Ranger 2WD V6-177 2.9L (1989)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
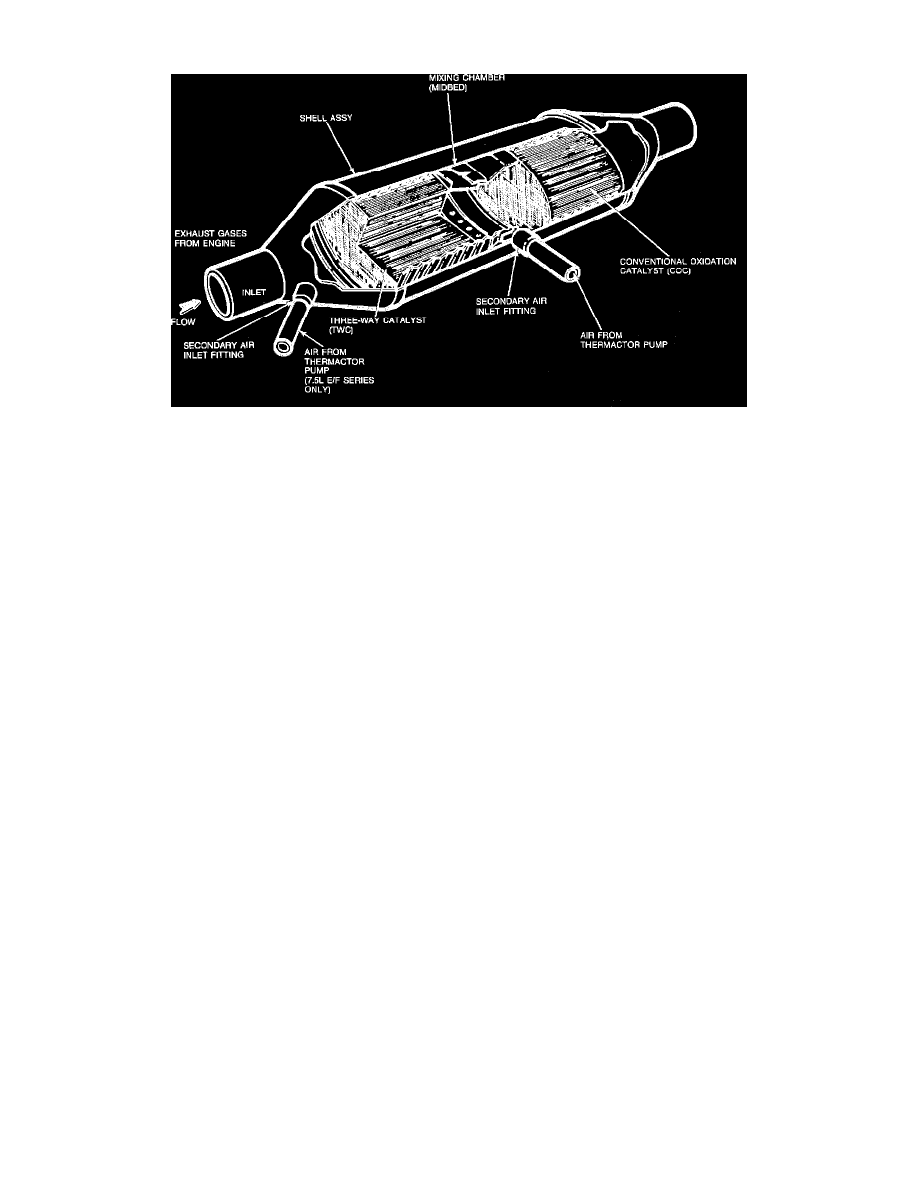
Dual Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter plays a major role in the emission control system. Mounted in the exhaust stream, the converter works as a gas reactor and its
catalytic function is to speed up the heat producing chemical reaction between the exhaust gas components in order to reduce the air pollutants in the
engine exhaust. The catalyst material contained inside the converter is made of a ceramic substrate that is coated with a high surface area alumina and
impregnated with catalytically active, precious metals. It is the surface of the catalyst material that plays a major role in the heat producing chemical
reaction. There are basically three types of catalyst:
COC: The conventional oxidation catalyst contains Palladium (Pd) and Platinum (Pt). The COC is used for catalyzing the oxidation reactions of
Hydrocarbons (HC) and Carbon Monoxide (CO).
TWC: The three way catalyst contains Platinum (Pt) and Rhodium (RH) or Palladium (Pd) and Rhodium (RH). The TWC is used to catalyzing the
oxidation reactions of HC and CO as well as reducing Nitrogen Oxides (NOx).
LOC: The light off catalyst is a single bed converter. Arranged in series with the main catalytic converter assembly (COC or TWC as the trailing
converter), this converter is designed to perform the specialized function of exhaust emission control during engine warm-up when the main converter is
not yet at the temperature required for full effectiveness. With the high temperature environment at the manifold flange area the LOC is designed to
operate in the conditions. The LOC was made with a minimum heat sink effect thus allowing the main converter to heat up quickly.
The converter is constructed of a shell containing a monolithic substrate (a ceramic, honeycomb construction). To maintain the converters high level of
(exhaust) oxygen, in order to maximize the oxidation for producing the heated chemical reaction, the catalyst needs the use of a secondary air source.
Thermactor or Pulse air systems are used to provide additional oxygen. There are several components used to block out the secondary air supplied by the
thermactor air injection system when the engine is under a load or under abnormal temperature conditions. Depending on engine calibration, these
components are used under one or more of the following conditions:
1.
Cold engine operation with rich mixture.
2.
High engine coolant temperatures above 107°C or 225°F.
3.
Wide open throttle.
4.
Engine deceleration.
5.
Extended idle operation.
For complete description and operation of these components refer to "Thermactor Air Systems".
