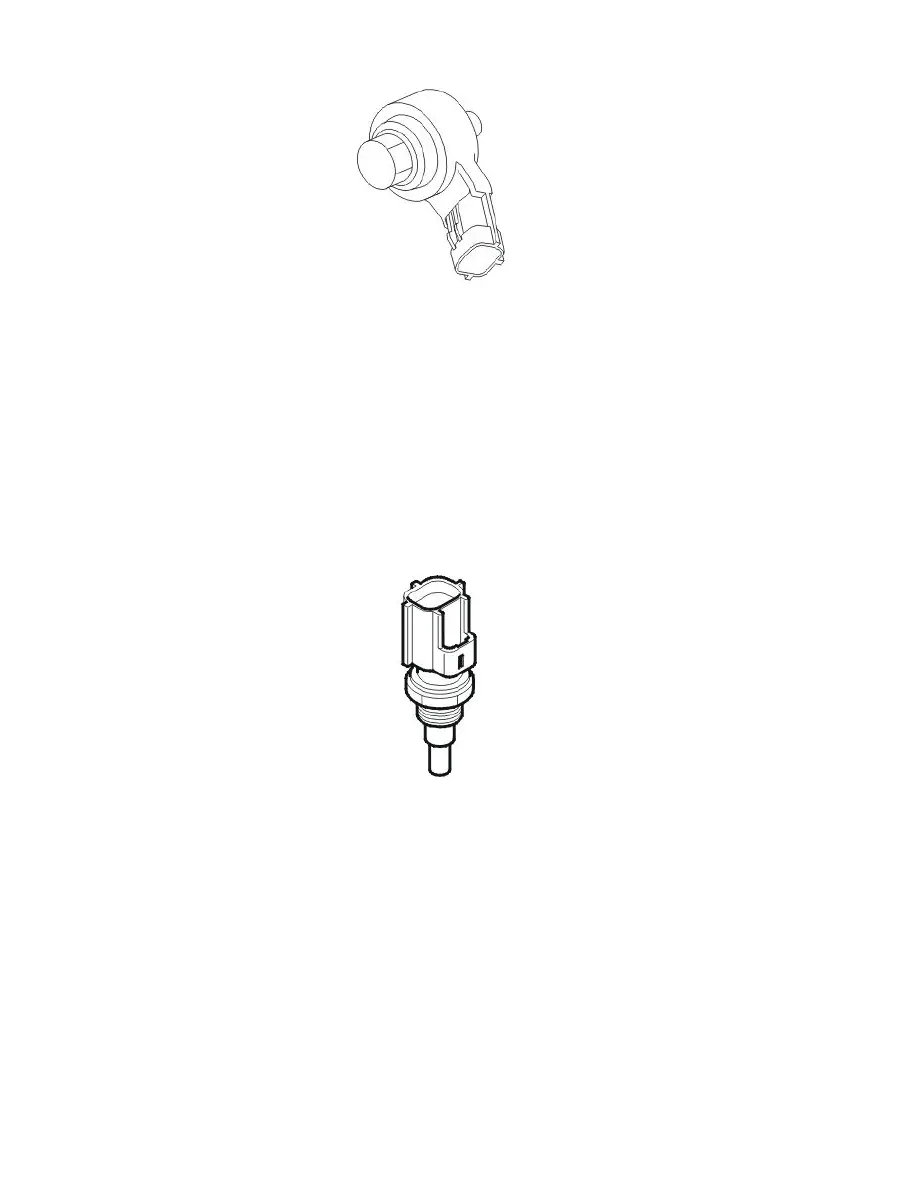
The knock sensors (KS) are located on the cylinder block under the intake manifold.
The engine control module (ECM) can diagnose the knock sensors (KS).
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor checks the temperature of the engine coolant. The temperature of the engine coolant is required so that the
engine control module (ECM) can regulate:
-
the injection period
-
the idle speed
-
the engine cooling fan (FC)
-
the ignition advance
-
engagement and disengagement of the A/C compressor
-
diagnostic functions.
The sensor is a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) type which is supplied with power from the control module (signal) and is grounded in the
control module.
The resistance in the sensor changes depending on the temperature of the coolant. Depending on the resistance in the sensor, voltage (signal) is
transmitted to the engine control module (ECM). The lower the temperature the higher the voltage (high resistance). A high temperature results in low
voltage (low resistance).
The engine temperature sensor is located by the thermostat under the intake manifold.
The engine temperature sensor can be diagnosed by the engine control module (ECM) and the sensor value can be read out.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor/Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
