SW1 L4-1.9L SOHC VIN 8 (1996)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
Catalyst Monitor Diagnosis
Converter Operation
CATALYST MONITOR DIAGNOSTICS
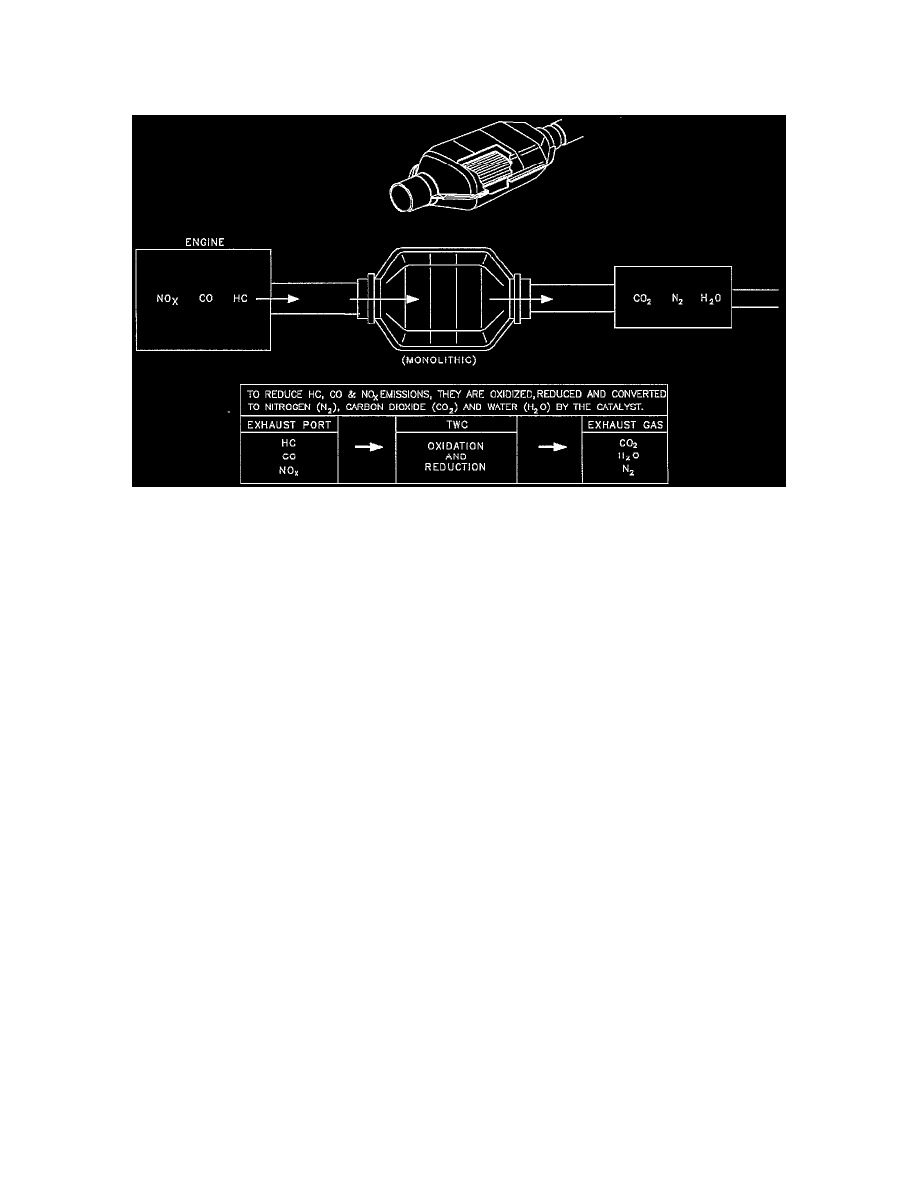
The three way catalytic converter (TWC) is an emission control device added to the exhaust system to reduce pollutants from the exhaust gas stream and
requires the use of unleaded fuel only.
The three way catalytic converter coating on the three way (reduction) catalytic converter contains platinum and rhodium which lowers the levels of
oxides of nitrogen (NOx) as well as hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide. Also to aid in the conversion process is a base metal added called cerium.
Cerium adds the ability of the converter to attract and release oxygen into the exhaust stream. As a catalyst becomes less efficient its capacity to store
and release oxygen generally degrades as well. Oxygen storage capability is used as a measure of converter condition, and its ability to perform its
function.
The output signal generated by the rear oxygen sensor is used to determine the oxygen storage capability of the catalytic converter. Oxygen storage
capability is used as a measure of converter condition, and its ability to perform its function. To diagnose the converter the signal from the front sensor
must meet certain conditions before reading the rear sensor signal. The front sensor must be switching, indicating a well controlled fuel system. Once the
front sensor is determined to be switching, the amplitude of the rear sensor is monitored and a catalyst monitor test is performed.
The catalyst monitor tests consist of two stages. The Scan tool can display the current value in millivolts for stage 1. This parameter ranges from -550 mv
to a positive 550 mv. When this value goes above 0 mv indicating stage 1 has failed, the stage 2 test will start to be used in determining the efficiency.
The Scan tool can indicate if a stage 1 test has passed or failed.
Several tests may have to be performed to determine the current state of the converter after a code clears or a battery disconnects.
The catalyst monitor test is performed once per drive cycle if all test conditions are met. The main enable criteria's to enable a catalyst test are:
^
Steady state cruise (TP sensor output not changing)
^
Using ECT sensor, IAT sensor, VSS load and run time the PCM will calculate the temperature of the catalytic converter. The test will be
enabled once it is determined the converter is hot enough to perform a good test.
Once the enable criteria are met 50 samples of the sensor voltage amplitude are collected. The results of the 50 samples are averaged and converted to a
millivolt (mv) reading which can be read with a Scan tool.
Whenever DTCs are cleared or the battery has been disconnected the results of stage 1 will be reset to a negative 555 mv and the stage 1 fail status will
indicate passing.
