Concorde V6-2.7L VIN V (2001)
Each module provides its own bias and termination in order to transmit and receive messages. The bus voltage is at zero volts when no modules
are transmitting and is pulled up to about seven and a half volts when modules are transmitting. The bus messages are transmitted at a rate
averaging 10800 bits per second. Since there is only voltage present when the modules transmit, and the message length is only about 500
milliseconds, it is ineffective to try and measure the bus activity with a conventional voltmeter. The preferred method is to use DRBIII(R) lab
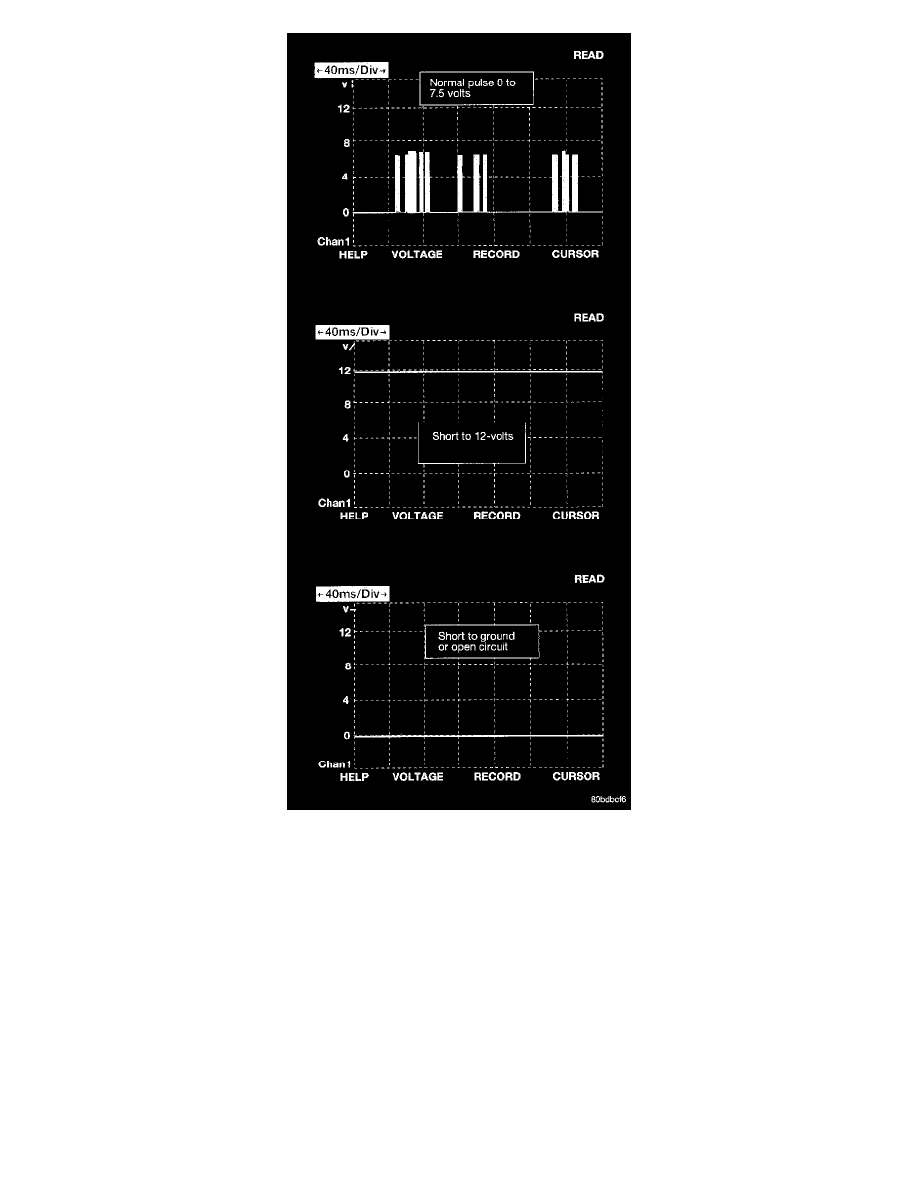
scope. The 12 V square wave selection on the 20-volt scale provides a good view of the bus activity. Voltage on the bus should pulse between
zero and about seven and a half volts. Refer to the following figure for some typical displays.
The PCI Bus failure modes are broken down into two categories. PCI Bus Communication Failure and individual module no response. Causes of a
PCI Bus communication failure include a short to ground or to voltage on any PCI Bus circuit. Individual module no response can be caused by an
open circuit at the BCM or at the module, or an open battery or ground circuit to the affected module.
Symptoms of a complete PCI Bus communications failure would include but are not limited to:
-
All gauges on the MIC stay at zero
-
All Telltales on MIC illuminated
-
MIC backlighting at full intensity
-
No response received from any module on the PCI Bus through the DRB
-
No start (if equipped with sentry key immobilizer system)
Symptoms of individual module failure could include any one or more of the above. The difference would be that at least one or more modules
