RAM 1500 Truck 2WD V8-5.7L VIN 2 (2006)
-
Target Idle
-
Torque Reduction Confirmation
-
Engine Coolant Temperature
-
Ambient/Battery Temperature
-
Scan Tool Communication
Based on the information received from these various inputs, the TCM determines the appropriate shift and shift points, depending on the present
operating conditions and driver demand. This is possible through control of various direct and indirect outputs.
Some examples of TCM direct outputs are:
-
Transmission Control Relay
-
Solenoids
-
Torque Reduction Request
Some examples of TCM indirect outputs are:
-
Transmission Temperature (to PCM)
-
PRNDL Position (to cluster/CCN)
In addition to monitoring inputs and controlling outputs, the TCM has other important responsibilities and functions:
-
Storing and maintaining Clutch Volume Indexes (CVI)
-
Storing and selecting appropriate Shift Schedules
-
System self-diagnostics
-
Diagnostic capabilities (with scan tool)
NOTE: If the TCM has been replaced, the Quick Learn Procedure must be performed.
BATTERY FEED
A fused, direct battery feed to the TCM is used for continuous power. This battery voltage is necessary to retain memory in the TCM. When the battery
(B+) is disconnected, this memory is lost. When the battery (B+) is restored, this memory loss is detected by the TCM and a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) is set.
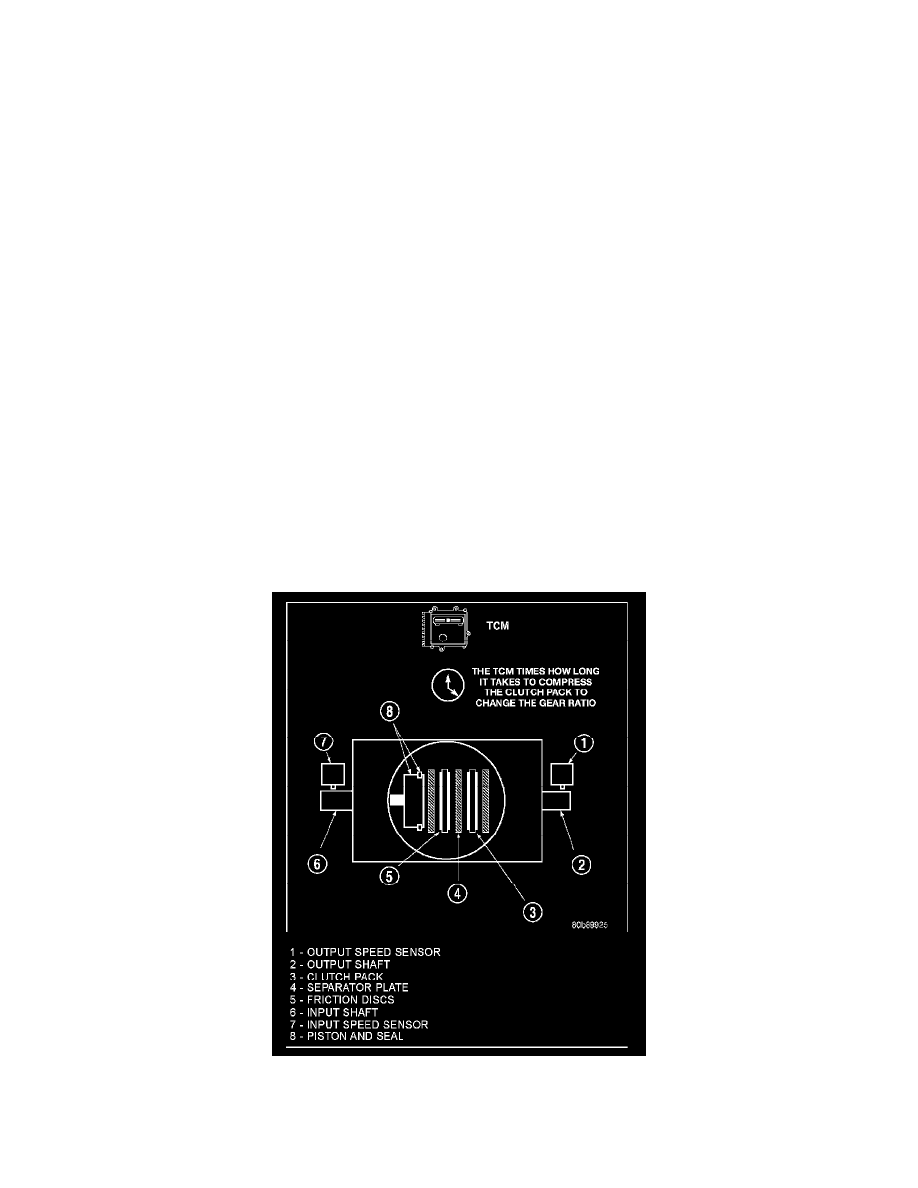
CLUTCH VOLUME INDEXES (CVI)
An important function of the TCM is to monitor Clutch Volume Indexes (CVI). CVIs represent the volume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
The TCM monitors gear ratio changes by monitoring the Input and Output Speed Sensors. The Input, or Turbine Speed Sensor sends an electrical signal
to the TCM that represents input shaft rpm. The Output Speed Sensor provides the TCM with output shaft speed information.
