Flex FWD V6-3.5L (2010)
REPAIR the circuit. CONNECT all modules. CONNECT the negative battery cable. CLEAR the DTCs. REPEAT the network test with the scan tool.
No
CONNECT the negative battery cable. GO to X50.
-------------------------------------------------
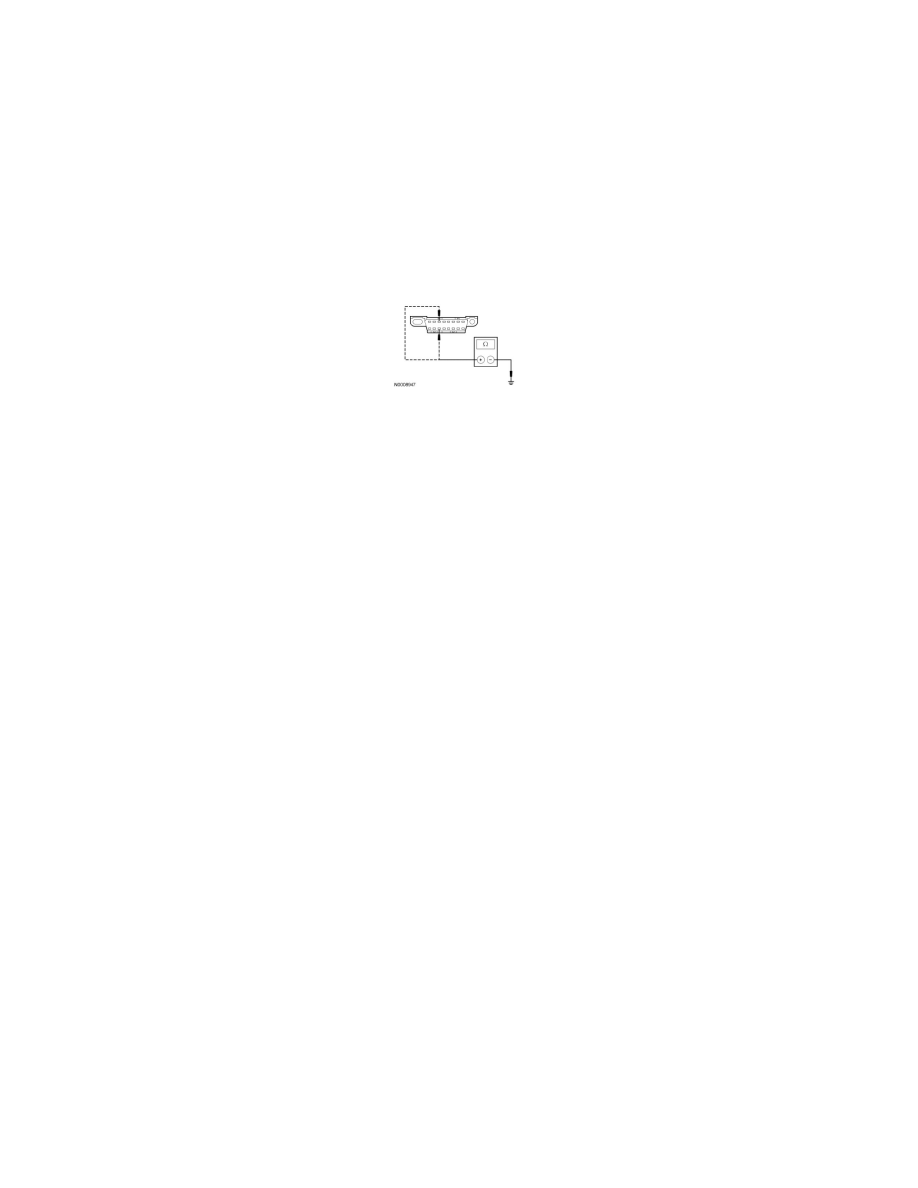
X25 CHECK THE MS-CAN (+) AND MS-CAN (-) CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT TO GROUND WITH THE SJB DISCONNECTED
-
Disconnect: SJB C2280b.
-
Measure the resistance between the DLC C251-3, circuit VDB06 (GY/OG), harness side and ground; and between the DLC C251-11, circuit
VDB07 (VT/OG), harness side and ground.
-
Are the resistances greater than 1,000 ohms?
Yes
CONNECT the negative battery cable. GO to X39.
No
If the vehicle is equipped with a Global Positioning System Module (GPSM), GO to X26.
If the vehicle is not equipped with a GPSM, GO to X27.
-------------------------------------------------
Part 2
Communications Network
Pinpoint Tests
Pinpoint Test X: No Medium Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN) Communication, All Modules Are Not Responding
Refer to Wiring Diagram Set 14, Module Communications Network for schematic and connector information. See: Diagrams/Electrical
Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
Normal Operation
The Medium Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN) uses an unshielded twisted pair cable.
This pinpoint test is intended to diagnose the following:
-
Wiring, terminals or connectors
-
Audio Control Module (ACM)
-
Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM)
-
Audio Digital Signal Processing (DSP) module
-
Driver Seat Module (DSM)
-
Front Controls Interface Module (FCIM)
-
Front Display Interface Module (FDIM)
-
Global Positioning System Module (GPSM)
-
HVAC module
-
Instrument Cluster (IC)
-
Liftgate/Trunk Module (LTM)
-
Rear Entertainment Module (RETM)
