Caravan AWD V6-201 3.3L (1991)
Load Compensator: Description and Operation
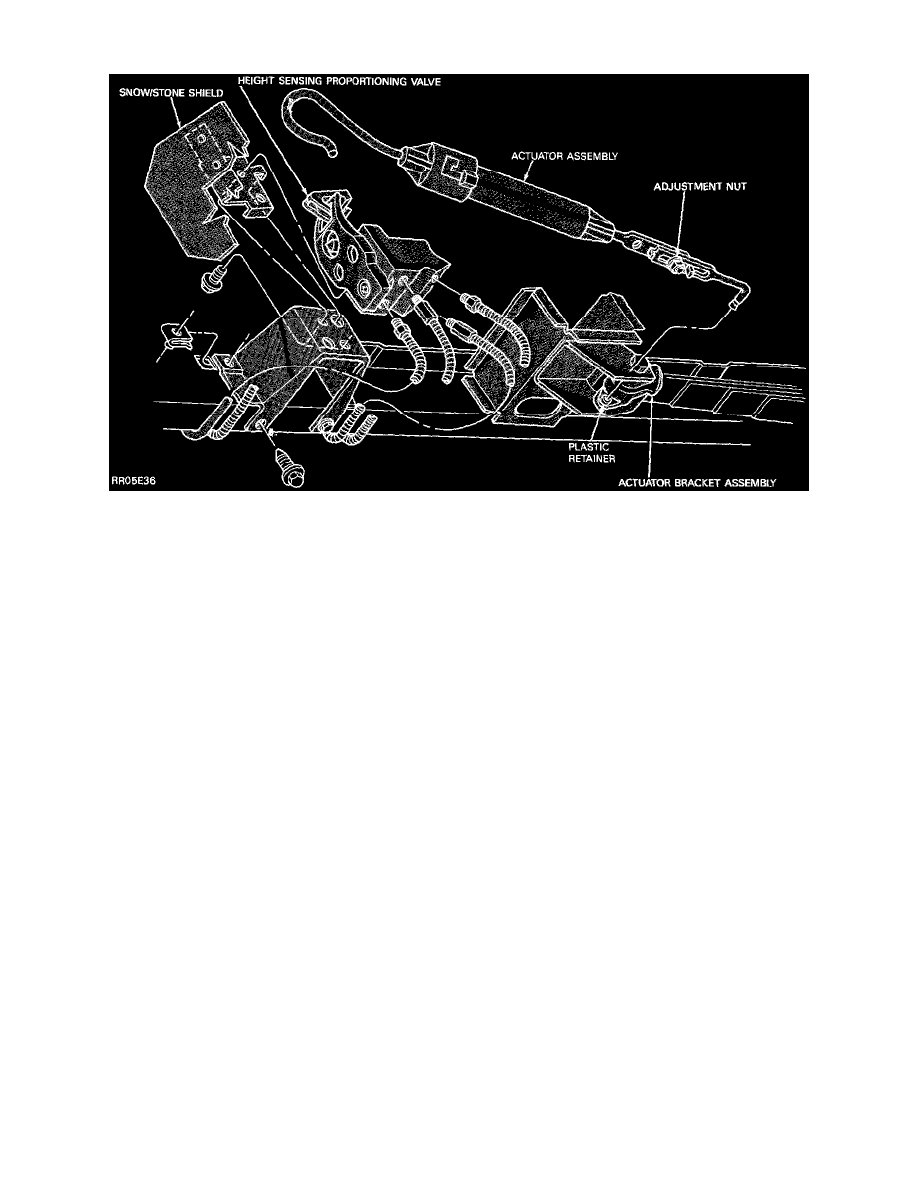
Height Sensing Proportioning Valve
CAUTION: The use of aftermarket load leveling or capacity increasing devices is prohibited. Use of air shock absorbers or helper springs will cause
the valve to inappropriately reduce the rear brake power potentially resulting in increased stopping distance.
PURPOSE
Proportioning valves balance front to rear braking by controlling at a given ratio, the increase in rear system hydraulic pressure above a preset
level. Under light pedal application, the valve allows full hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes.
OPERATION
These vehicles use a height sensing dual proportioning valve in addition to the regular differential warning switch. This valve is located under the
load bed just forward of the rear axle. The height sensing rear brake proportioning valve automatically provides optimum brake balance
front-to-rear regardless of the vehicle load condition. The valve modulates the pressure to the rear brakes sensing vehicle load condition through
relative movement between the rear axle and the load floor.
The valve is mounted to a load floor cross member. A large external spring is connected between a lever mounted on the valve and an adjustable
bracket mounted on the rear axle. In conditions of light load the line pressure to the rear brakes is minimized. As the load increases (resulting in
decreasing vehicle height) higher brake line pressure is allowed.
The proportioning valve section operates by transmitting full input pressure to the rear brakes up to a certain point, called the split point, and
beyond that point it reduces the amount of pressure increase to the rear brakes according to a certain ratio.
Thus, on light pedal applications, approximately equal brake pressure will be transmitted to the front and rear brakes, while at higher pressures, the
pressure transmitted to the rear brakes will be lower than to the front brakes to prevent premature rear wheel lock-up and skid.
