XC90 2.5T AWD L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 59 B5254T2 (2003)
(DTCs) on the MOST network.
If a control module in the MOST network stops working and is unable to transmit light pulses onwards, or if there is an open-circuit in the fiber optic
cable, the entire MOST network will stop working. This means that all the control modules on the MOST network will stop working. For more
information about remedying this, see fault management on the MOST network.
The infotainment control module (ICM) must always be connected on the MOST network for communication on the MOST network to work.
The MOST network connections increase and the signal routing may change when control modules are added because adapter wiring is used to connect
the new control module.
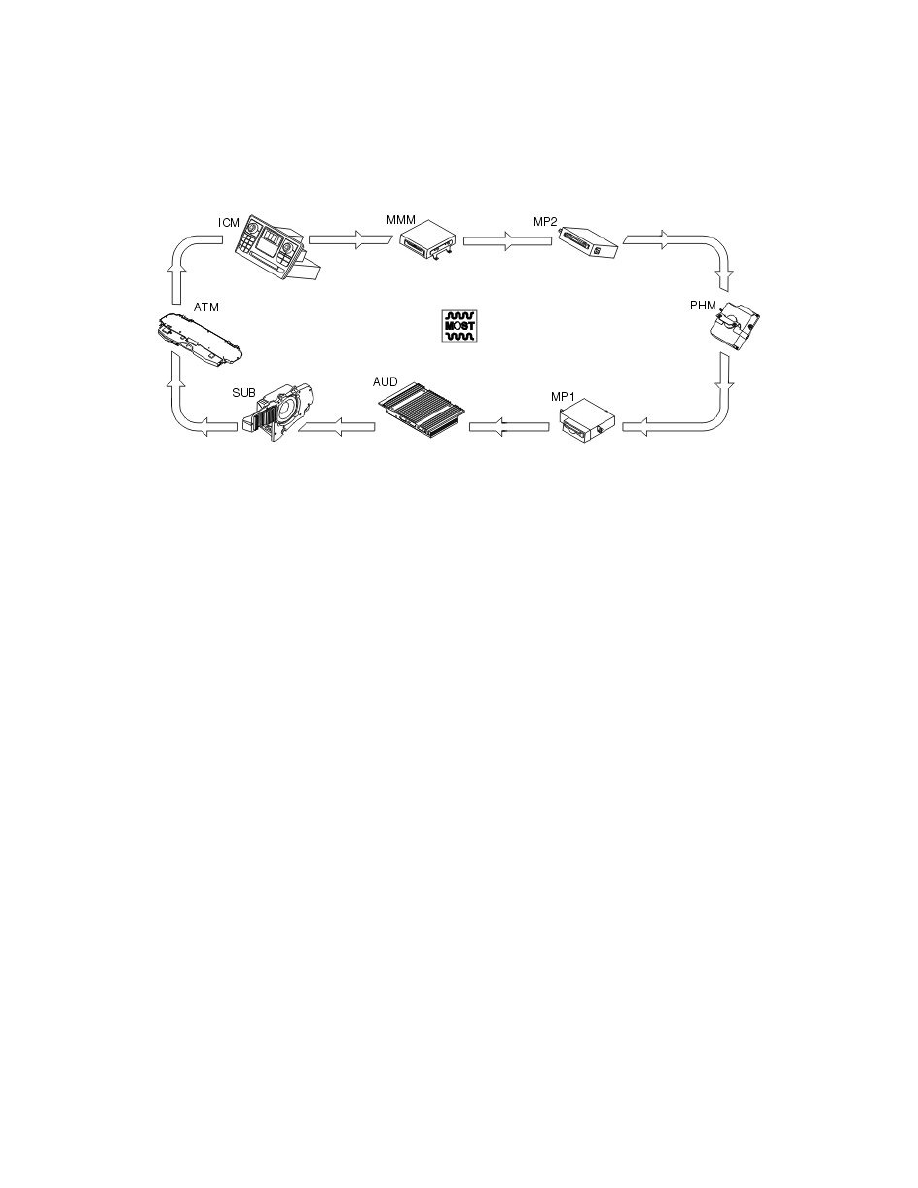
Location of control modules on the MOST network
The control modules on the MOST network should be positioned in a particular order. If this order is not followed, the fault-tracing of the MOST
network will deteriorate.
When further control modules are added to the MOST network, these should be placed in the correct order on the network to make it easier to fault-trace
the control modules. If the control modules are connected in another order, this does not effect the function of the MOST network, but fault-tracing will
be compromised. The control modules should be placed in the following order:
1. Infotainment Control Module (ICM) (16/1)
2. Multimedia module (MMM) (16/108)
3. CD module (MP2) (16/106)
4. Phone module (PHM) (16/60)
5. MD module (MP1) (16/107)
6. Audio module (AUD) (16/105)
7. Subwoofer module (SUB) (16/79)
8. Antenna module (ATM) (16/110).
If the MD module (MP1) is installed as an aftermarket accessory in a car with a phone module (PHM) and CD module (MP2), the MD module (MP1)
will change positions with the phone module (PHM).
If the configuration of the MOST network in the car is minimal, the following control modules are connected:
-
infotainment control module (ICM)
-
the audio module (AUD)
-
the antenna module (ATM).
MOST Network
MOST network
General
MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) is a standardized network communication system for multimedia applications. The MOST protocol is
optimized for fiber optic communication. This means that signals are sent as light pulses.
MOST data
The MOST protocol determines how light pulses, or the absence of light pulses should be interpreted. Each pulse or absent pulse is called a "bit". The
number of "bits" transmitted on the MOST network is 24.8 million per second (24.8 Mbps). A bit can be:
-
binary 0, i.e. no light pulse
-
binary 1, i.e. light pulse.
The light pulses are transmitted in data frames. A data frame consists of different types of data. The size of a data frame is 64 bytes, which is 64 x 8 =
512 bits.
The data frame has a frequency of 48 kHz. This means that 48000 data frames are sent per second on the MOST network.
The data types which are included in a data frame sent on the MOST network are:
-
control data
