Venture V6-3.4L VIN E (1997)
Alignment: Description and Operation
Definition of Terms
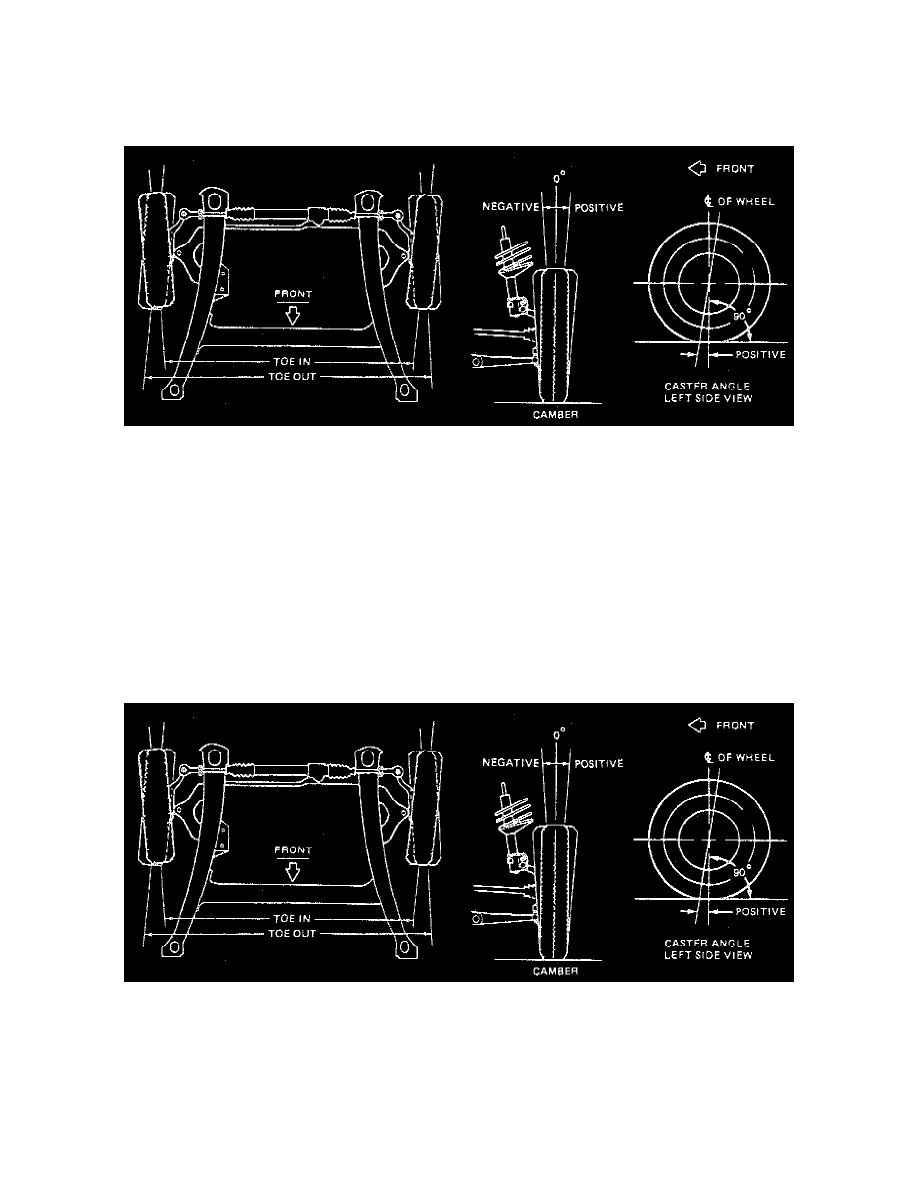
Camber
Camber is an important wheel alignment angle because it is both a tire wear angle and a directional control angle. Camber is the inward or outward tilt of
the top of the tires when they are viewed from the front of the vehicle. If the center line of a tire is perfectly vertical, the tire will have zero camber.
Positive (+) camber means the top of the wheel tilts outward. Negative (-) camber means the top of the wheel tilts inward. An excessive amount of
positive camber will cause outside shoulder wear on the tires. Likewise, an excessive amount of negative camber will cause inside shoulder wear.
Not only will excessive camber result in tire wear, but it will also cause the vehicle to pull or lead to the side with the most positive camber. If there is a
difference in camber from one side of the vehicle to the other, the vehicle will pull to the side with the most positive camber. To better understand
camber's effect on directional control, think of it as a tapered cone that will not roll in a straight line.
Camber is measured in degrees. The actual camber specification is the angle which provides the best tire wear and directional stability.
Camber adjustment is only available at the front wheels.
Caster
Caster is the forward or rearward tilting of the wheel axis (the center line is an imaginary line that passes through the upper mount and the lower ball
joint) from vertical. A rearward tilt (at the top) is positive (+) and a forward tilt is negative (-). Zero caster indicates that the start is directly above the
ball joint. Caster influences directional control of the steering but does not affect tire wear.
Weak springs or overloading a vehicle will affect caster. Caster affects the vehicle's directional stability and steering effort. The caster angle is
calculated to deliver the best in steering effort, normal wheel-returning forces and wheel-pulling sensitivity.
Caster, like camber, is measured in degrees. The caster specification, along with Steering Axis Inclination (SAI), is used to give good directional]
