Fusion FWD V6-3.5L (2010)
No
The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. CLEAR the DTCs. REPEAT the
network test with the scan tool.
-------------------------------------------------
Pinpoint Test AA: The Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM) Does Not Respond To The Scan
Tool
Communications Network
Pinpoint Tests
Pinpoint Test AA: The Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM) Does Not Respond To The Scan Tool
Refer to Wiring Diagram Set 14 (Fusion/Milan/MKZ, Fusion Hybrid/Milan Hybrid), Module Communications Network for schematic and connector
information. See: Diagrams/Electrical Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
Refer to Wiring Diagram Set 130 (Fusion/Milan/MKZ, Fusion Hybrid/Milan Hybrid), Audio System/Navigation for schematic and connector
information. See: Diagrams/Electrical Diagrams/Diagrams By Number
Normal Operation
The Accessory Protocol Interface Module (APIM) communicates with the scan tool through the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN).
This pinpoint test is intended to diagnose the following:
-
Fuse
-
Wiring, terminals or connectors
-
APIM
PINPOINT TEST AA: THE APIM DOES NOT RESPOND TO THE SCAN TOOL
NOTICE: Use the correct probe adapter(s) when making measurements. Failure to use the correct probe adapter(s) may damage the
connector.
NOTE: Failure to disconnect the battery when instructed will result in false resistance readings. Refer to Battery.
-------------------------------------------------
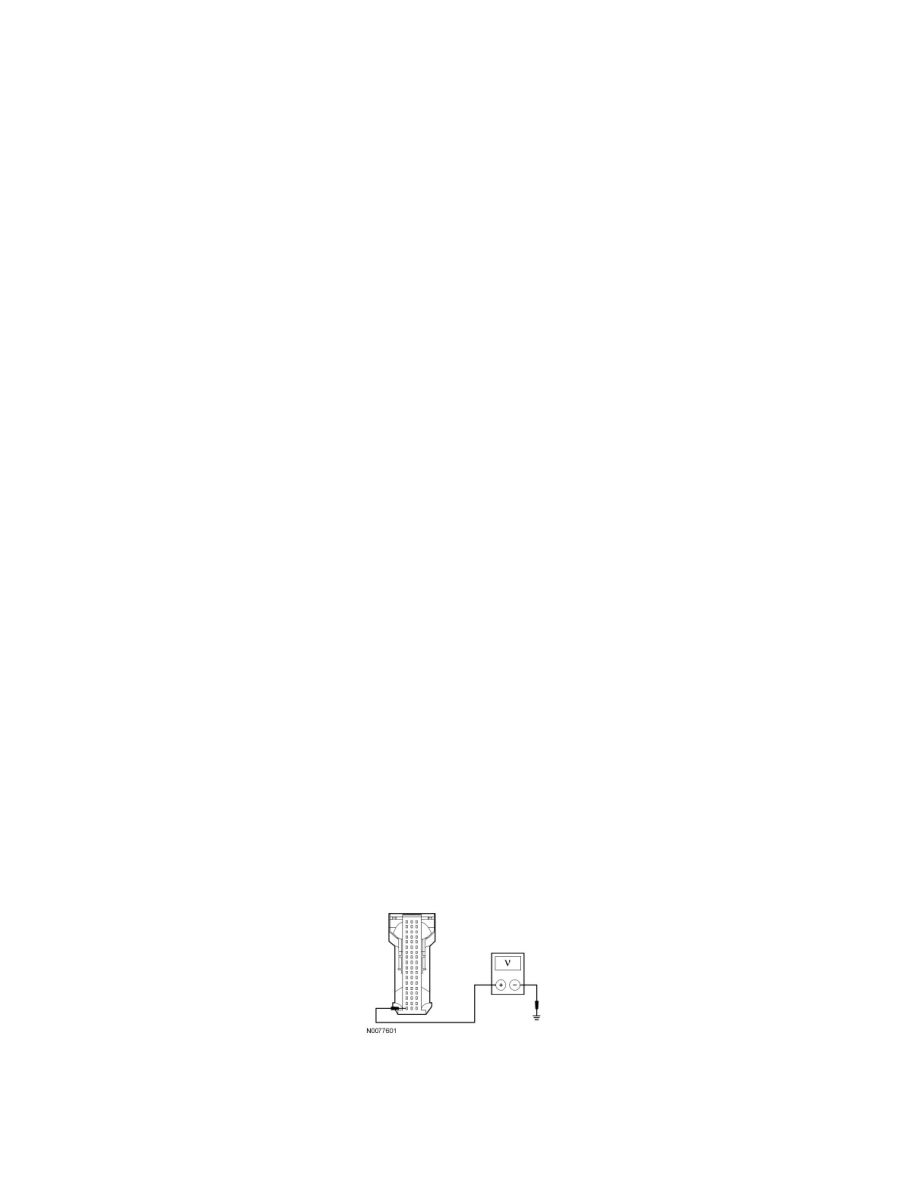
AA1 CHECK THE APIM VOLTAGE SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN
-
Disconnect: APIM C3338 .
-
Ignition ON.
-
Measure the voltage between the APIM C3338-1, circuit SBP13 (GY/RD), harness side and ground.
-
Is the voltage greater than 10 volts?
Yes
GO to AA2.
