Yugo L4-1300cc 1.3L (1991)
Air Injection: Description and Operation
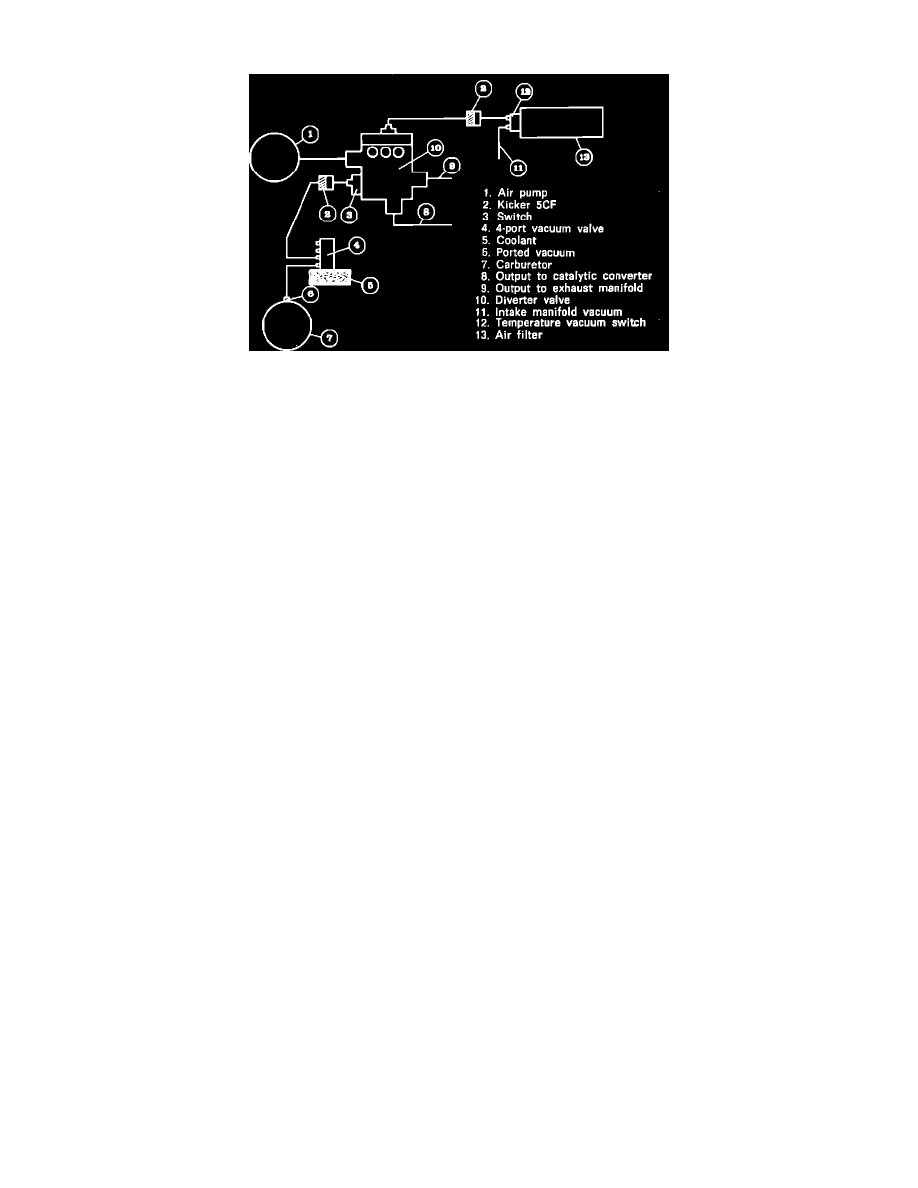
Fig. 1 Air Injection System
DESCRIPTION
The air injection system, Fig. 1, supplies fresh air through injectors mounted downstream of each exhaust valve. The fresh air mixes with the
exhaust charge as it leaves the combustion chamber. An unburned portion of the exhaust charge will unite with the oxygen content in the injected
air and be consumed in the exhaust manifold before the charge is released, through the exhaust system, into the atmosphere. The air pump is driven
at approximately 70 percent of engine speed by a belt from the water pump pulley. Belt tension adjustment is provided by the air pump upper
mounting bolt. The air pump uses rotating vanes on the pulley as a centrifugal filter. The pressure relief valve, which opens when the supply of air
from the pump becomes excessive, is in the diverter valve. A check valve is mounted in the air supply line to prevent exhaust gases from entering
the diverter valve and air pump in case exhaust pressure becomes excessive. All air pump output is delivered through the output hose to the
diverter valve, which controls the flow of fresh air to the injection manifold and the catalytic converter. The primary function of the diverter valve
is to shut off the supply of oxygen to the air injectors during engine deceleration in order to prevent backfiring in the exhaust system. A vacuum
signal from the intake manifold operates the diverter valve and on deceleration will divert the pump output for about four seconds, through an
exhaust orifice, to the atmosphere.
OPERATION
WITH ENGINE COLD
All air pump output is routed to the diverter valve. There is no vacuum signal applied to either diaphragm of the diverter valve. At idle and part
throttle applications, air pump output is directed through the diverter valve upper outlet, through the check valve and into the exhaust manifold. At
wide open throttle applications, air will vent into the atmosphere.
WITH ENGINE WARM
With engine coolant temperature above approximately 128°F, the four port temperature vacuum valve opens. Vacuum from above the throttle
plate is applied through the temperature vacuum switch and a kicker to the diverter. Manifold vacuum is also applied through a temperature
vacuum switch within the air cleaner at ambient temperature above 60°F. Pump output is channeled to the exhaust manifold at idle, to the catalytic
converter at part throttle applications, and vented to the atmosphere at wide open throttle applications.
