A3 Mk1
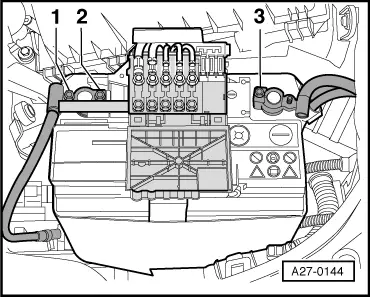 |
|
|
 |
|
Install in reverse order, paying attention to the following:
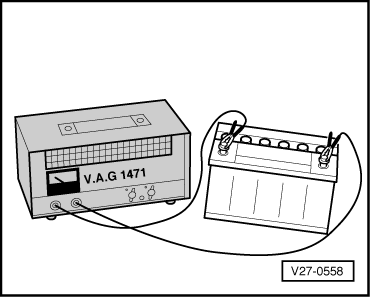
Explanatory notes on exhausted batteries Batteries which have not been used for lengthy periods, e.g. in vehicles which have not been driven, are subject to self-discharge. A battery is considered to be exhausted if the no-load voltage has dropped below 11.6 V. With exhausted batteries, the electrolyte (mixture of sulphuric acid and water) is more or less all water, with a greatly reduced sulphuric acid content. Exhausted batteries become sulphated, i.e. all the plate surfaces of such batteries become hard. As opposed to being clear, the electroyte has a slightly milky appearance. If an exhausted battery is re-charged immediately after exhaustive discharge, the sulphation can be reversed. If this is not done, the plates become even harder and their ability to absorb charge is impaired, thus resulting in a loss of power reserves. Procedure for charging sulphated exhausted batteries Sulphated exhausted batteries must be charged as follows using a low charging current:
Charge battery => Page 27-38. Rapid charging is never to be implemented on exhausted batteries. |
