Freelander System Description and Operation
STEERING
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
57-11
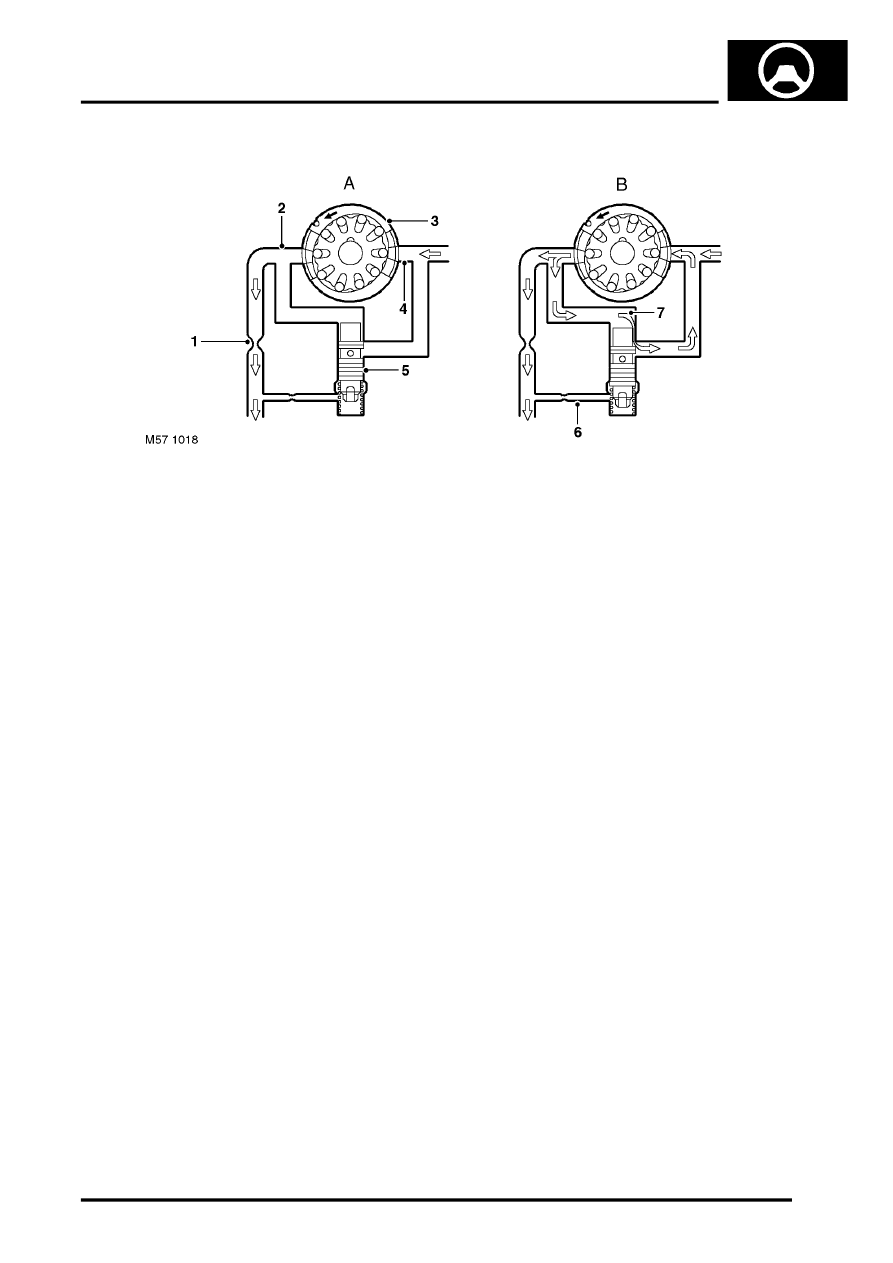
Pump Flow Control Valve Operation
1 Metering orifice
2 Discharge port
3 Pump
4 Inlet port
5 Flow control valve
6 Relief valve passage
7 Recirculation passage
The pump is a positive displacement type pump and potential output from the pump increases proportionally with
engine speed. The flow control valve maintains a constant predetermined flow to the control unit regardless of engine
speed. The flow control valve controls the flow of fluid and increases or decreases the flow discharged from the pump
to compensate for engine speed variations.
With the engine at idle the discharge flow from the pump is low and the full flow from the pump is delivered to the valve
unit. As engine speed increases, the flow delivered by the pump increases proportionally. A pressure difference is
created between each side of the metering orifice as the engine speed increases, the higher pressure being felt at the
pump side of the metering orifice. This higher pressure is also felt at the top of the flow control valve via the
recirculation passage. The lower pressure on the discharge side of the metering orifice is felt at the bottom of the flow
control valve via the relief valve passage.
When the pressure at the top of the flow control valve exceeds the rating of the flow control valve spring, the valve
begins to open against the spring pressure and the lower pressure at the discharge side of the metering orifice. Fluid
is allowed to flow through the recirculation passage and recirculate through the pump.
As engine speed increases, the flow control valve is pushed down further, increasing the flow through the recirculation
passage.
