Caravan AWD V6-201 3.3L (1991)
-
All "Overheat" shift schedule features apply
-
2nd gear PEMCC above 22 MPH
-
Above 22 MPH the torque converter will not unlock unless the throttle is closed (i.e. at 50 MPH a 4th FEMCC to 3rd FEMCC shift will be made
during a part throttle kick-down or a 4th FEMCC to 2nd PEMCC shift will be made at wide open throttle) or if a wide open throttle 2nd PEMCC
to 1 kickdown is made.
Causes for operation in the wrong temperature shift schedule:
Extreme Cold or Cold shift schedule at start up:
-
Defective Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (calculated oil temperature vehicles only)
-
Defective Battery/Ambient Temperature Sensor (calculated oil temperature vehicles only)
-
Defective PCM (calculated oil temperature vehicles only)
-
Defective sensor circuit (TRS equipped only)
Overheat or Super Overheat shift schedule after extended operation:
-
Operation in city traffic or stop-and-go traffic
-
Engine idle speed too high - Stuck AIS motor
-
Aggressive driving in low gear
-
Trailer towing in OD gear position (use "3" position if frequent shifting occurs)
-
Cooling system failure causing engine to operate over 230° F
-
Engine coolant temperature stays low too long - If engine coolant temperature drops below 150° F. the transmission will disengage EMCC.
Extended operation with the EMCC disengaged will cause the transmission to overheat.
-
A defective brake switch will cause the EMCC to disengage. Extended operation with the EMCC disengaged will cause the transmission to
overheat.
-
Transmission fluid overfilled (TRS equipped only)
-
Transmission cooler or cooler lines restricted (TRS equipped only)
-
Defective sensor circuit (TRS equipped only)
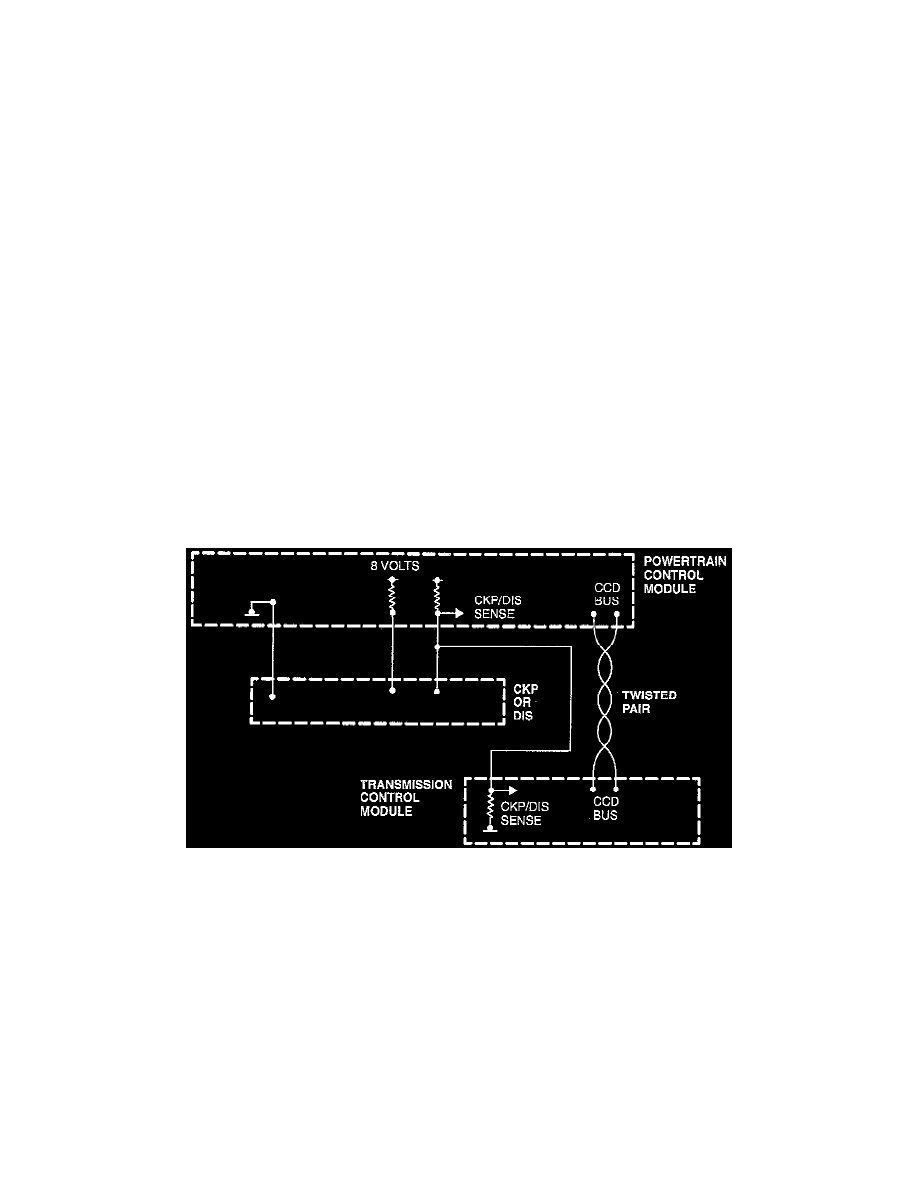
Engine Speed (Hard-Wired and CCD Broadcast)
The TCM uses both direct engine speed input from the Crankshaft Position Sensor or distributor, as well as calculated engine speed input from the PCM
over the CCD Bus. The direct input is required to provide immediate information for use by the TCM control logic. The CCD engine speed data is used
by the TCM fail-safe logic to confirm that the direct engine speed data is valid.
MAP Sensor (CCD Broadcast)
The MAP Sensor provides engine load input directly to the PCM, which determines engine torque load on the transaxle input shaft. These signals are
broadcast over the CCD Bus to the TCM. The TCM uses this information to modify shifting and reduce 2-3 and 3-4 shift hunting on grades.
Engine Idle Speed (Hard-Wired and CCD Broadcast)
The TCM uses direct engine idle speed input and calculated engine idle speed (or target idle speed) input from the PCM over the CCD Bus. Target idle
speed is compared against actual engine speed to determine the learned Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) value for closed-throttle idle.
Brake Switch (CCD Broadcast)
The Brake Switch signal is a CCD broadcast message and is used to ensure that the torque converter clutch is disengaged when the brakes are applied. It
is used also to cancel cruise control when the brakes are applied. The Brake Switch is hard-wired to the PCM and bussed to the TCM.
