RAM 1500 Truck 4WD V8-5.9L VIN Z (2002)
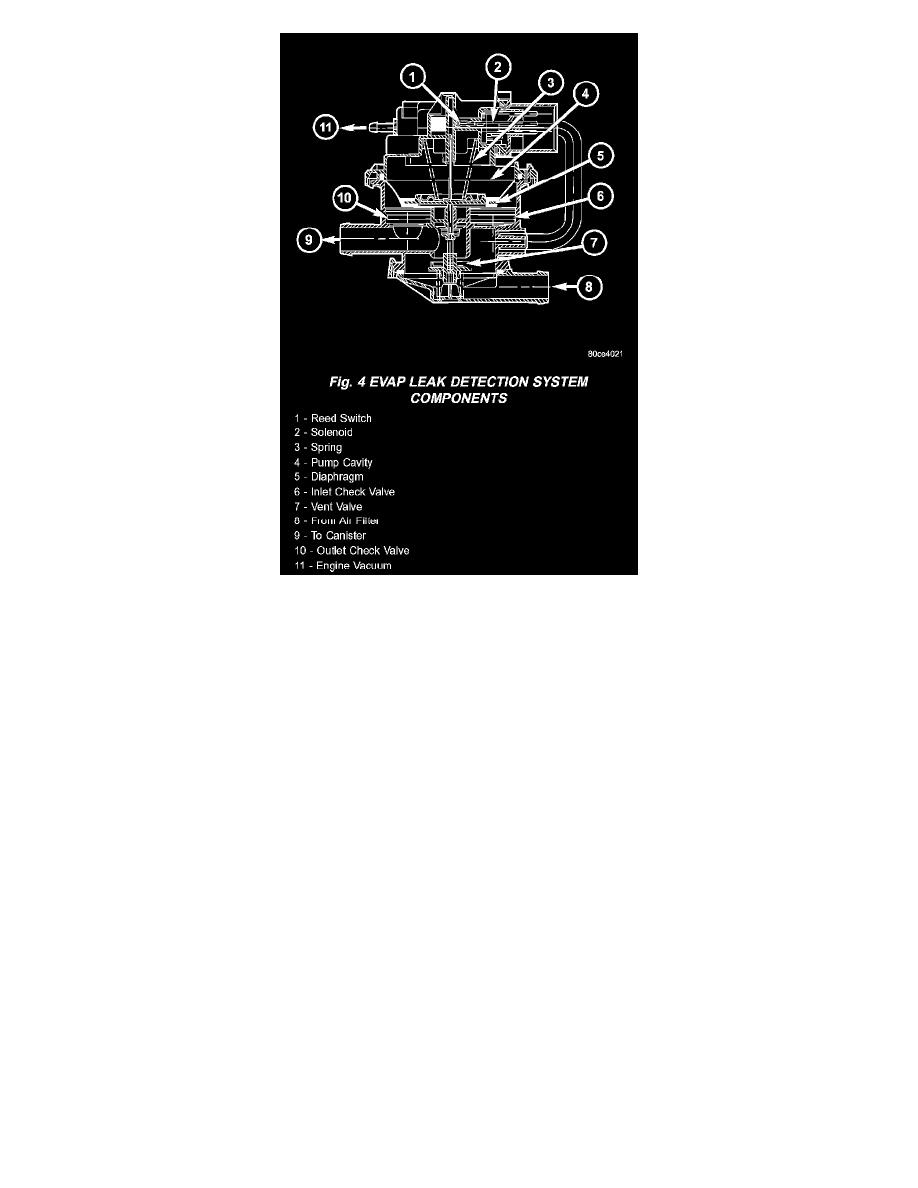
Fig. 4 EVAP Leak Detection System Components
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP system vent to atmospheric pressure so the
system can be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the EVAP system to develop a pressure
of about 7.5" H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm. The PCM uses the reed
switch input to monitor how fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system. This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP assembly
consists of several parts. The solenoid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects the upper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmospheric
pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP system to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in through the air filter and inlet check valve, and pump it out through an outlet check valve into
the EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the LDP solenoid turns ON and OFF.
The LDP also has a magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is closed, which
sends a 12V (system voltage) signal to the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it turns the LDP solenoid ON and OFF.
