Commander 4WD V8-4.7L VIN N (2006)
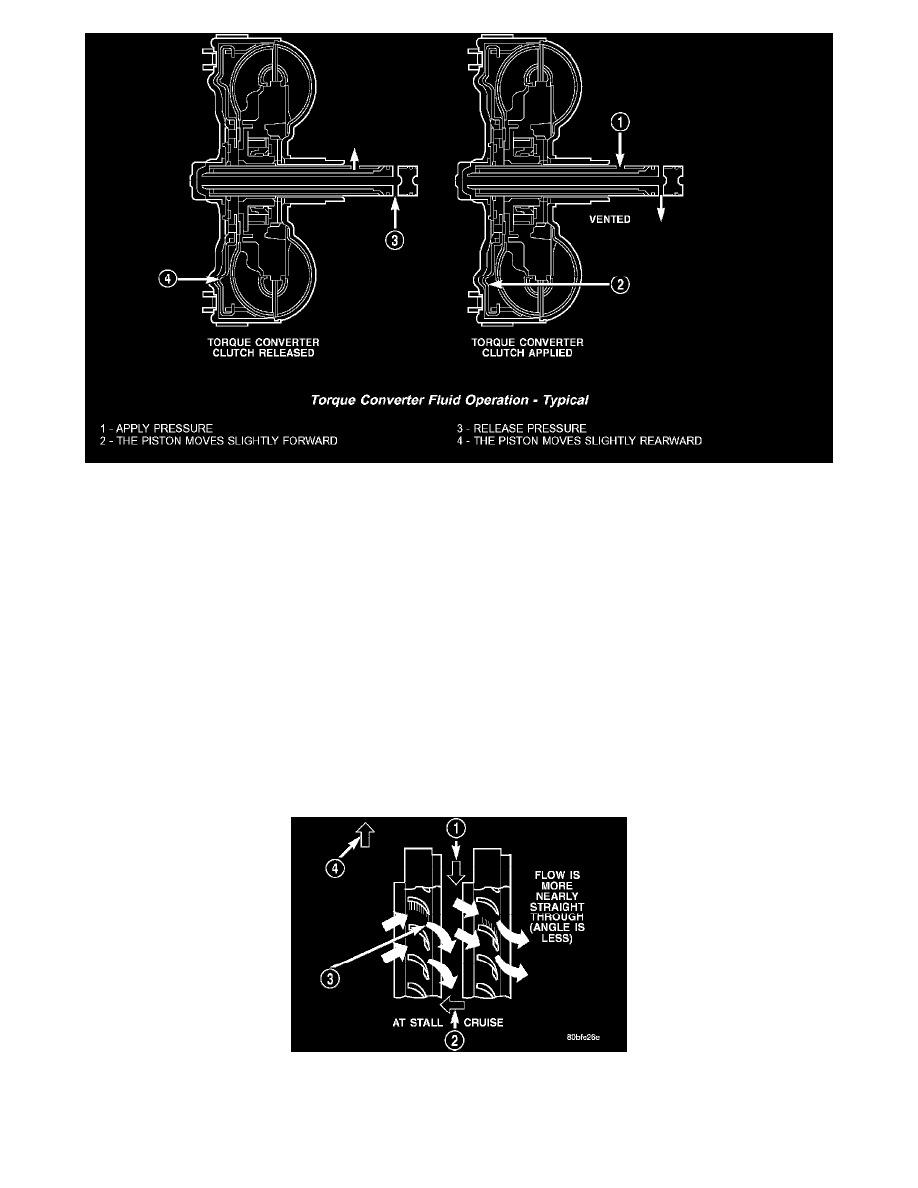
The converter impeller (driving member), which is integral to the converter housing and bolted to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed. The
converter turbine (driven member), which reacts from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impeller blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of the energy and rotational force is transferred into
the turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them (turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise direction following the impeller. As the fluid
is leaving the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it continues in a "hindering" direction back toward the impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before
it strikes the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the stator's over-running clutch to its shaft. Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the oil
leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counterclockwise direction. When this happens the
over-running clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes the stator blades and is redirected into a
"helping" direction before it enters the impeller. This circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a
maximum torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid that was hitting the stator in such as
way as to cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this condition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel and the converter acts as a fluid
coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the stator is freewheeling, providing no torque
multiplication. By applying the turbine's piston and friction material to the front cover, a total converter engagement can be obtained. The result of this
engagement is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine and the transmission.
The clutch can be engaged in second, third, fourth, and fifth gear ranges depending on overdrive control switch position. If the overdrive control
