Forester F4-2.5L SOHC (2004)
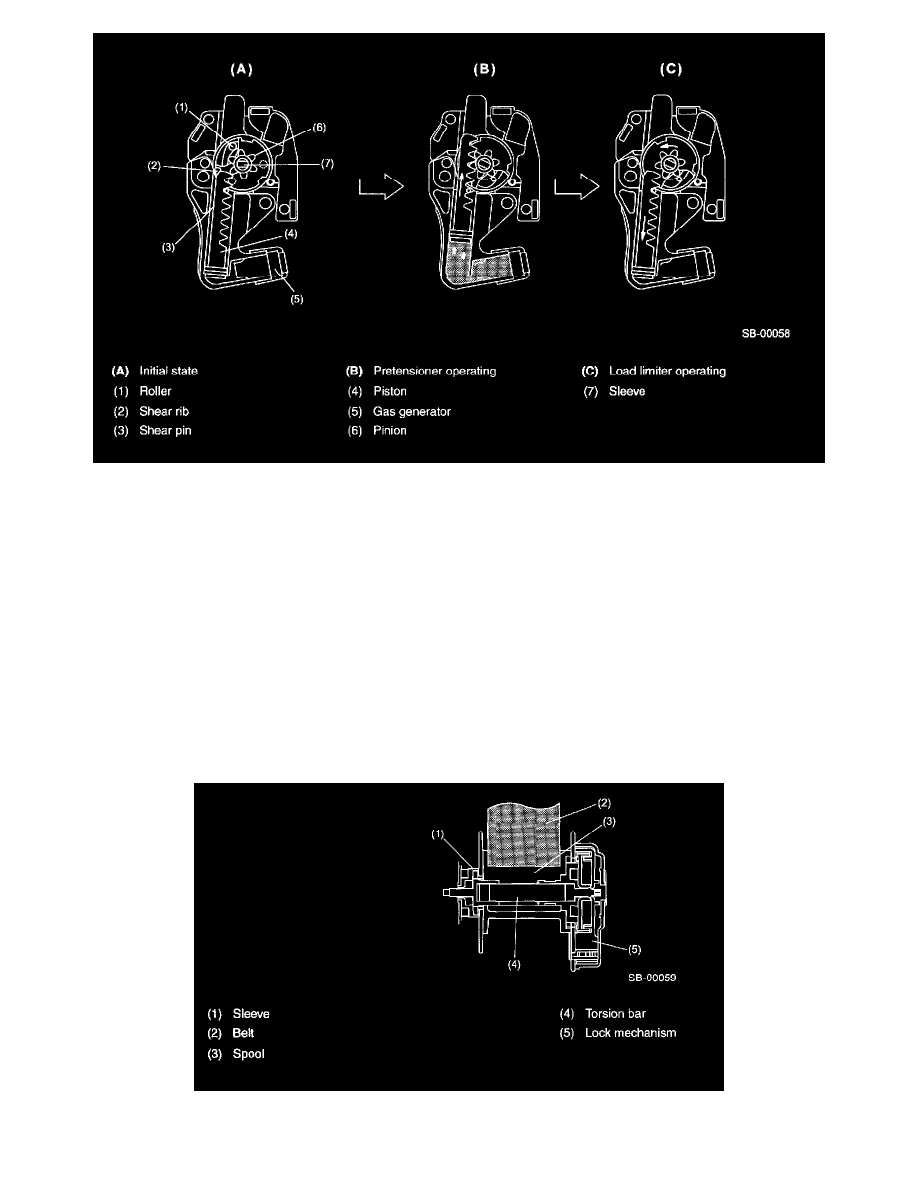
Operation of pretensioner
1. Initial state
-
The piston is held in place by the shear pin in the case gear, and the pinion is held in place by the shear rib in the case gear (when operated, the
shear pin and shear rib are sheared off).
-
The sleeve rotates while transmitting torque of the spring to the spool, and the roller and sleeve rotate freely because a gap is maintained.
2. Pretensioner starts operating and the belt is retracted
-
When the gas generator is triggered in response to the ignition signal from the airbag control unit, the piston moves upward by gas pressure. As
a result, the rack gear of the piston becomes engaged with the pinion and the linear motion is converted into a rotating motion.
-
When the pinion rotates, the slant of the pinion causes the roller to move in an axial direction and be caught in the sleeve engaging the clutch.
The pinion, sleeve, and spool starts to rotate together as a unit and retract the belt.
3. Load limiter
When the passenger restraining load increases and the torsion bar begins to be twisted, the rotation of spool, sleeve and piston is reversed thus
returning the piston. The piston moves downwards while releasing pressure from the gas vent hole, and when the piston reaches the bottom
position it is disengaged with the pinion enabling it to rotate freely.
a. Initial state
The draw out of the belt is detected and the lock mechanism operates. When the belt is drawn out further, the spool and lock mechanism try to
