XC90 AWD V8-4.4L VIN 85 B8444S (2005)
The navigation function displays the location of the car and directions to the entered destination.
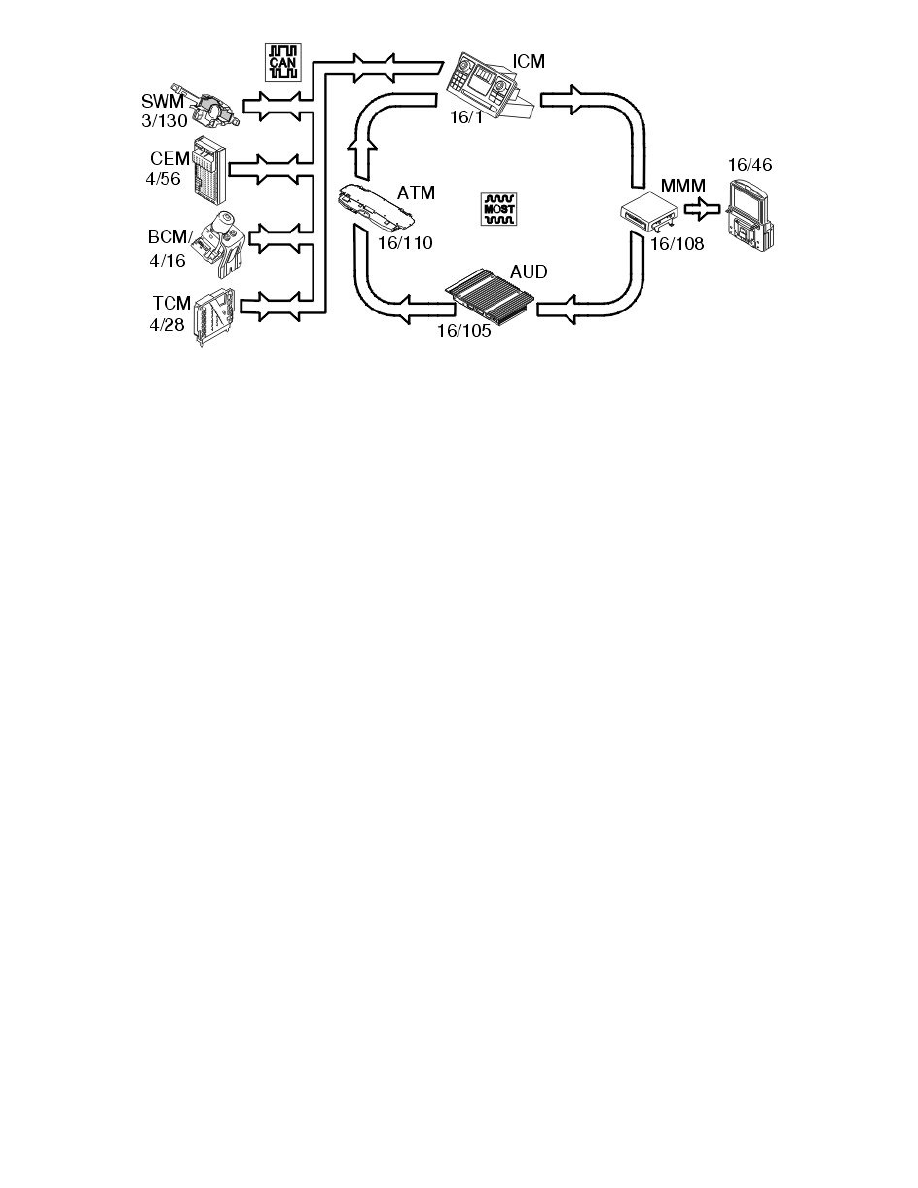
The navigation buttons on the steering wheel module (SWM) (3/130) are used to control the on-screen menu for navigation.
The multimedia module (MMM) (16/108) receives GPS signals from the antenna module (ATM) (16/110) via the MOST network.
Two signals are transmitted via the high speed side of the Controller area network (CAN) to the central electronic module (CEM) (4/56):
-
information about the wheel rotation counter is transmitted from the brake control module (BCM) (4/16)
-
information about the back-up gear position is transmitted from the transmission control module (TCM) (4/28).
The central electronic module (CEM) transmits both signals to the infotainment control module (ICM) (16/1) via the low speed side of the Controller
area network (CAN). The vehicle speed is also transmitted to the infotainment control module (ICM) from the central electronic module (CEM). This in
turn sends the signals on to the multimedia module (MMM) on the MOST network.
Information for voice guiding for the selected destination is transmitted on the MOST network between the multimedia module (MMM) and the audio
module (AUD) (16/105).
A DVD with the required road network must be installed in order for the multimedia module (MMM) to select a route and display the position of the car.
The multimedia module (MMM) is then able to calculate the position and display it on the directly connected screen (16/46).
Diagnostic Functions
Diagnostic functions
General
The control module has a built-in diagnostic system, Volvo Diagnostic, which continuously monitors internal functions as well as input and output
signals.
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is stored if the control module detects a fault. A fault which is detected in the most recent operating cycle is defined as
permanent. Other faults are defined as intermittent.
Should a fault disappear for any reason after being permanently stored in the control module as a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), the information remains
stored in the control module.
If a fault is no longer permanent, the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) remains as intermittent.
Reading and erasing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
Stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can be read off and erased using this function.
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can only be erased once all the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) have been read off at least once.
Note! Certain functions are unavailable until the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) have been erased.
Reading off the control module identification
VIDA identifies control modules by reading off a number of codes from the control module memory.
The codes contain information about the control module:
-
hardware P/N (control module without software)
-
hardware serial number (control module without software)
-
software P/N
