D 350 Pickup L6-359 5.9L DSL (1989)
Fuel Injector: Description and Operation
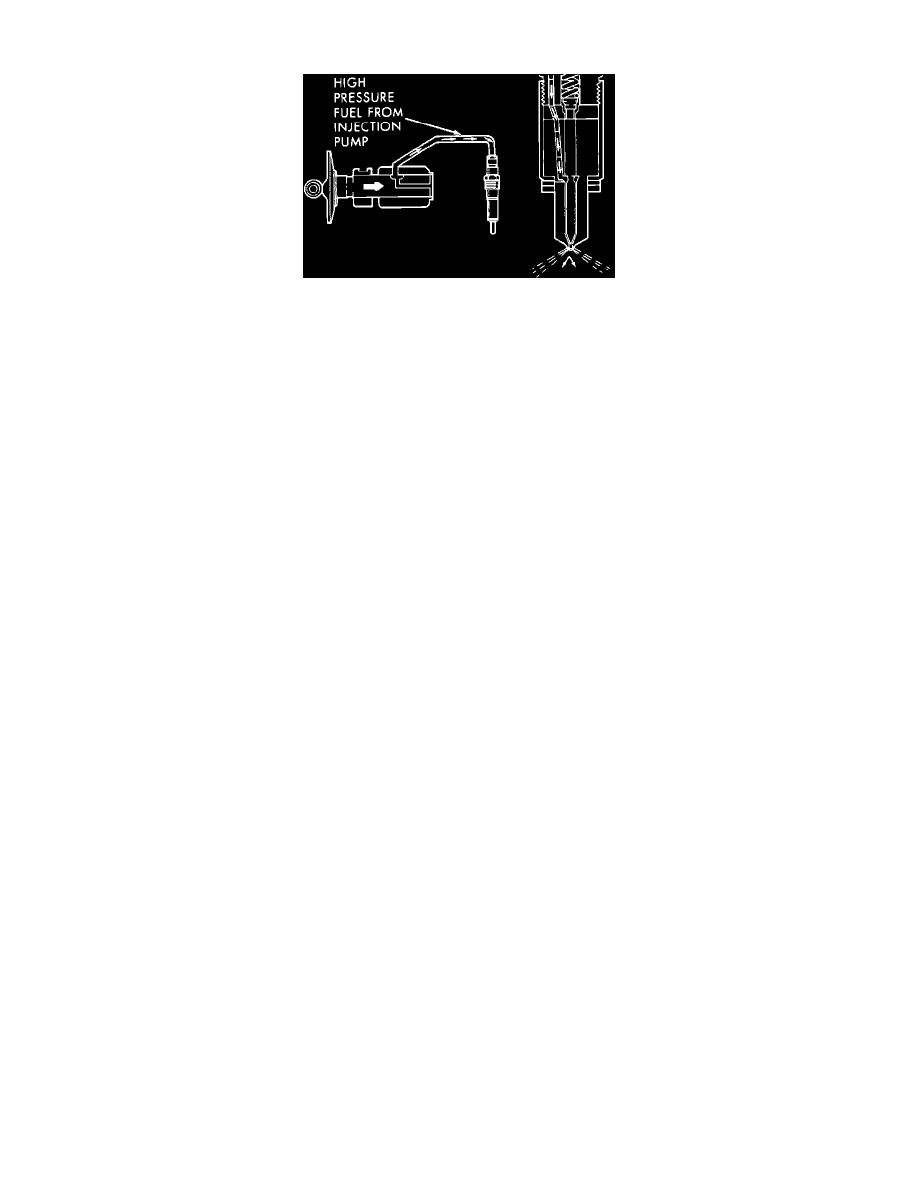
Fuel Injector Operation
The fuel injectors are located on the right side of the cylinder head and they are connected to the injection pump with high pressure fuel lines. The
injector nozzles are positioned inside the combustion chambers and are thus exposed to the high pressures and temperatures of combustion, compression,
and exhaust strokes. The injectors are made of high quality metals to withstand the environment inside the combustion chambers. As the combustion
and exhaust temperatures (acting on the injectors) build, so does the temperature of the fuel inside the injectors and fuel lines. To keep the fuel at a low
temperature, the warm fuel (at the injectors) is returned to the cool fuel in the fuel tank. The following is a list of the components found in the fuel
injectors:
^ Nozzle holder
^ O-ring water seal
^ Shims
^ Spring
^ Needle valve
^ Nozzle
Fuel enters the injector at the fuel inlet (top of the injector) and flows to the needle valve bore. When the fuel pressure rises to 3550 psi (24,445 kPa) the
needle valve spring pressure is overcome. As this spring tension is overcome, the needle valve lifts off of its seat and fuel flows out of the fuel holes in
the nozzle tip and into the combustion chamber. The pressure required to lift the needle valve off of its seat is the operating pressure setting. The
operating pressure setting is sometimes referred to as the "POPPING" pressure of the injectors. Excessive fuel is returned to the fuel tank to help reduce
the temperature of the fuel.
Fuel pressure in the injector circuit drops after injection occurs. This drop in pressure causes the needle valve to fall back into its seat, injection into the
combustion chamber then ceases. Exhaust gases are prevented from entering the fuel system by the needle valve.
