NSX V6-3.0L DOHC (1991)
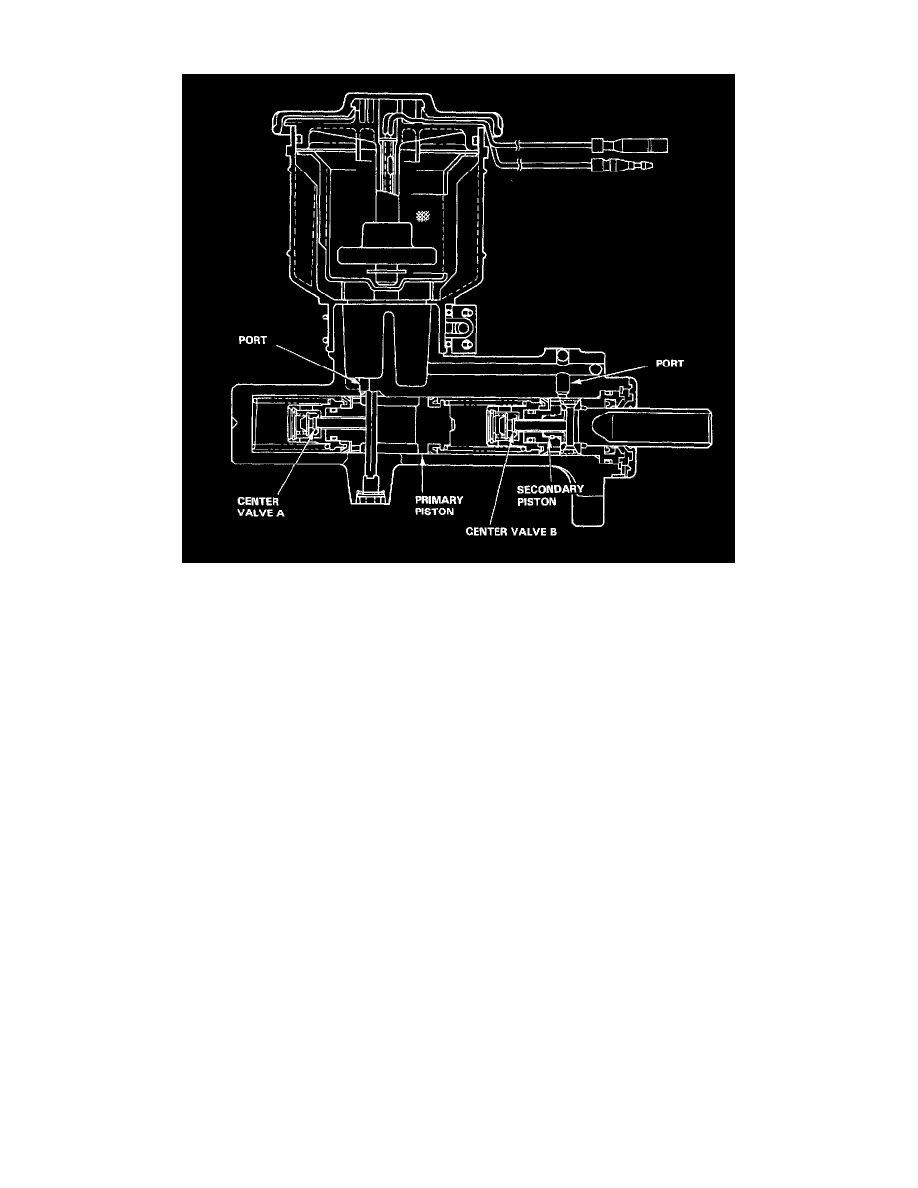
Brake Master Cylinder: Description and Operation
1. Construction
-
A tandem master cylinder with center valves are used to improve braking system safety.
-
The master cylinder has one reservoir tank which is connected to the cylinder sections by two small holes. It has two pistons-primary and
secondary, which are diagonally connected with the calipers so that the fluid pressure works separately on each system Front right wheel &
rear left wheel, and front left wheel & rear right wheel.
-
A stop bolt for controlling movement of the primary piston is provided at the side of the master cylinder body. A reed switch for detecting the
brake fluid volume is also provided on the cap of the reservoir tank.
2. Operation
-
When the brake pedal is depressed, the secondary piston is pushed through the brake booster and center valve B is closed so that the fluid
pressure is generated on the secondary side. At the same time, the primary piston is pushed by the secondary fluid pressure and center valve A
is closed so that braking fluid pressure is generated both on the primary and secondary sides.
-
When the brake pedal is released, the primary and secondary pistons are returned to the original positions by the brake fluid pressure and
piston spring.
3. Responses when fluid is leaking
