XC90 2.5T AWD L5-2.5L Turbo VIN 59 B5254T2 (2003)
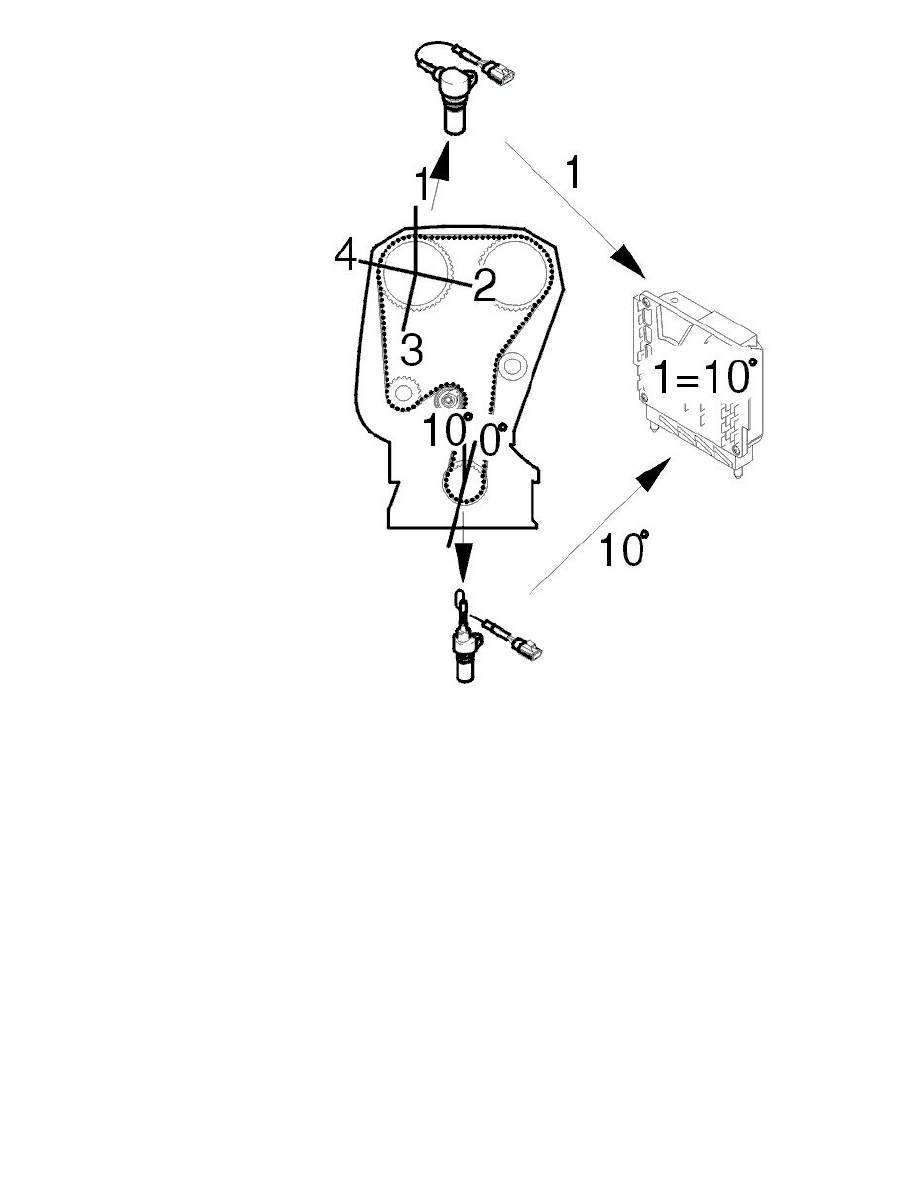
The camshaft (A) is divided into four flanks per revolution of the camshaft (flanks 1-4). The angle between flanks 1-2 = 103°, flanks 2-3 = 90°, flanks
3-4 = 90° and flanks 4-1 = 77°. The angle between the flanks is different, allowing the control module to determine which flank it is detecting and
therefore determine which combustion cycle the cylinders are in,
The crankshaft has four reference positions, one for each camshaft flank. The camshaft turns at half the speed of the crankshaft. This means that two
reference positions are detected for each turn of the crankshaft. Therefore two engine revolutions are required to detect all flanks on the camshaft. For
example (may vary between different engine variants): flank 1 at 0°, flank 2 at 206°, flank 3 at 386° and flank 4 at 576° (flanks 3 and 4 are detected
during the second engine revolution).
The reference positions of the crankshaft coincide exactly with each camshaft flank if the camshaft cam timing is 0°. If the cam timing deviates from 0°,
i.e. the flanks deviate from the reference positions of the crankshaft, the control module calculates the number of crankshaft degrees by which the flank is
deviating.
The control module detects the reference positions for the camshaft flanks using the signal from the engine speed (RPM) sensor.
Example:
If camshaft flank 1 is detected at 10° from the crankshaft reference position for flank 1 (0° +10°), the cam timing is 10°. If the cam timing is the same (10
°), flank 2 is detected at 216° (206° + 10°), flank 3 at 396° (386° + 10°), and flank 4 at 586° (576° + 10°). The cam timing can be positive (+) or
negative (-) depending on whether the flank is detected before or after the different reference positions for the crankshaft.
The engine control module (ECM) controls the camshaft reset valve smoothly in order to regulate the camshaft cam timing. The valve controls the flow
of engine oil to the continuous variable valve timing (CVVT) unit which is affected by the oil pressure that builds up.
Also see Design See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control Systems/Description and Operation/Bosch ME7.01 Engine Management
System/Design.
Control
