S15/T15 4WD P/U V6-262 4.3L VIN W CPI (1992)
Spark Plug: Description and Operation
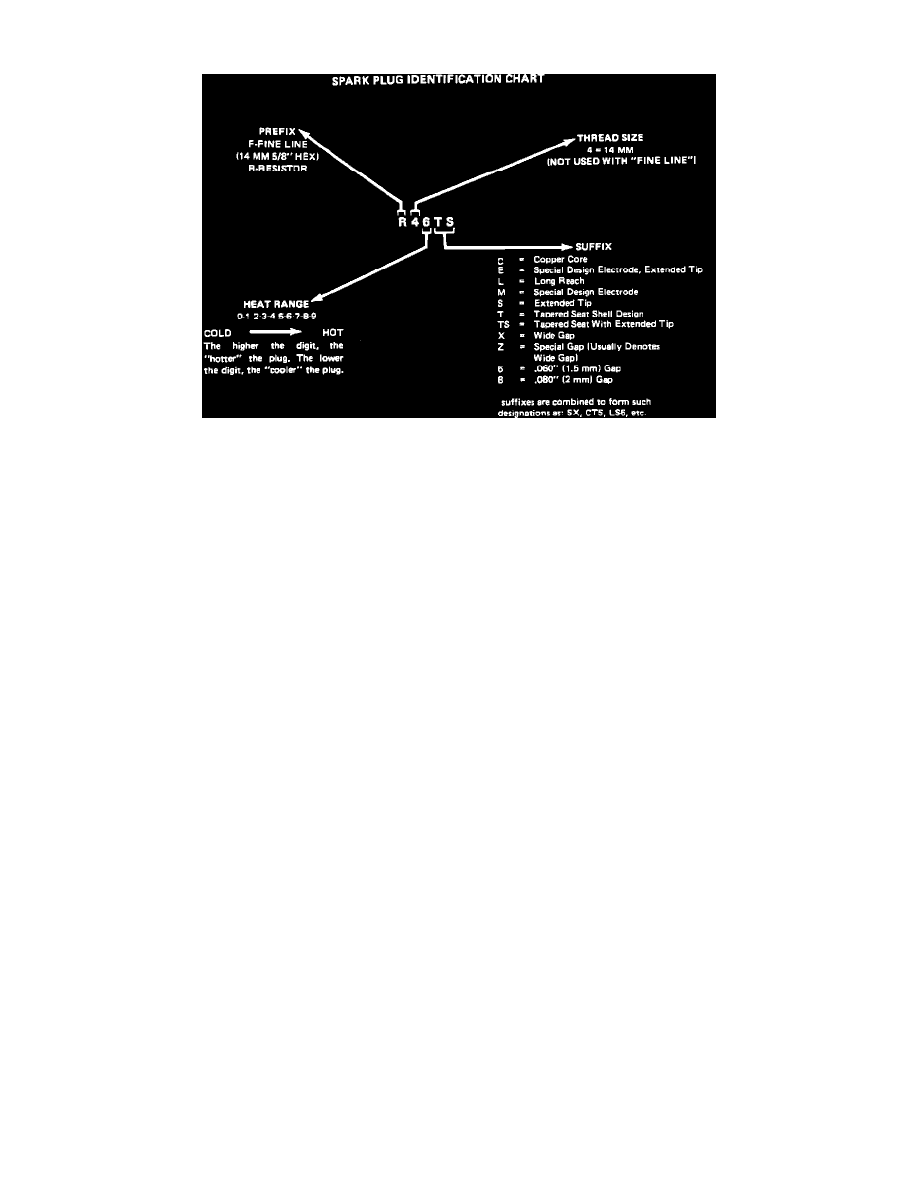
Spark Plug Identification Chart
IDENTIFICATION
Resistor-type, tapered-seat spark plugs are used on all engines. No gasket is used on these tapered seat plugs. Refer to image for an explanation of
letter coding on spark plugs. A dot before the spark plug code or the letter "C" after the number in the code indicates the spark plug has a copper
core.
CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
Normal or average service is assumed to be a mixture of idling, slow speed, and high speed operation with some of each making up the daily total
driving. Occasional or intermittent high-speed driving is essential to good spark plug performance as it provides increased and sustained combustion
heat that burns away any excess deposits or carbon or oxides that may have accumulated from frequent idling or continual stop and go or slow speed
driving. Spark plugs are protected by an insulating boot made of special heat-resistant material which covers the spark plug terminal and extends over
a portion of the plug insulator. These boots prevent flash-over with resultant missing of the engine, even though a film is allowed to accumulate on
the exposed portion of the plug porcelains.
DO NOT mistake corona discharge for flash-over or a shorted insulator. Corona is a steady blue light appearing around the insulator, just above the
shell crimp. It is the visible evidence of a high-tension field, and has no effect on ignition performance. Usually it can be detected only in the
darkness. This discharge may repel dust particles, leaving a clear ring on the insulator just above the shell. This ring is sometimes mistakenly
regarded as evidence that combustion gases have blown out between the shell and the insulator.
SPARK PLUG SELECTION
Spark plus must operate within a certain temperature range if they are to provide the performance and service life expected of them. The spark plug
selected for an engine is based on the normal service for which the engine is designed.
The spark plug may not perform satisfactorily under other-than-normal operating conditions. For almost-exclusively city driving, a spark plug 1 step
higher in heat range might deliver a longer service life than the spark plug recommended for normal operation. Conversely, a spark plug rated 1 step
colder will perform better for heavy loads or continual high-speed driving.
There are three rules to follow when selecting spark plugs for an engine in good condition:
-
Select a plug with a specific heat range.
-
Should spark plug overheating occur, select a spark plug that is one heat range lower than the specified range.
-
If fouling is a problem, select a spark plug that is one step higher that the specified range.
