Express 4500 V8-6.0L (2010)
4. Disconnect the harness connectors with the high speed GMLAN serial data circuits at another control module, in the direction of the open circuit.
5. Ignition OFF for 60 seconds, test for greater than 100k ohm between each pair of serial data circuits at the control module connector that was just
disconnected. Verify that one pair of serial data circuits are greater than 100k ohm.
‹› If each pair of serial data circuits is less than the specified range, replace the control module that was just disconnected.
6. Repeat step 3 until one of the following conditions are isolated:
*
An open/high resistance on the serial data circuit between 2 control modules
*
An open/high resistance on the serial data circuit between a control module and a terminating resistor
*
An open/high resistance terminating resistor
Repair Instructions
Perform the Diagnostic Repair Verification (See: Testing and Inspection/Diagnostic Trouble Code Tests and Associated Procedures/Verification Tests
and Procedures) after completing the repair.
*
GMLAN Wiring Repairs (See: Testing and Inspection/Component Tests and General Diagnostics/General Electrical Diagnostic
Procedures/Wiring Repairs/GMLAN Wiring Repairs)
*
Control Module References (See: Testing and Inspection/Programming and Relearning) for control module replacement, setup, and programming
Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with Low Speed GMLAN Device
Scan Tool Does Not Communicate with Low Speed GMLAN Device
Diagnostic Instructions
*
Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Diagnostic System
Check - Vehicle) prior to using this diagnostic procedure.
*
Review Strategy Based Diagnosis (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Strategy Based Diagnosis) for an
overview of the diagnostic approach.
*
Diagnostic Procedure Instructions (See: Testing and Inspection/Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview/Diagnostic Procedure Instructions)
provides an overview of each diagnostic category.
Diagnostic Fault Information
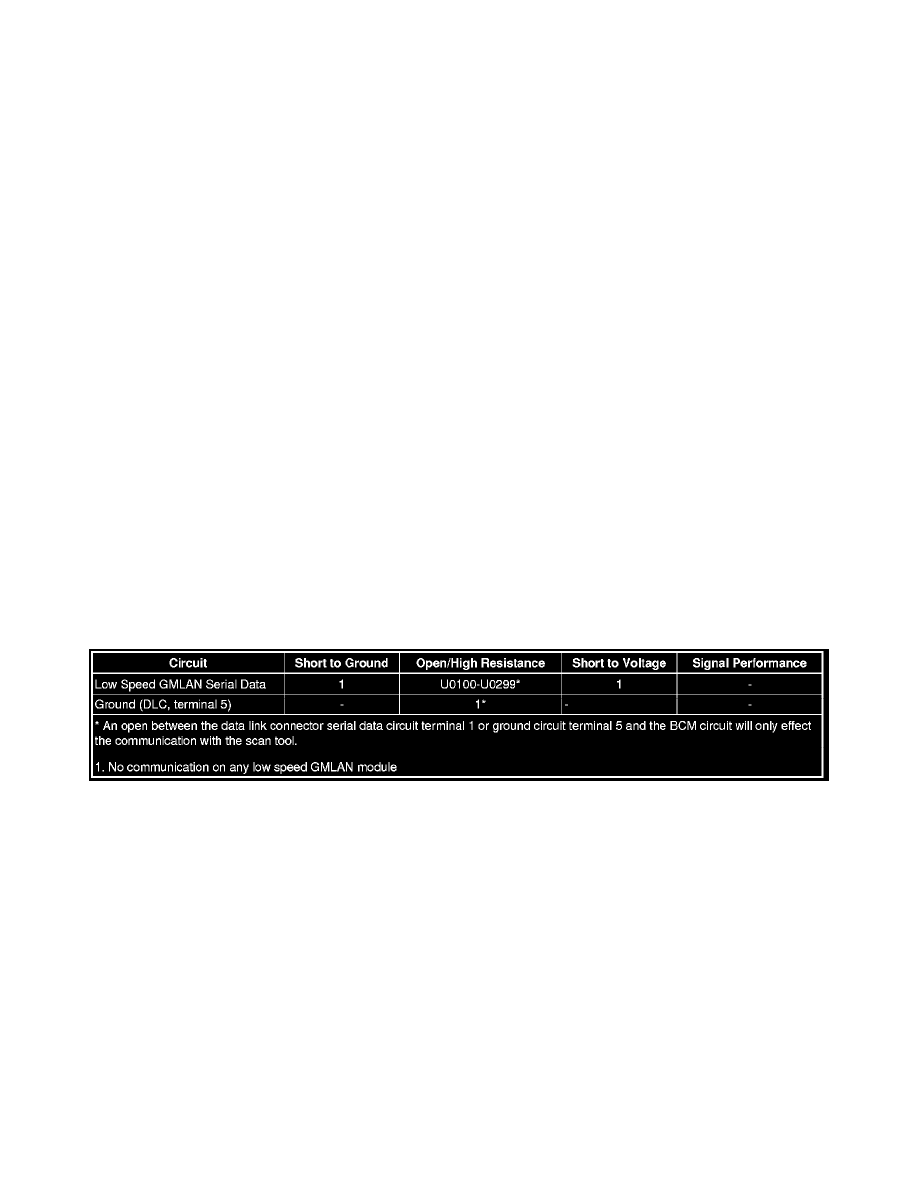
Circuit/System Description
The serial data is transmitted over a single wire to the appropriate control modules. The transmission speed for GMLAN low speed is up to 83.33 Kb/s.
Under normal vehicle operating conditions, the speed of the buss is 33.33 Kb/s. The control modules toggle the serial data circuit between 0-5 V during
normal communications. To wake the control modules connected to the GMLAN low speed serial data circuit, a voltage wake up pulse of 10 V is sent
out. If serial data is lost, control modules will set a no communication code against the non-communicating control module. Note: a loss of serial data
communications DTC does not represent a failure of the module that set it.
Diagnostic Aids
*
Sometimes, while diagnosing a specific customer concern or after a repair, you may notice a history U-code present. However, there is no
associated "current" or "active" status. Loss-of- communication U-codes such as these can set for a variety of reasons. Many times, they're
transparent to the vehicle operator and technician, and/or have no associated symptoms. Eventually, they will erase themselves automatically after
a number of fault-free ignition cycles. This condition would most likely be attributed to one of these scenarios:
-
A control module on the data communication circuit was disconnected while the communication circuit is awake.
-
Power to one or more modules was interrupted during diagnosis
-
A low battery condition was present, so some control modules stop communicating when battery voltage drops below a certain threshold.
-
Battery power was restored to the vehicle and control modules on the communication circuit did not all re-initialize at the same time.
-
If a loss-of-communication U-code appears in history for no apparent reason, it is most likely associated with one of the scenarios above.
