Accord LX Sedan L4-2156cc 2.2L SOHC MFI (1997)
Hydraulic Control Assembly - Antilock Brakes: Description and Operation
Hydraulic Assembly
Purpose
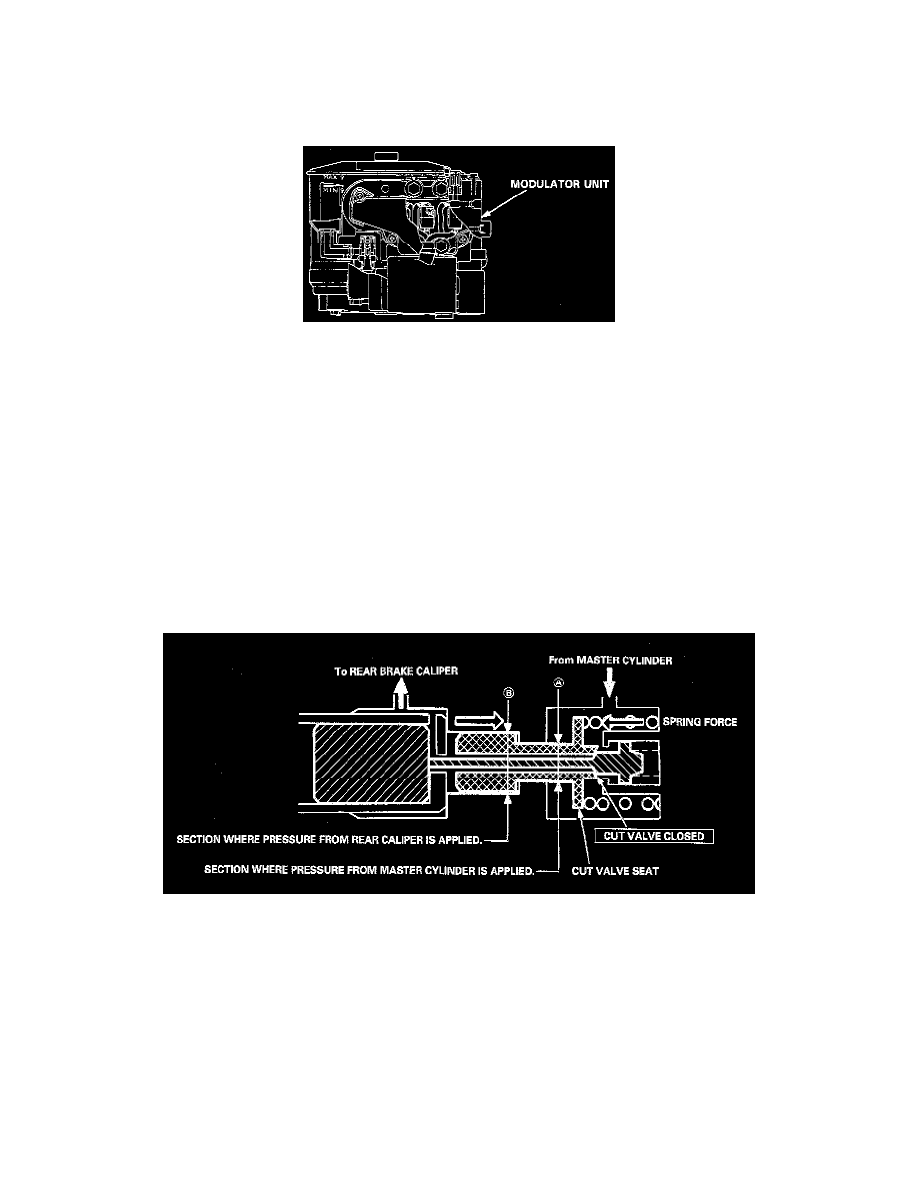
ABS Modulator Unit
It adjusts the hydraulic pressure applied to each caliper on the basis of the signals received from the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) control unit. The
modulator unit consists of the following sub-units.
-
ABS Pump And Motor: Supplies high-pressure brake fluid to control the ABS operation.
-
Accumulator: Stores high-pressure brake fluid in it.
-
Pressure Switch: Detects the pressure in the accumulator and transmits signals to the ABS control unit.
-
Solenoid Valves: Switches the ABS high-pressure passage according to the signals from the ABS control unit.
-
Pistons And Related Parts: Receives the high-pressure brake fluid, and controls pressure to the calipers accordingly.
Function
Piston Cut/Proportioning Valve
REAR MODULATORS SERVE AS PROPORTIONING VALVE
-
The modulators for the rear brakes serve as proportioning control valves to prevent the rear wheels from locking if the Anti-lock Brake System
(ABS) malfunctions or when the ABS is not activated.
-
When this function is not provided, the hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder and the hydraulic pressure to the rear brake system are
equal.
-
If the fluid pressure is transmitted to the rear brakes at the same rate as the front brakes, the rear wheels will lock first because the rear axle
load becomes lighter when the brakes are applied.
-
To prevent the rear wheels from locking, the proportioning control valve function changes the distribution rate of the fluid pressure to the rear
wheels when the pressure in the rear brake system exceeds the given value of the fluid pressure from the master cylinder.
-
The fluid pressure point where the distribution rate changes is called the turning point.
