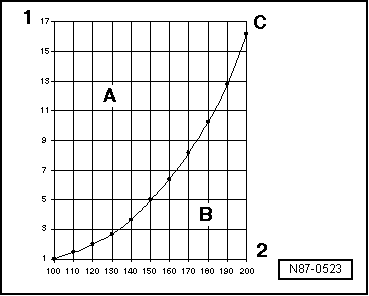
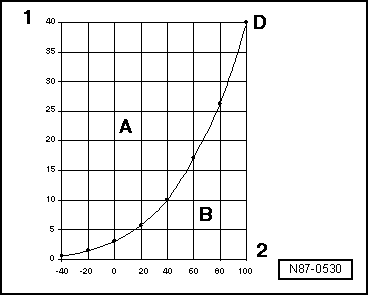
| Pressure and boiling point |
| The boiling point given in tables for a liquid is always referenced to an atmospheric pressure of 1 bar. If the pressure acting on a liquid changes, its boiling point also changes. |

Note | Pressure can be measured in various units: 1 MPa (megapascal) is equivalent to 10 bar gauge pressure, or 145 psi; 1 bar absolute pressure is the same as 0 bar gauge pressure, which is roughly equivalent to atmospheric pressure. |
| For example, water boils at a lower temperature the lower the pressure. |
| The vapour pressure curves for water and refrigerant R134a show, for example, that, at constant pressure, reducing the temperature changes vapour to liquid (in the condenser) or that, for instance, reducing the pressure causes the refrigerant to change from liquid to vapour (in the evaporator). |
|
|
|