XL-7 2WD V6-3.6L (2007)
Camshaft Position Sensor: Description and Operation
Camshaft Actuator System Description
Camshaft Actuator System Description
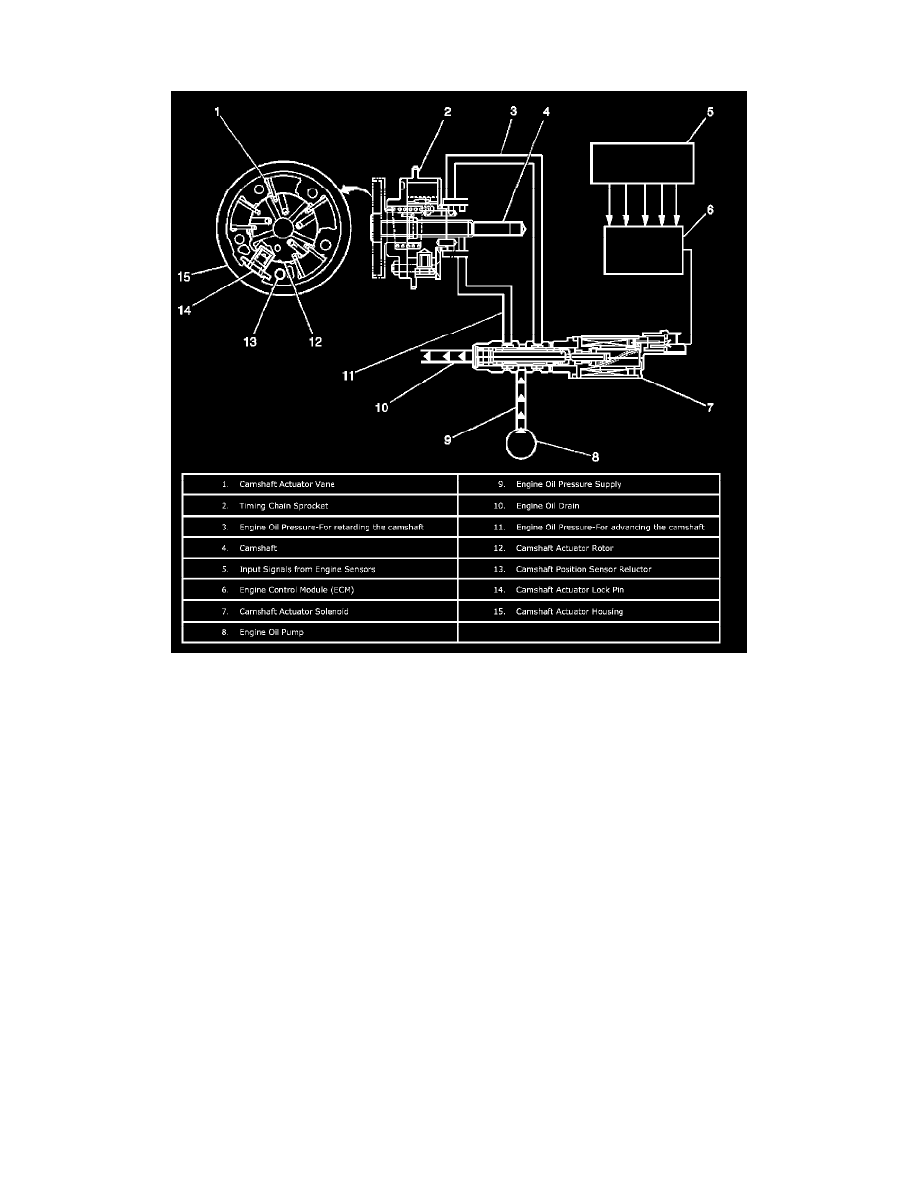
The camshaft actuator system enables the engine control module (ECM) to change camshaft timing of all 4 camshafts while the engine is operating. The
CMP actuator assembly (15) varies the camshaft position in response to directional changes in oil pressure. The CMP actuator solenoid valve controls
the oil pressure that is applied to advance or retard a camshaft. Modifying camshaft timing under changing engine demand provides better balance
between the following performance concerns:
^
Engine power output
^
Fuel economy
^
Lower tailpipe emissions
The CMP actuator solenoid valve (7) is controlled by the ECM. The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the CMP sensors are used to monitor changes
in camshaft positions. The ECM uses the following information in order to calculate the desired camshaft positions:
^
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
^
The calculated engine oil temperature (EOT)
^
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor
^
The throttle position (TP) sensor
^
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS)
^
The volumetric efficiency
Operation
The CMP actuator assembly has an outer housing that is driven by an engine timing chain. Inside the assembly is a rotor with fixed vanes that is attached
to the camshaft. Oil pressure that is applied to the fixed vanes will rotate a specific camshaft in relationship to the crankshaft. The movement of the
intake camshafts will advance the intake valve timing up to a maximum of 50 crankshaft degrees. The movement of the exhaust camshafts will retard the
exhaust valve timing up to a maximum of 50 crankshaft degrees. When oil pressure is applied to the return side of the vanes, the camshafts will return to
0 crankshaft degrees, or top dead center (TDC). The CMP actuator solenoid valve directs the oil flow that controls the camshaft movement. The ECM
commands the CMP solenoid to move the solenoid plunger and spool valve until oil flows from the advance passage (11). Oil flowing thru the CMP
actuator assembly from the CMP solenoid advance passage applies pressure to the advance side of the vanes in the CMP actuator assembly. When the
