Stealth R/T Turbo V6-2972cc 3.0L DOHC Turbo (1996)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
PURPOSE
Three-way Catalytic Converter reduces the emission of Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrocarbons (HC) and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx), by up to
90%.
OPERATION
Oxidation Reaction
^ As exhaust gasses pass through converter, the platinum in the converter triggers an oxidation (burning) reaction.
^ During this process the HC and CO combine with oxygen, forming water vapor (H2O) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2).
^ This process has no effect on NOx emissions.
Reduction Reaction
^ The Rhodium in the converter converts the NOx into nitrogen and oxygen, in a "reduction" (removal of oxygen), reaction.
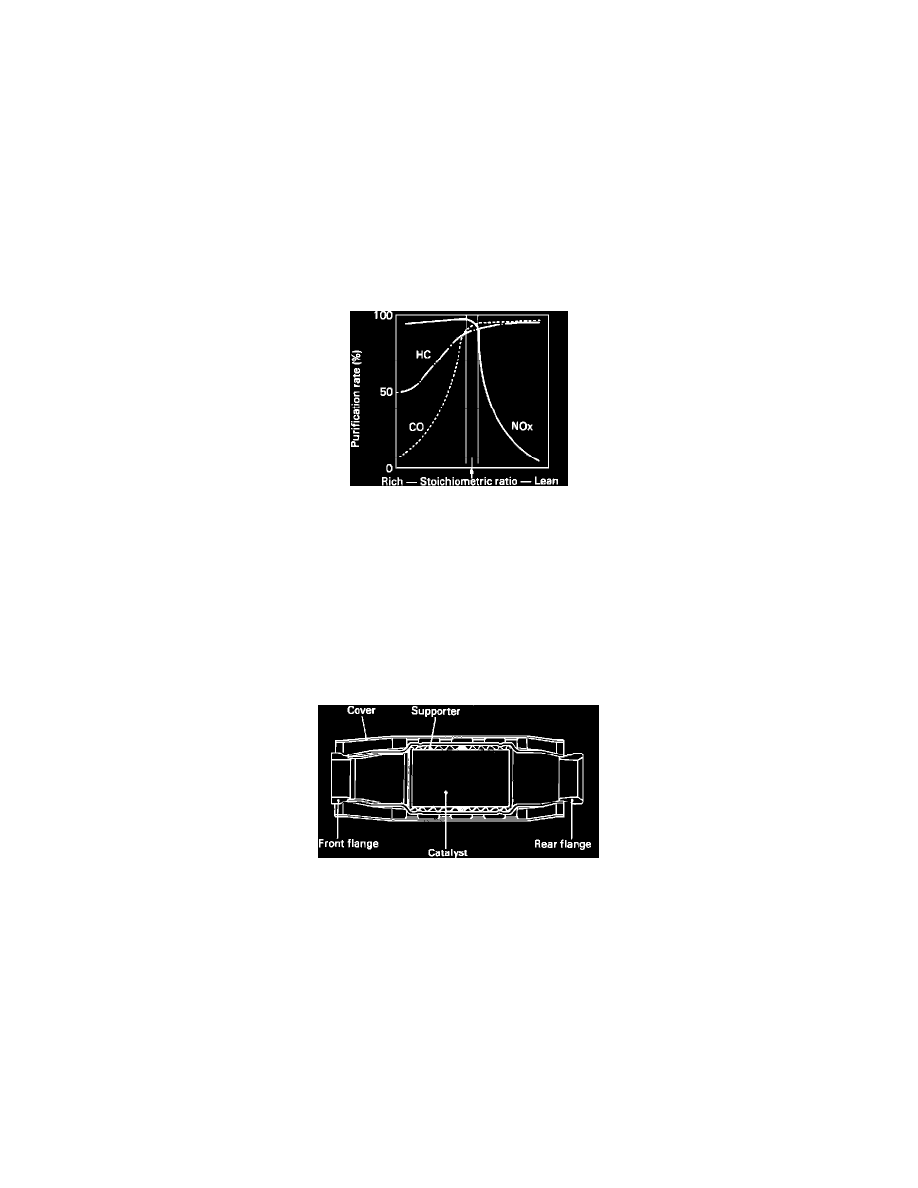
Converter Efficiency VS. Stoichiometric Fuel/Air Ratio
Optimum performance of the catalytic converter is obtained, with a fuel-air mixture ratio of 14.7 to 1 ± 1%, and exhaust gas temperatures between
400 to 800 degrees C (750 to 1500 degrees F).
CAUTION: Engine malfunctions such as misfiring can result in exhaust temperatures exceeding 1400 degrees C (2500 degrees F). These extreme high
temperatures can cause the substrate to melt, destroying the converter.
CAUTION: The use of leaded fuels will coat the catalyst preventing catalytic action. Excessive oil residues in the exhaust have the same effect.
CONSTRUCTION
Fig. 38 Underfloor Catalytic Converter
The converter has a monolythic type, ceramic honeycomb. Platinum and rhodium catalysts cover the surface.
