B250 3/4 Ton Van V8-318 5.2L VIN T FI (1992)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
Three Way Catalyst (TWC)
FUNCTION
The three way catalytic converter simultaneously removes up to 90% of all three major pollutants, (HC, CO, and oxides of nitrogen). A complete
catalytic reaction depends on the fuel mixture staying within a very narrow range (±1% of 14.7:1) which can only be achieved with a properly
functioning oxygen sensor feedback system.
CONSTRUCTION
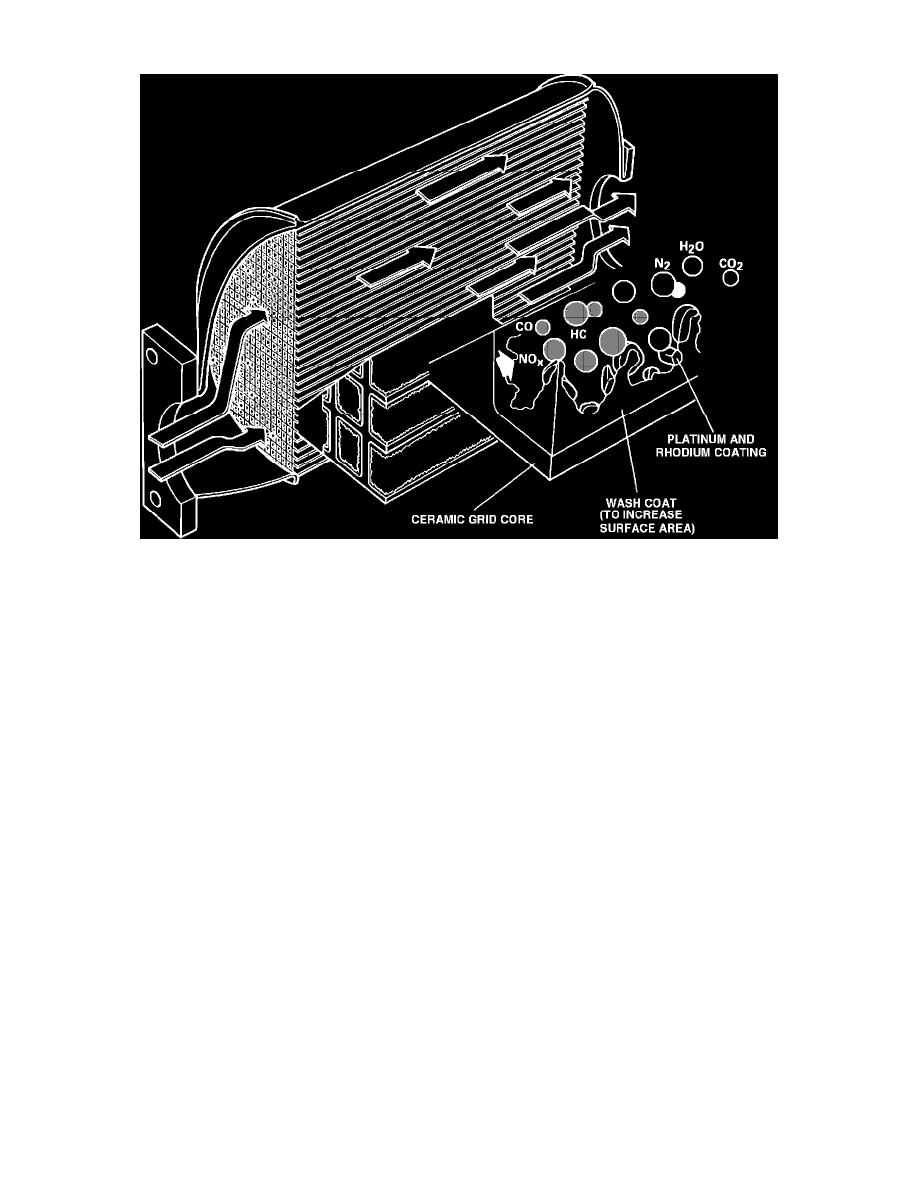
The catalytic converter consists of a metal housing, a ceramic grid substrate, and a catalytic coating of platinum and rhodium. The active metal
content is about 2 grams of platinum/rhodium.
OPERATION
As the exhaust gasses containing HC and CO pass through the converter in the presence of oxygen, the platinum catalyst starts the oxidation
(burning) process. The HC and CO then unite with oxygen to form water vapor and carbon dioxide. This oxidation process has no effect on the
NOx emissions.
To reduce the oxides of nitrogen (NOx), a separate reaction is necessary called "reduction." A reduction reaction is the removal of oxygen from a
material. In Three Way Catalyst type converters, rhodium is used as a catalyst to break down oxides of nitrogen into nitrogen and oxygen. The
effective conversion of pollutants begins at about 250°C (480°F).
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT
The ideal operating temperature for maximum conversion and long service life is 400°C - 800°C (750°F - 1500°F). Engine malfunctions, for
example misfires, can cause the temperature in the converter to increase to more than 1400°C (2500°F). Such temperatures can lead to complete
destruction of the converter by melting the substrate material.
CAUTION: DO NOT use leaded fuel except in emergencies. It will permanently render the converter ineffective. Lead compounds deposited in the
pores and on the surface of the active material reduce or eliminate exposure to exhaust gasses. Excessive engine oil residues can also ruin the catalyst.
