LR3/Disco 3
During the engine warm-up period, the ATCM manages the electrical load to make sure that the battery voltage is
maintained above a pre-determined level. The battery voltage level that is maintained and the duration of the start period
varies with ambient air temperature and engine coolant temperature. After the engine warm-up period, the ATCM
manages the electrical load to make sure that the requested electrical load does not exceed the generator output.
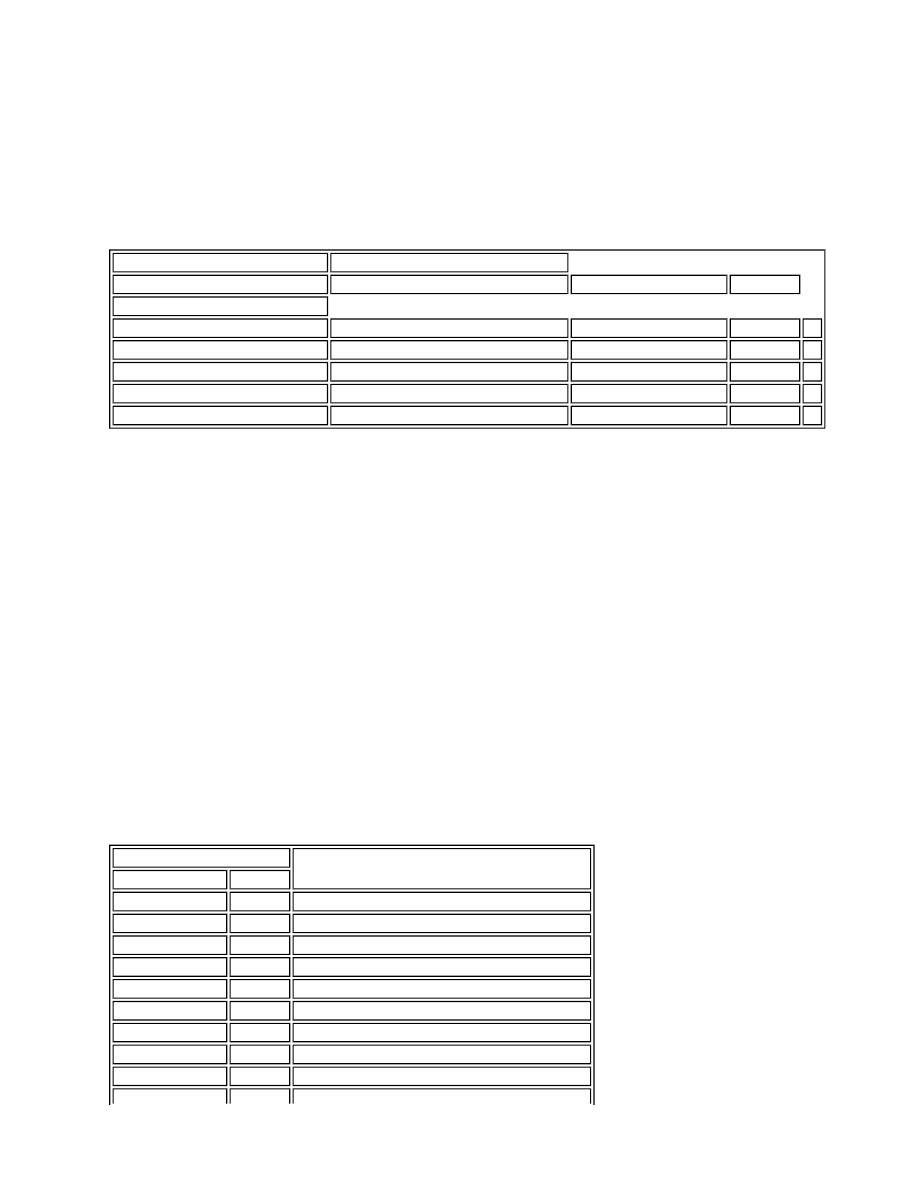
The duration of the engine warm-up period depends on the ambient air temperature and the engine coolant temperature
when the ignition is switched on, as detailed in the following table:
Engine Warm-up Times
The ATCM calculates the electrical load from the battery voltage and generator output voltage, and compares the result
against the maximum load available from the generator. The calculation is averaged across the first 20 seconds after the
engine starts, and subsequently averaged every 60 seconds. When the ignition is turned off, the ATCM stores the status
of the electrical load management for 20 seconds. If the engine is re-started within the 20 seconds, the ATCM resumes
electrical load management using the stored status. If the engine is re-started after the 20 seconds, the timers are reset
and the ATCM re-calculates the status.
If the electrical load is more than the maximum load available, the ATCM requests an increase of engine idle speed using
the medium speed CAN bus message to the ECM. If an electrical load imbalance remains after an increase in engine idle
speed, or if the electrical load is more than the capacity of the charging system, the ATCM reduces the electrical load by
reducing the power of some vehicle systems or inhibiting their operation. The number of systems controlled depends on
the electrical load reduction required. The systems controlled, and the order in which their power is reduced or they are
inhibited, are contained in three priority tables. The table used depends on the ambient air temperature, battery
temperature and engine coolant temperature:
The cold start table is used when the ambient air temperature is less than 5 °C (41 °F) and the engine coolant
temperature is less than 30 °C (86 °F).
The hot start table is used when the ambient air temperature is 5 °C (41 °F) or more and the engine coolant
temperature is less than 30 °C (86 °F).
The continuous table is used when battery temperature is more than 5 °C (41 °F) and the engine coolant
temperature is more than 50 °C (122 °F).
If none of above conditions are met, the ATCM adopts the last used table.
Cold Start Electrical Load Management
Ambient Air Temperature, °C (°F) Engine Coolant Temperature, °C (°F)
<10 (<50)
>10 to <30 (>50 to <86)
>30 to <60 (>86 to <140) >60 (>140)
Warm-up Period, Minutes
>10 (>50)
15
15
15
15
>5 to <10 (>41 to <50)
15
15
15
15
>0 to <5 (>32 to <41)
10
15
15
15
>-10 to <0 (>14 to <32)
10
10
15
15
<-10 (<14)
5
5
10
15
Priority
System
Power Reduction Inhibited
1
-
Air suspension
2
-
Front seat heaters
3
-
Entertainment system
-
4
Front seat heaters
5
-
Auxiliary climate control blower
6
-
Rear window heater
7
-
Windshield washer jet and exterior mirror heaters
-
8
Windshield washer jet and exterior mirror heaters
9
-
Windshield heater
