Milan FWD L4-2.3L (2008)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
CATALYST AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS
Overview
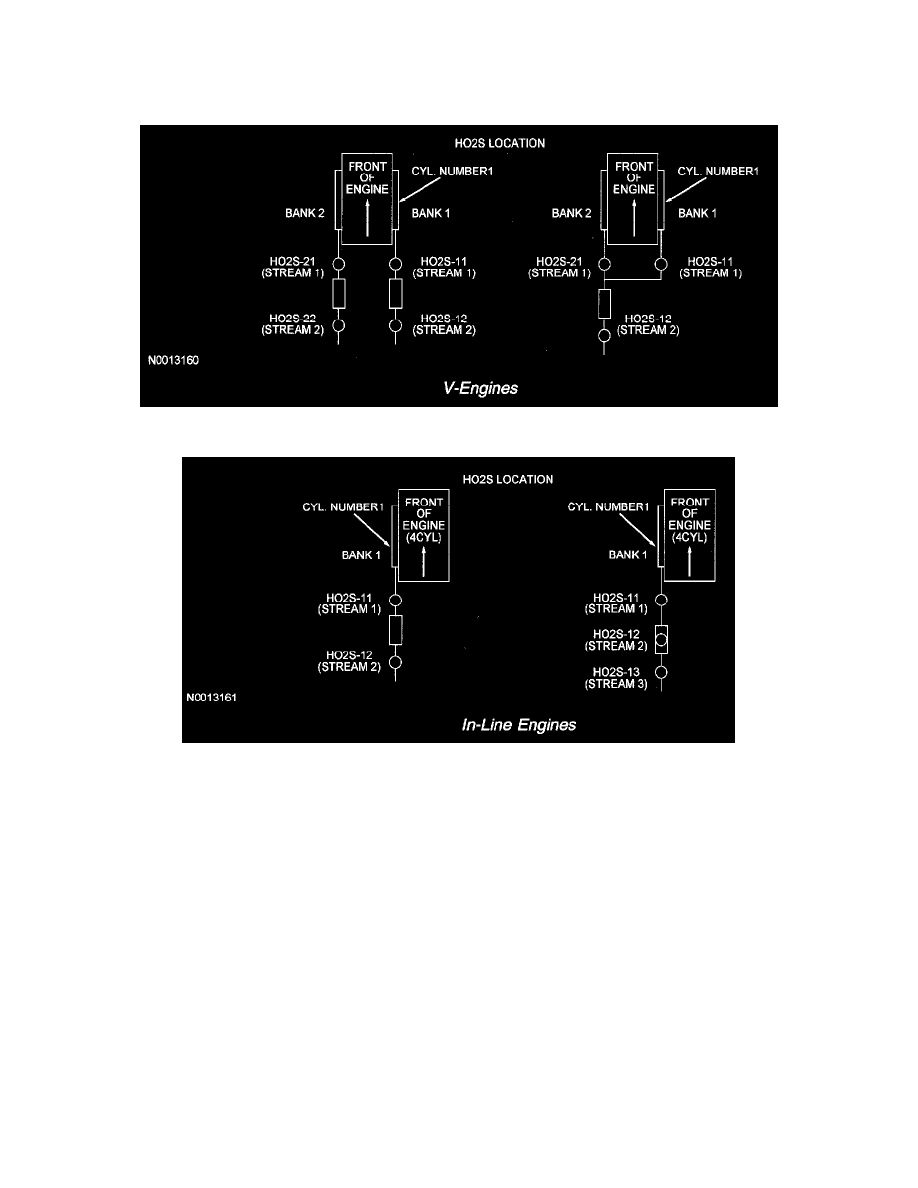
V-Engines
In-Line Engines
The catalytic converter and exhaust systems work together to control the release of harmful engine exhaust emissions into the atmosphere. The engine
exhaust gas consists mainly of nitrogen (N), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). However, it also contains carbon monoxide (CO), oxides
of nitrogen (NOx), hydrogen (H), and various unburned hydrocarbons (HCs). The major air pollutants of CO, NOx,and HCs, and their emission into
the atmosphere must be controlled.
The exhaust system generally consists of an exhaust manifold, front exhaust pipe, front heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), rear exhaust pipe, catalyst
HO2S, a muffler, and an exhaust tailpipe. The catalytic converter is typically installed between the front and rear exhaust pipes. On some vehicle
applications, more than one catalyst is used between the front and rear exhaust pipes. Catalytic converter efficiency is monitored by the on board
diagnostic (OBD) system strategy in the powertrain control module (PCM). For information on the OBD catalyst monitor, refer to the description for
the Catalyst Efficiency Monitor. See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control Systems/Testing and Inspection/Monitors, Trips, Drive Cycles
and Readiness Codes/Catalyst Efficiency Monitor
For most vehicles, only 2 HO2Ss are used in an exhaust stream. The front sensors (HO2S11/HO2S21) before the catalyst are used for primary fuel
control while the ones after the catalyst (HO2S12/HO2S22) are used to monitor catalyst efficiency. However, some partial zero emission vehicles
(PZEV) use 3 HO2Ss for each engine bank. The stream 1 sensors (HO2S11/HO2S21) located before the catalyst are used for primary fuel control, the
stream 2 sensors (HO2S12/HO2S22) are used to monitor the light-off catalyst, and the stream 3 sensors (HO2S13/HO2S23) located after the catalyst
are used for long term fuel trim control to optimize catalyst efficiency (fore aft oxygen sensor control).
Catalytic Converter
A catalyst is a material that remains unchanged when it initiates and increases the speed of a chemical reaction. A catalyst also enables a chemical
reaction to occur at a lower temperature. The concentration of exhaust gas products released to the atmosphere must be controlled. The catalytic
