Front Drive Shafts for L322 Range Rover - Description | Page 231
DRIVE AND PROPELLER SHAFTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
47-3
The outer CV joint has a target on the outer diameter. This is used by the ABS wheel speed sensor for vehicle and
wheel speed calculations.
BRAKES, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Foundation Brakes.
Each drive shaft comprises two CV joints and gaiters, an outer tube, a solid shaft and a ball cage assembly.
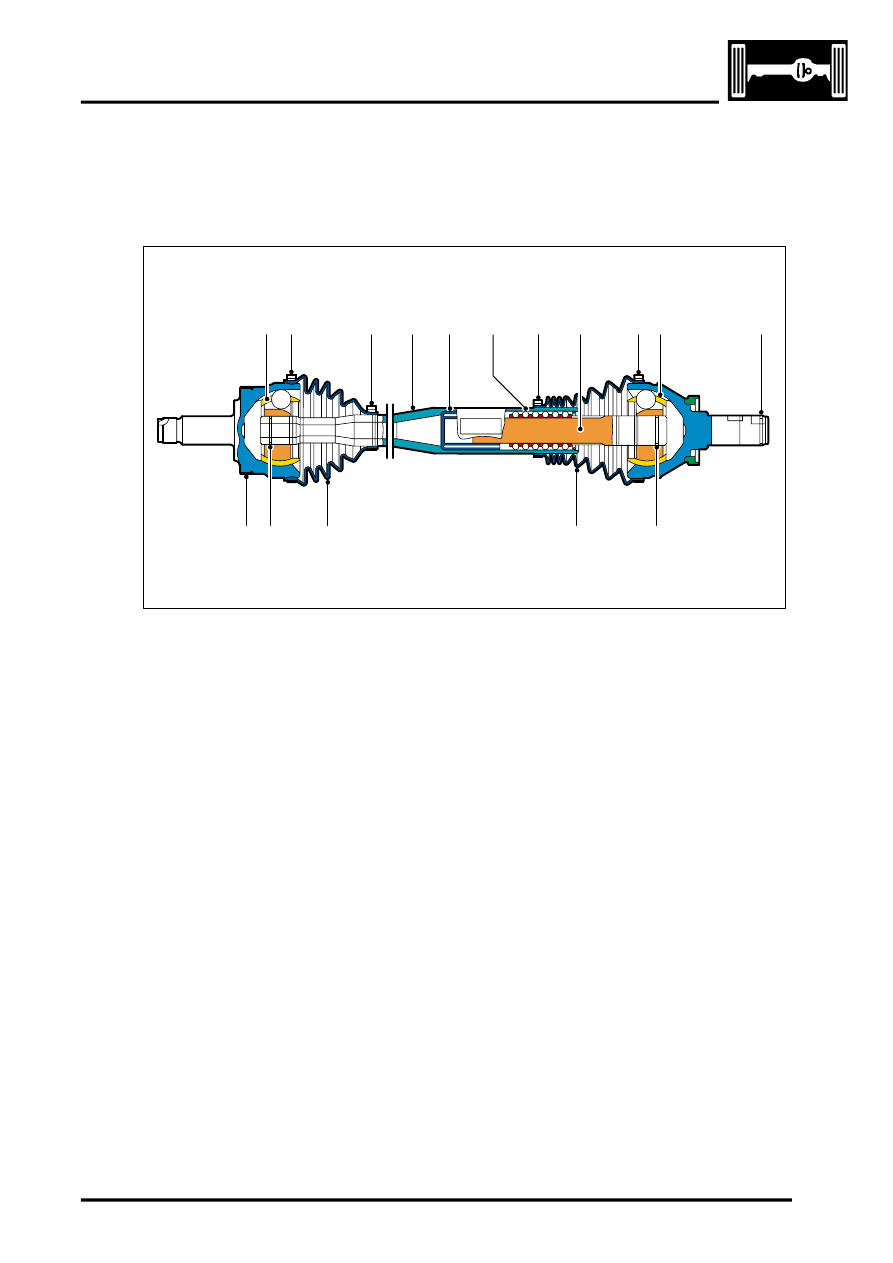
Front Drive Shaft – Sectional View
LH drive shaft shown, RH drive shaft similar
1 Outer CV joint
2 Clamp
3 Outer tube
4 Sealing plug
5 Ball cage
6 Shaft
7 Inner CV joint
8 Snap ring – differential
9 Snap ring
10 Gaiter
11 ABS sensor target ring.
The CV joints are of the Birfield design. This design uses longitudinal, elliptical grooves which retain six steel balls.
The balls are further retained by a cage. The constant velocity is achieved by the position of the steel balls. If a centre
line is drawn through the balls and the driven hub or differential shaft, the two centre lines always bisect each other
at the angle of drive. This condition allows the rotational speed of the driven shaft to be passed to the driven hub or
differential shaft with no loss of rotational speed regardless of the shaft angle. The CV joints are packed with grease
which is retained in the joint by a synthetic rubber gaiter. The gaiter is retained at each end by a metal clamp which
provides a water tight seal to prevent the ingress of dirt and moisture. The CV joints are retained on their respective
shaft or tube by an internal snap ring. The snap rings are located in a groove on each shaft or tube end and locate in
a mating groove in the CV joint. The CV joints can be removed by a sharp tap with a soft mallet on the CV joint housing
which releases the snap ring from the groove.
The shaft is a sliding fit inside the outer tube which allows for the small length changes which occur with articulation
of the suspension. The shaft is located in a ball cage which is retained inside the outer tube. The ball cage ensures
that the shaft is held rigidly in the outer tube whilst allowing it to freely move in and out of the tube as necessary. A
sealing plug is pressed into the outer tube and retains grease around the balls in the cage.
The inner CV joint shaft is splined and mates with splines in the front differential. A snap ring is located around the
inner shaft and, when fitted in the differential, locates in a mating groove in the differential splined bore. The CV joint
shaft is removed from the differential in a similar manner as removing a CV joint.
9
10
10
9
M47 0439
1
8
7
2
6
2
5
4
2
3
2
11
