Concorde V6-3.5L VIN F (1994)
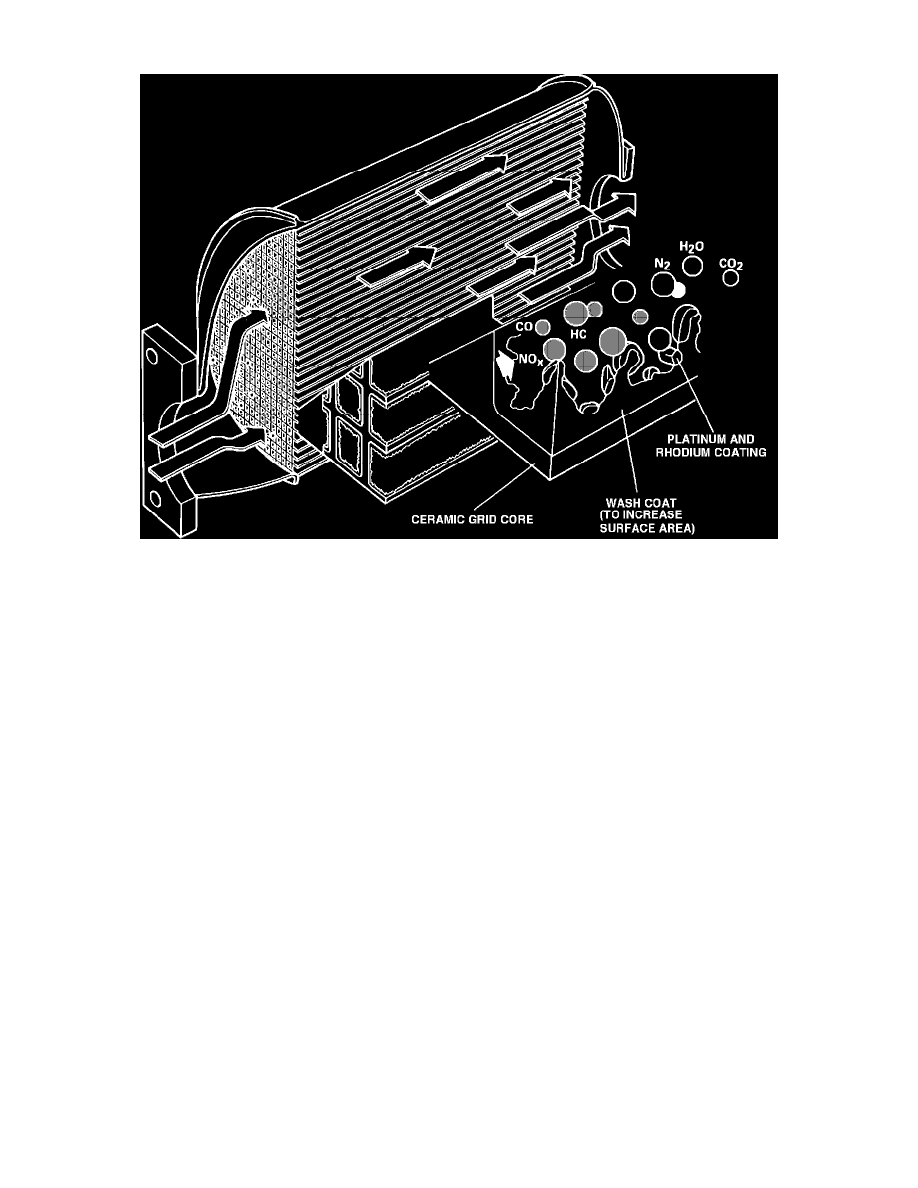
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
Three Way Catalyst (TWC)
PURPOSE
Reduces emission of the three major pollutants, (Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbon (HC) and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx)), by up to 90%.
OPERATION
Oxidation Reaction
As exhaust gasses pass through converter, the platinum in the converter triggers an oxidation (burning) reaction. During this process the HC
and CO combine with oxygen, forming water vapor (H2O) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
This process no effect on NOx emissions.
Reduction Reaction
The Rhodium in the converter converts the NOx into nitrogen and oxygen, in a "reduction" (removal of oxygen), reaction.
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT
A complete catalytic reaction requires that the air/fuel mixture remains near 14.7:1. This can only be achieved in a properly functioning feedback
system with oxygen sensor.
The ideal converter operating temperature, for maximum emission reduction and long service life is, 400°C - 800°C (750°F - 1500°F).
Engine malfunctions, (for example misfires), can cause temperatures in the converter to excede 1400°C (2500°F), which can melt substrate
material.
CONSTRUCTION
Converter consists of: metal housing, ceramic grid substrate, and catalytic coating, (approximately 2 grams of platinum and rhodium).
CAUTION: Never use leaded fuel, as lead compounds tend to coat pores and active material, reducing or eliminating catalyst activity.
