Sidekick JSS 4D Hard Top 2WD L4-1.8L (1997)
Exhaust Gas Recirculation: Description and Operation
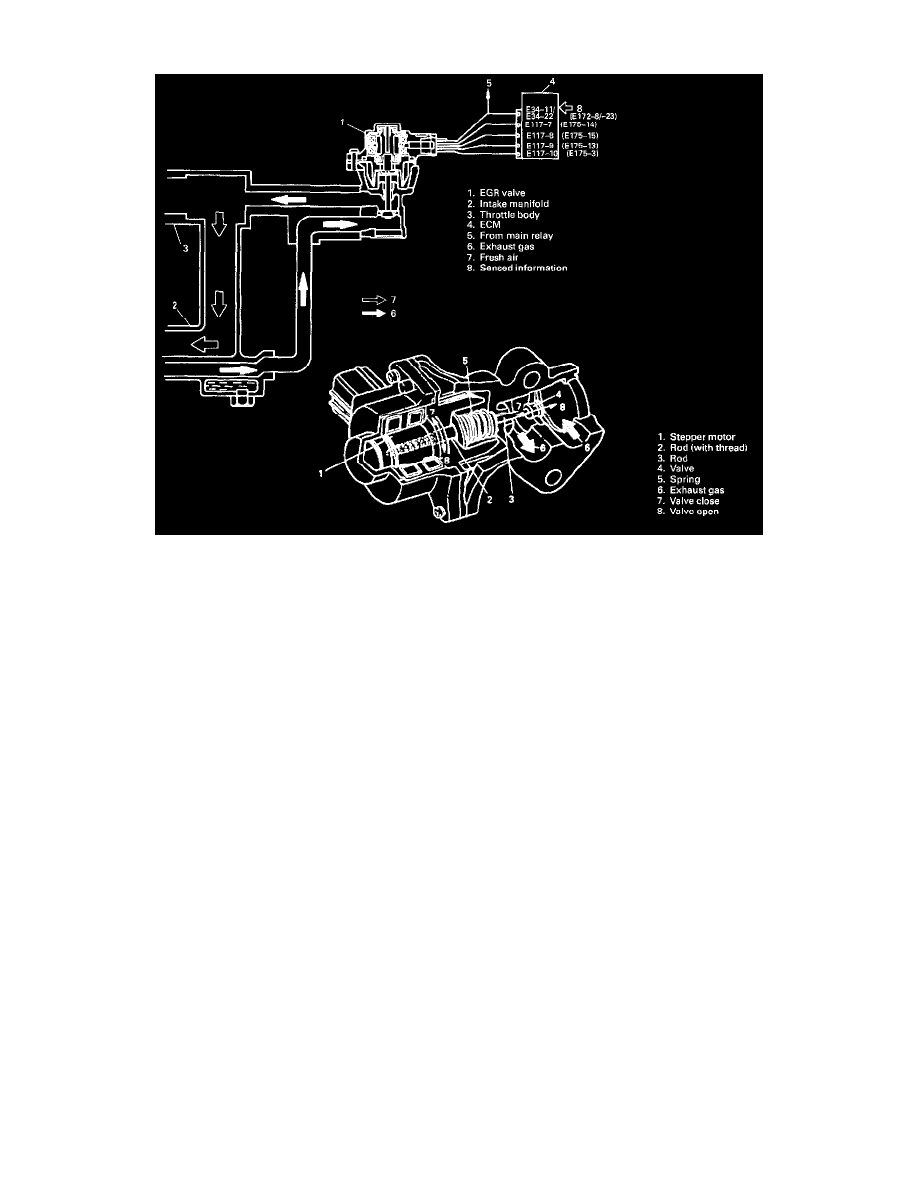
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION SYSTEM
This system controls the formation of NOx emission by recirculating the exhaust gas into the combustion chamber through the intake manifold.
The EGR system consists EGR valve and piping for exhaust gas.
The EGR valve is controlled by ECM according to the signals from CMP sensor, ECT sensor, MAF sensor and VSS.
The EGR valve consists of a stepper motor, rods, valve, etc.
When the EGR valve stepper motor receives "open" signal from ECM, it turns in the "open" direction according to the number of steps and pushes out
the rod which is in mesh with the worm of the stepper motor. As the rod installed to the EGR valve is pushed by this rod, the EGR valve opens by the
amount corresponding to the number of steps of the "open" signal from ECM to let the exhaust gas flow from the exhaust manifold to the intake
manifold.
To close the EGR valve, the stepper motor turns in the "close" direction according to the number of steps of the "close" signal from ECM and pulls up
the rod. In this way, the valve is closed by the spring force.
And in this state, the exhaust gas is not allowed to flow to the air intake system or the combustion chamber.
Under any one of the following conditions, ECM closes the EGR valve.
-
When engine coolant temperature is low
-
When throttle valve opening is less than specification.
-
When engine is running under high load
-
When vehicle is stopped.
Also, in order to check the EGR passage and its valve for clogging, ECM opens the EGR valve to the specified opening while the EGR system is
operating and then closes it.
ECM checks variation in the manifold pressure at this time to check whether the EGR passage or valve is clogged.
