Legacy Outback Ltd Sedan F4-2.5L SOHC (2000)
Evaporator Core: Description and Operation
An airstream produced by a blower passes through the cooling fins and tubes. This air is warmer than the refrigerant and gives up its heat to the fins,
tubes and then to the refrigerant itself. As the low pressure refrigerant moves through the evaporator, heat given up by the air passing through the
evaporator causes the refrigerant to begin to boil. By the time the refrigerant has passed through the evaporator, it becomes a vapor. As the heat is
absorbed by the boiling refrigerant, the fins and tubes turn cold and in turn cool the air passing over them. Moisture contained in the air condenses to
water drops as it passes around the cooling tubes and fins of the evaporator. Water and dirt are then discharged outside the vehicle through the drain
hose.
The evaporator is a laminated type and consists of thin, rectangular aluminum plates arranged in many layers and fins that are attached between them.
The operation of the evaporator is as follows:
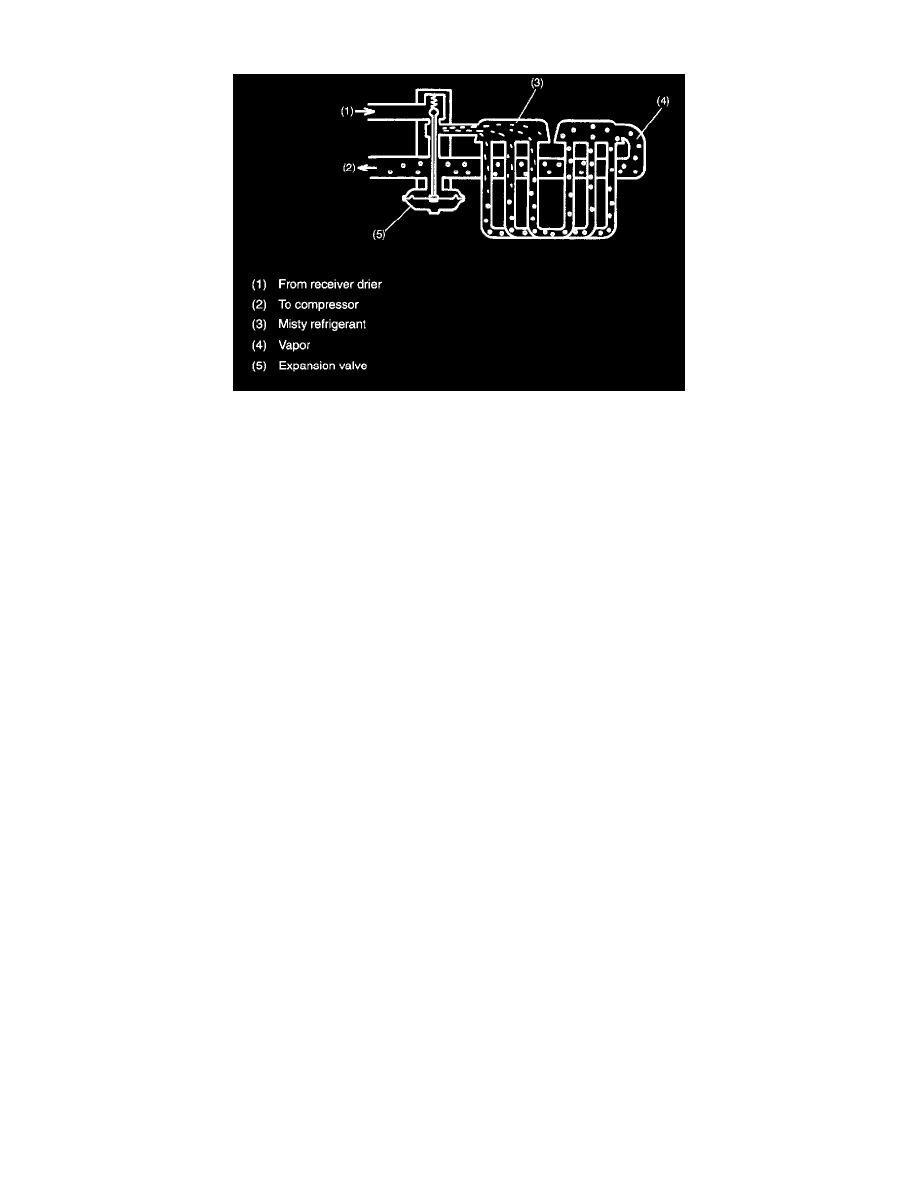
Misty refrigerant (very close to liquid form) from the expansion valve at a low pressure, enters the lower tube of the evaporator, where it soaks up heat
from the compartment. The refrigerant boils and vaporizes quickly due to the rapid heat exchange. Then the refrigerant is pushed upward by the force of
the bubble generated during the exchange and passes evaporating into the upper tube. When it reaches to upper tank, the refrigerant is in a thoroughly
vaporized form.
The evaporator has a single tank, and its surface has been given a multiple treatment.
-
Rustproof treatment
-
Waterproof treatment
-
Moldproof treatment
